P0420 is a well-recognized error code within the automotive industry, notorious for its persistence. Luckily, this article is designed to guide you through understanding the implications of this error code, exploring its possible causes, and navigating potential fixes.
Drawing on our experience, we acknowledge that resolving P0420 can be challenging without appropriate knowledge. This complexity arises as the error can take a significant amount of time to reappear, even after parts replacement and code resetting. Throughout this blog post, we will address these issues and more, providing you with comprehensive insight into the P0420 code.
What Does The P0420 Code Mean?
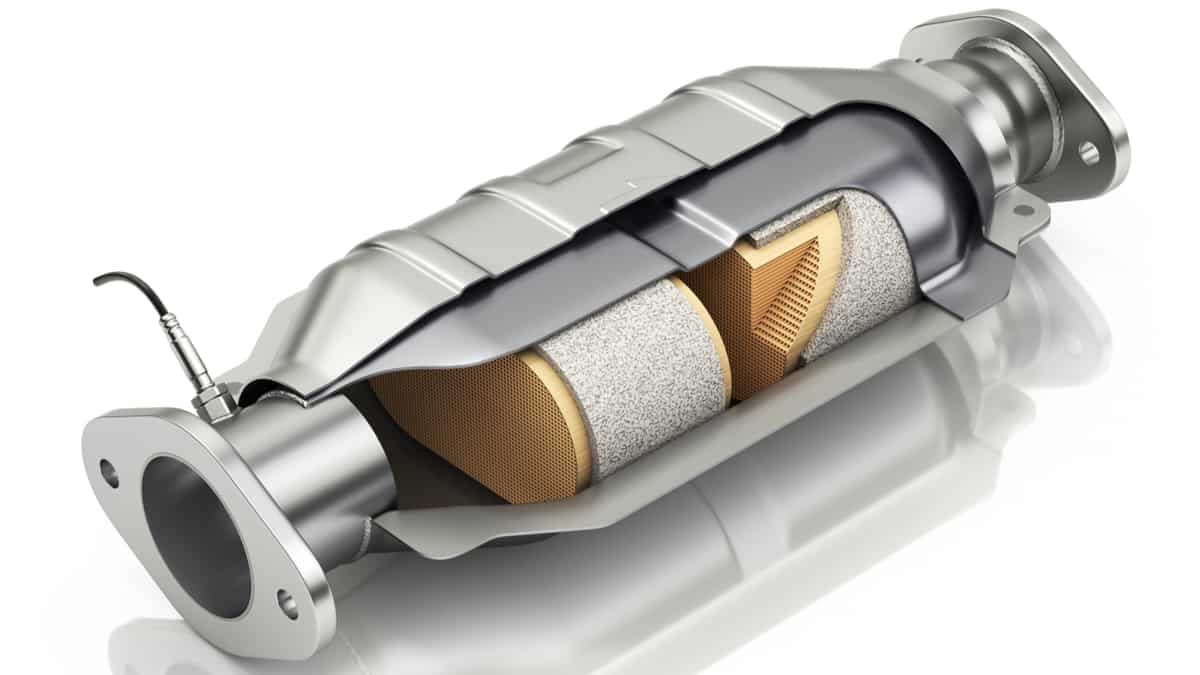
The P0420 code indicates that the Engine Control Module (ECM) has identified a decline in the efficiency of the catalytic converter on Bank 1. This could be attributed to a malfunctioning catalyst or potentially be a false alarm triggered by a defective O2 sensor.
The engine control module (ECM) uses two O2 sensors, one in front, and one behind the catalytic converter to measure its efficiency. If the catalyst system efficiency is low, the P0420 code will be triggered. In most cases, a P0420 trouble code is caused by a bad catalytic converter.
An incorrect air/fuel mixture can also temporarily or permanently reduce the catalyst’s efficiency, resulting in a P0420 code.
Code Definition
P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
What Causes A P0420 Code?
The most common cause of the P0420 code is a faulty catalytic converter. It can also be caused by a faulty oxygen sensor, exhaust system leak, intake leak, or incorrect placement of the catalytic converter.
It may be due to a defective catalyst, but I have also seen many cases where the catalyst is new but is not an original OEM part. Some cheaper catalysts may not be efficient enough, and it could result in you needing to buy a brand-new catalyst from the manufacturer.
I have also seen non-OEM catalytic converters that have been installed too far away from the engine on the exhaust pipe towards the last muffler. Because of this, the catalytic converter will not become hot enough, and it will trigger the P0420 trouble code.
If the car’s air-fuel mixture is incorrect due to a faulty injector, high fuel pressure, faulty fuel system, or a damaged sensor, it may cause the catalytic converter not to function properly.
The main causes of the P0420 code include:
- Damaged catalytic converter (most common)
- Oil contamination in the catalytic converter
- Incorrect placement of the catalytic converter
- Damaged upstream or downstream oxygen sensor / faulty wirings
- Exhaust manifold or exhaust system leak
- Wrong type of fuel (leaded fuel instead of unleaded)
- Rich/lean mixture (damaging the catalytic converter)
- Misfires (damaging the catalytic converter)
- A faulty engine control module (rare)
How To Fix The P0420 Code
You should first check the function of the catalytic converter with the methods further down in the article before replacing any parts. You will most likely waste your money if you try to replace parts without a diagnosis, so it is much better to make a proper diagnosis. Here are some things that could fix the error code P0420:
- Cleaning the catalytic converter
- Replace catalytic converter
- Replace front or rear oxygen sensor
- Repair damaged sensor wiring
- Replace damaged engine sensors
- Fix high oil consumption
- Fix misfires
- Fix lean or rich fuel mixture
- Replace engine control unit (rare)
Common Symptoms of A P0420 Trouble Code

The most common symptom of code P0420 is a check engine light on your car’s dashboard. In rare cases, you may also notice issues like misfires, higher fuel consumption, or a bad odor from the exhaust pipe.
However, in most cases, you will most likely not notice any symptoms except the check engine light with the P0420 code stored in the engine control module or powertrain control module (PCM).
How serious is the P0420 code?
Not very serious. The P0420 code will in most cases not create any further problems with your car’s engine.
The only thing that could potentially happen is that the catalytic converter is so damaged that the catalytic converter’s internal parts come loose and block the exhaust flow, but this is pretty unlikely to happen.
However, the P0420 trouble code could result in worse emissions from your car, which is bad for the environment, so you should fix it as soon as possible.
What are the common P0420 diagnosis mistakes?
The most common mistake is replacing the oxygen sensors without diagnosing them properly. The cause of this engine code is in most times the catalytic converter, which may get damaged by other issues with your car’s engine, like misfires or a rich or lean air/fuel ratio.
Check for any other trouble codes with your diagnostic scanner. If you find codes like P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, P0306, P0307, and P0308, you have a misfiring engine and the misfires may be causing the P0420 error code. In this case, you should fix the misfires first, clear the codes, and see if the P0420 code comes back.
If you find DTC codes like P0171, P0172, P0174, or P0175, it means that your engine is running rich or lean. This could be due to a faulty fuel injector, high or low fuel pressure, MAF sensor, engine coolant temperature sensor, or almost any faulty engine sensor. The air-fuel mixture needs to get addressed, and when you have done so, wait and see if the P0420 code comes back.
In some cases, if there are no other issues with your engine, you can try to use a catalytic converter cleaner before replacing the catalyst. There are many different additives on the market, so we recommend choosing one of the best catalytic cleaners from our list.
Common P0420 Code Causes by Car Model
The P0420 trouble code is more common in some car models than others. Certain car models are known to have a problem with this diagnostic trouble code. Here is a list of the most common causes by car brands.
Remember that these are only general guidelines, and you should make a diagnosis before replacing any parts.
1. Chevrolet
If you experience a P0420 code in your Chevy, it is often due to an exhaust leak before the catalyst. It can also be caused by a faulty downstream oxygen sensor (rear) or a faulty catalytic converter.
Chevy engines are known to leak around the exhaust manifold, so you should definitely take a look there if you can find some strange blowing sounds when your engine is running. You will also find P0420 recalls for GM vehicles.
2. Toyota & Nissan
The most common cause for P0420 in Toyota and Nissan cars is a bad catalytic converter. You should also ensure your engine is not burning motor oil.
Check for vacuum leaks and exhaust leaks first. Then check to see if you notice any blue smoke coming from the exhaust pipe. Blue smoke coming from the exhaust pipe is a sign that you might have an issue with the crankcase ventilation, or even something as bad as a damaged turbocharger or bad piston rings.
If you do not notice any blue smoke at any RPM, it is most likely that your catalytic converter is worn out. You may find similar issues on Nissan cars.
2. Ford
Ford engines often have vacuum leaks or a broken solenoid for the EGR or other components, which causes a faulty air-fuel mixture and then causes the trouble code.
Check the code memory with a diagnostic scanner to see if you can find any trouble codes about the air-fuel mixture. If everything looks fine, check for exhaust leaks.
Diagnose and replace the catalytic converter if you can’t find any trouble codes or other problems with the air/fuel mixture.
3. Subaru & Honda
If you find a P0420 code in your Subaru or Honda, it’s most likely the catalytic converter to blame. It can also be caused by an exhaust leak or a bad oxygen sensor.
Check for vacuum leaks or other fuel mixture-related engine codes. Check for any exhaust leaks before the catalytic converter. However, the most common problem with Subaru engines is the catalytic converter. They seem to wear down fast on these boxer engines.
Acura does also have some P0420 recalls you should look into, because they share many similarities with Honda.
4. Volkswagen (VW) / Skoda / Seat / Audi A4 1.8T / V6 2.4
There is a Check Valve/PCV Valve under the intake manifold on many VAG engines, which is the first thing you need to check if you see this trouble code. You must also ensure that the crankcase ventilation is free from sludge, because clogged-up crankcase ventilation causes the engine to burn oil, which in turn clogs the catalytic converter.
Check for exhaust leaks around any flex pipes on the exhaust pipe – this is a common cause – and check for any engine codes related to the oxygen sensors. If no problems were found, replace the catalytic converter. It’s a widespread problem on both the 1.8T and the V6 petrol engines.
P0420 Diagnosis
P0420 is usually caused by a faulty catalytic converter, as mentioned before. You should always diagnose it properly with the methods below before replacing any parts.
- Connect an OBD2 Scanner and look for related trouble codes. Repair any trouble codes related to the ignition or fuel first.
- Check the live data to see the front and read the O2 sensor voltage signals. The car engine should be scorching and the front sensor should fluctuate between 0–1 volts, and the rear should be steady at 0.7–0.9 volts. If you get similar readings, there is a chance that the catalytic converter is defective.
- Heat up the engine and check the temperature of the front of the catalytic converter and then the rear with a laser thermometer. If the engine is hot and there is no difference in temperature in front of and behind the catalytic converter, your catalytic converter may not be working as intended.
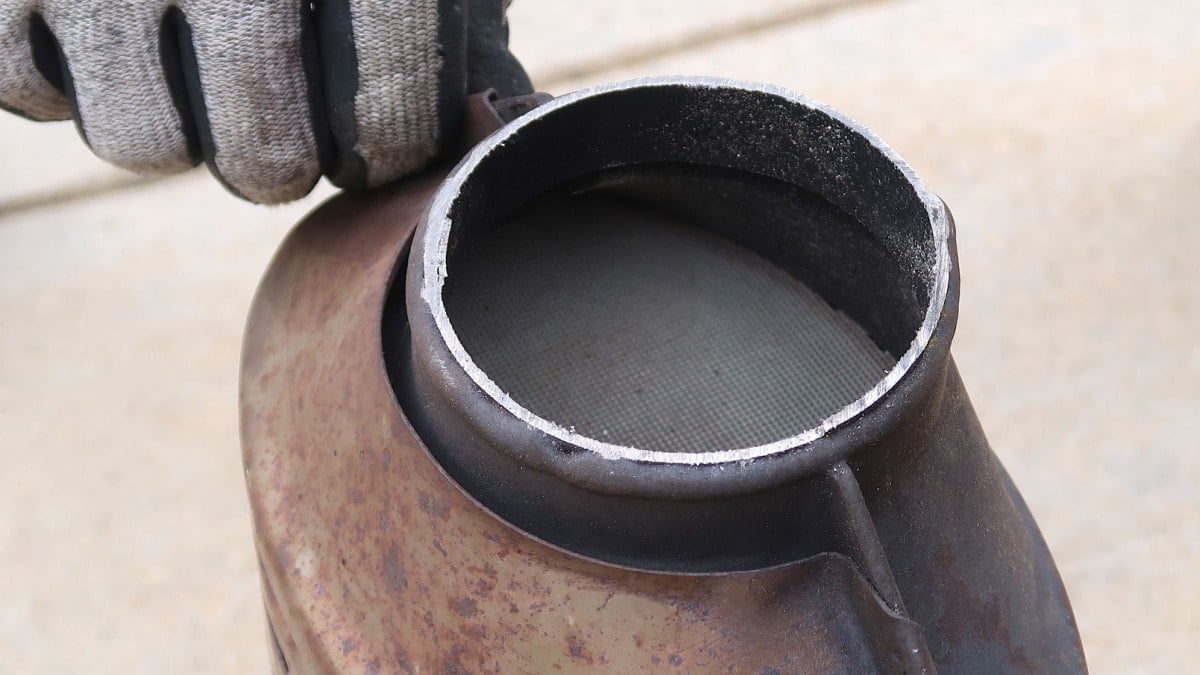
- If the catalyst is installed in a way that’s reachable, it may be worth removing the pipe from one end and checking inside the catalyst for visual damage.
- If everything points to a faulty catalytic converter, replace it. If you can’t find any problem with the temperature, voltage, or a visual inspection, you should try to repair other related trouble codes and then clear the codes and try again.
- If you still can’t find any problems, make sure it is a genuine OEM catalytic converter and installed in the original place. If everything seems fine, replace the catalytic converter.
What could damage the catalytic converter?
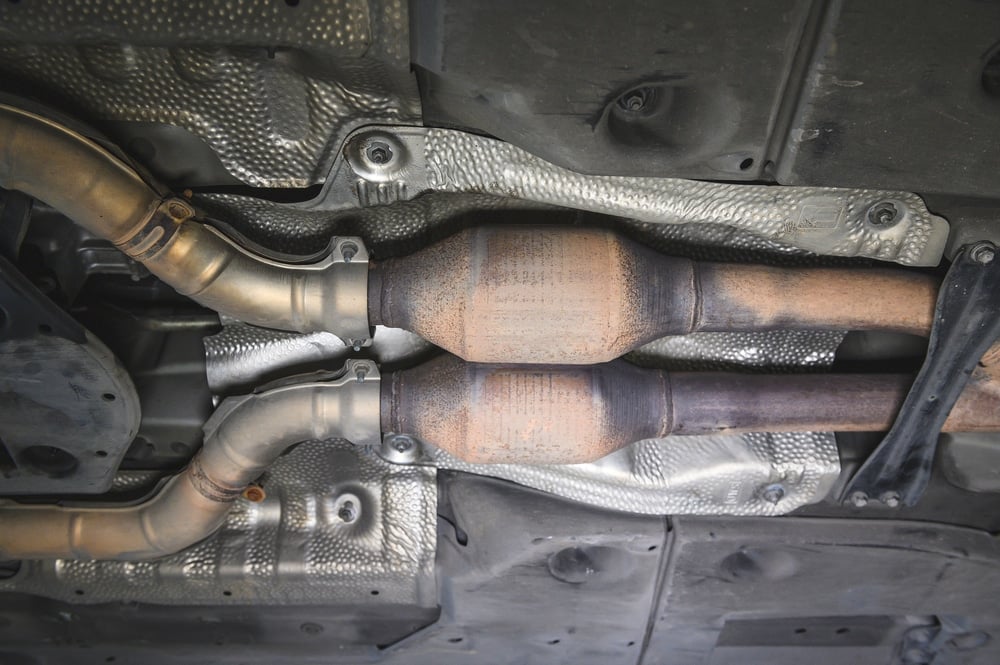
The catalytic converter reduces the three main causes of pollution produced through gasoline combustion – nitrogen oxide (NOX), carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons. It does this by converting these harmful substances into less noxious ones that are easy on our health and contribute to clean air quality.
There are a few things that are known for damaging the catalytic converter, which can cause the P0420 trouble code; here are the most common ones:
- Misfires
- Oil consumption
- Exhaust leak
- Intake leak
- Rich mixture
- Lean mixture
- Bad ECM/PCM
P0420 Repair Cost
There is no fixed cost to fix the P0420 code because of the wide range of different causes. However, it is often caused by a faulty catalytic converter, which usually costs between $500 to $1500.
The estimated cost of repairing the code is the following. The prices include parts and labor work at a workshop. The costs do not include diagnosis costs.
- Catalytic Converter Replacement – $500 to 1500
- Front Oxygen Sensor Replacement – $150 to $300
- Rear Oxygen Sensor Replacement – $150 to $300
Can I remove any parts to get rid of the P0420 code?
You cannot just remove parts to fix this trouble code, because it will likely give you another trouble code or other issues. In theory, you could reprogram the engine control unit to remove the catalytic converter’s monitoring system. However, doing so would be illegal in most states and countries, so even if it’s theoretically possible, you shouldn’t do it.
If you want to reprogram the function, you can also remove the catalytic converter completely. Remember that if you remove the catalytic converter, you will most likely not pass any emission tests and you may experience legal issues.
There is also another way to trick the engine control module by installing the rear oxygen sensor inside of a small pipe. This method can work if you desperately want to get rid of the P0420 code, but it’s not a recommended method, and it may get you into trouble.
Can I drive with a P0420 code?
Yes. You may be able to drive your car with a P0420 code, but it is not advisable. This code indicates that your catalytic converter is not functioning properly, which can lead to increased emissions and decreased fuel efficiency. In some cases, driving with a faulty catalytic converter can damage other parts of the engine. If you have a P0420 code, it’s best to get it fixed as soon as possible.
Can a bad O2 sensor cause a P0420 code?
Yes. A P0420 code is typically caused by a problem with the catalytic converter, but it can also be caused by a bad O2 sensor. The rear O2 sensor monitors the catalyst efficiency, so if it fails, it can give a false alarm and cause a P0420 code. If the front O2 sensor is faulty, it can cause the engine to run lean, which can damage the catalytic converter.
I hope you now have the knowledge to understand what the PO420 code is and how to get rid of it. If you liked this article, don’t forget to check out our other articles and our YouTube channel!
Learn more:

















