When it comes to car emissions systems, no part is as well-known as the catalytic converter. This valuable component is often stolen from gas-powered cars and trucks because of how much precious metal is inside. That might lead you to wonder, do diesel engines have catalytic converters?
In this guide, I answer that important question. I also explain how the system works on diesel-powered motors. Plus, I look at ways to tell when it’s time to replace the diesel catalytic converter.
Do Diesel Engines Have Catalytic Converters?
Yes. Many diesel cars have a catalytic converter, but not in the same way that a gas-powered car does. Some diesel engines contain a two-way catalytic converter with a diesel oxidization catalyst, but it could be a three-way design that adds an SCR reduction.
Diesel engine emissions go through four stages: there’s the EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation), as well as the DPF (Diesel Particulate Filtration), plus the DOC (Diesel Oxidization Catalyst) and the SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction). The catalysts produce chemical reactions to reduce harmful emissions in the DOC and SCR stages.
How Does the Diesel Catalytic Converter Work?
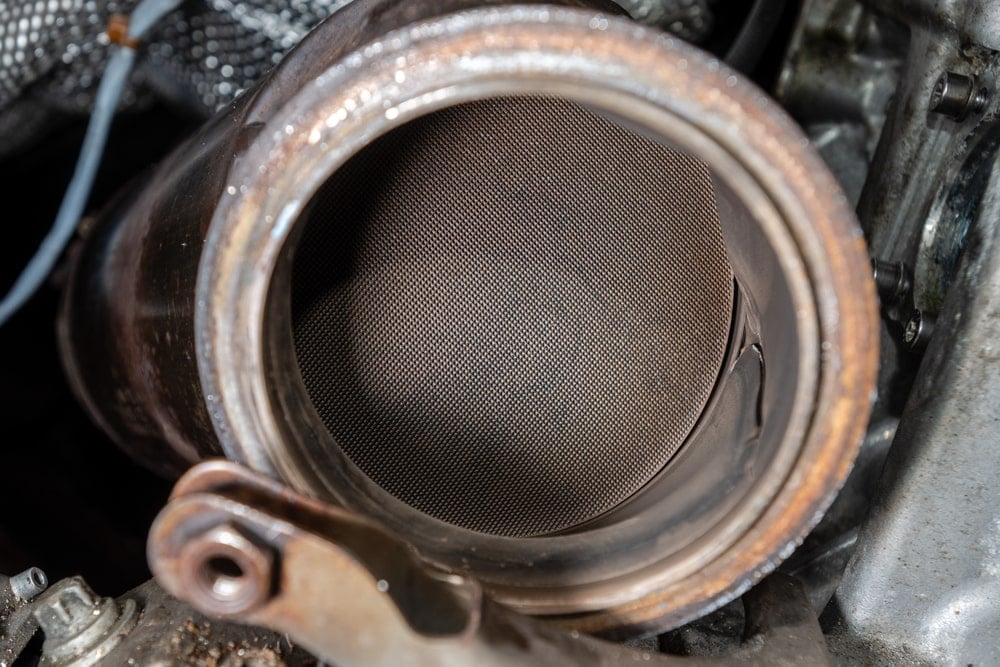

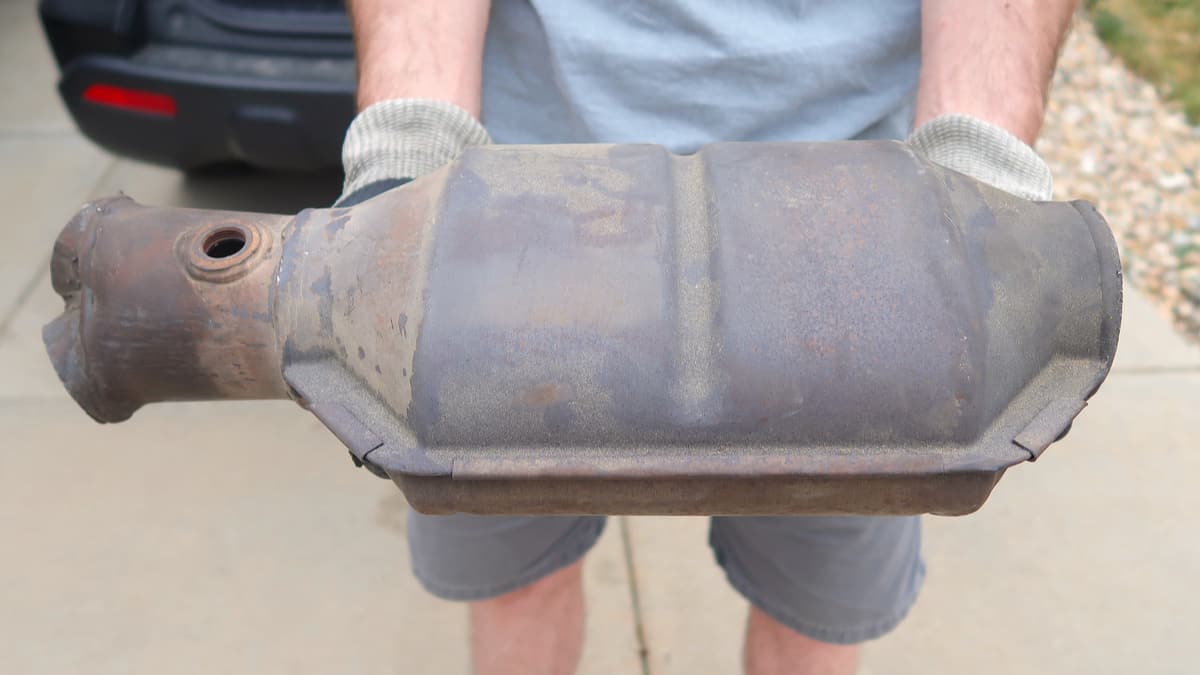
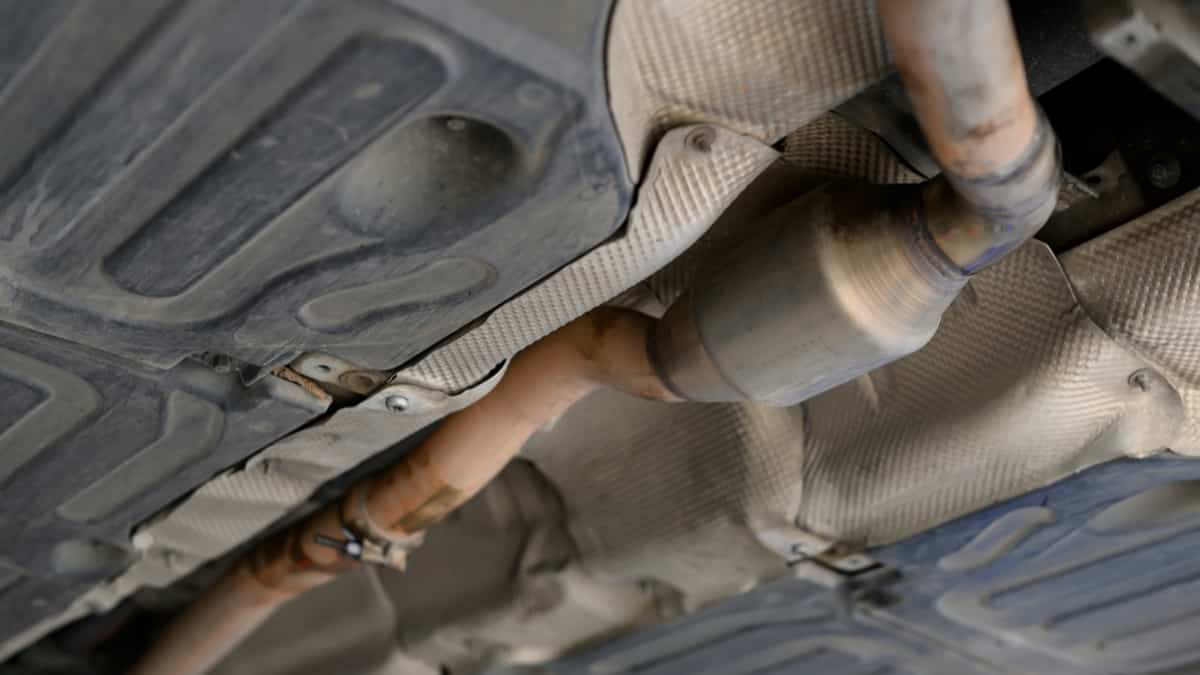
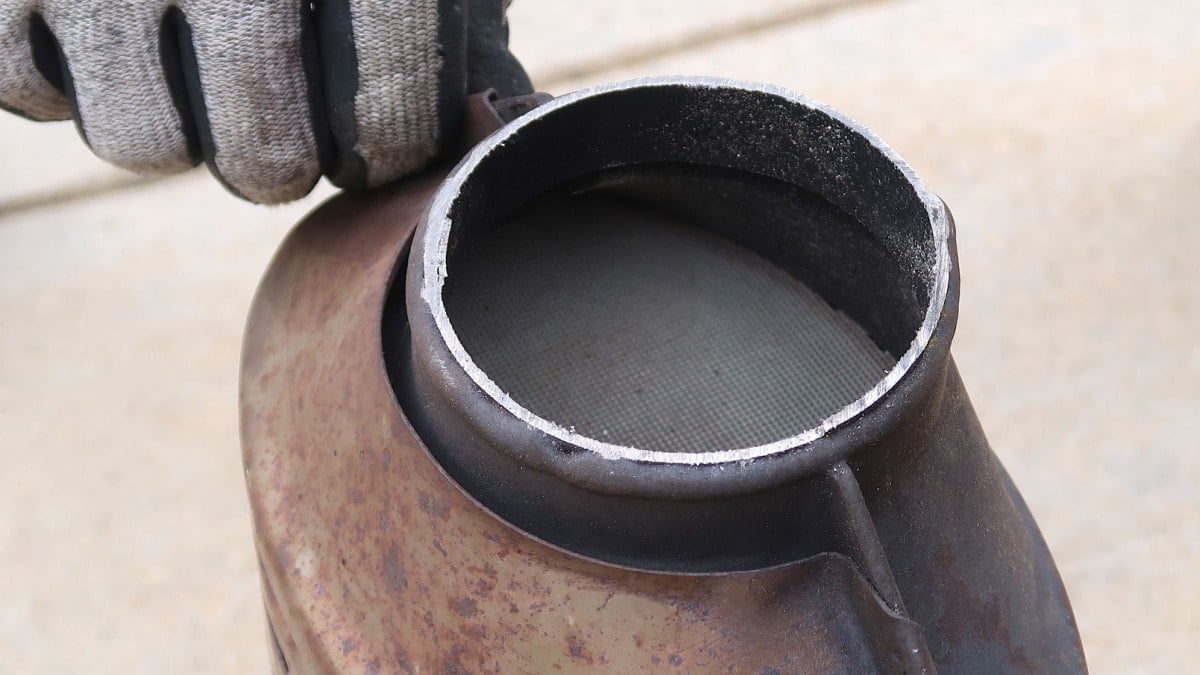
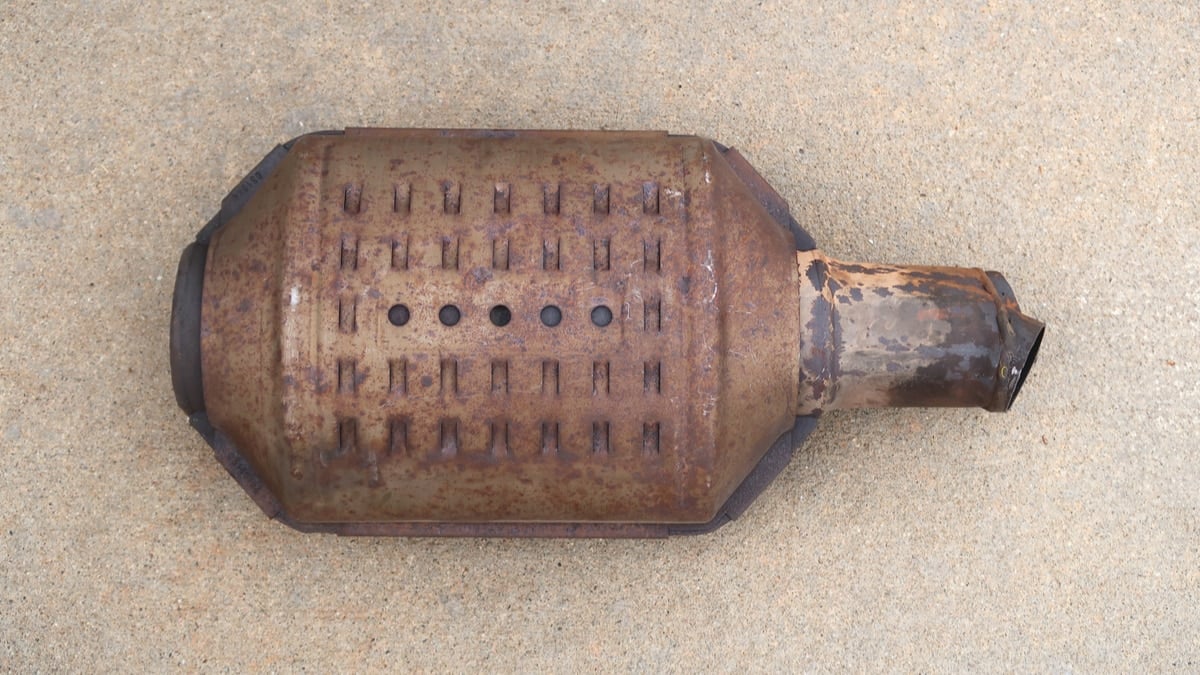
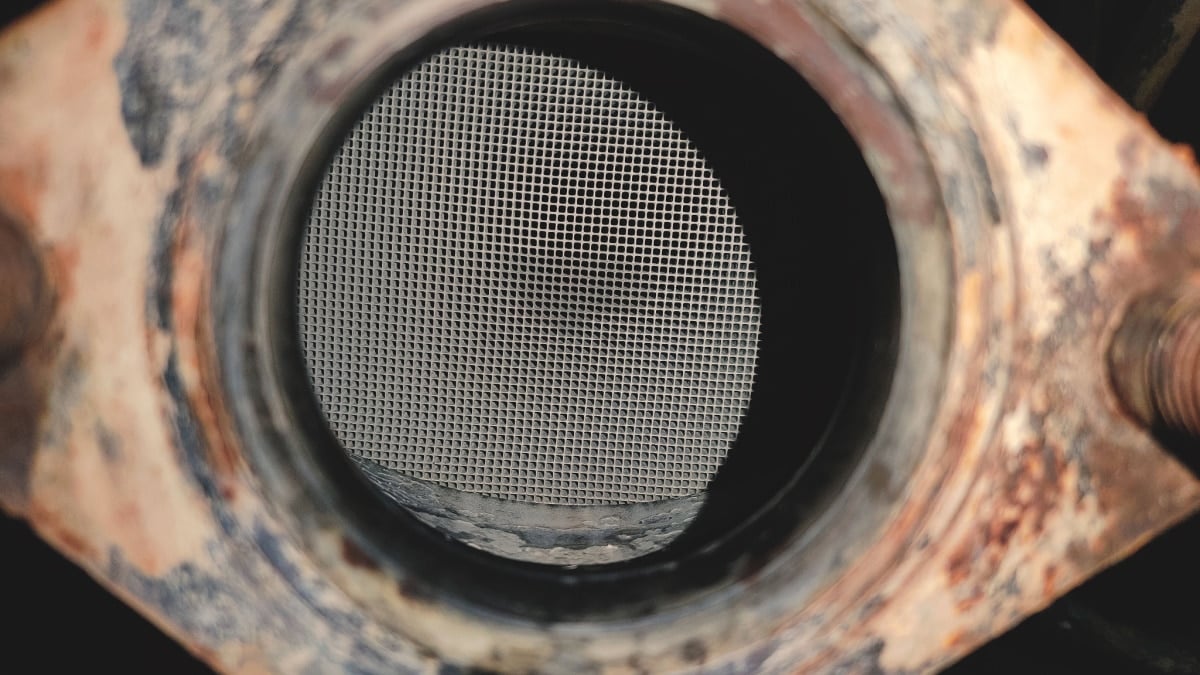
The diesel catalytic converter is responsible for converting harmful substances into forms that are non-toxic. Inside the metal casing are two ceramic blocks that contain thousands of micro-cellular units, looking like a honeycomb.
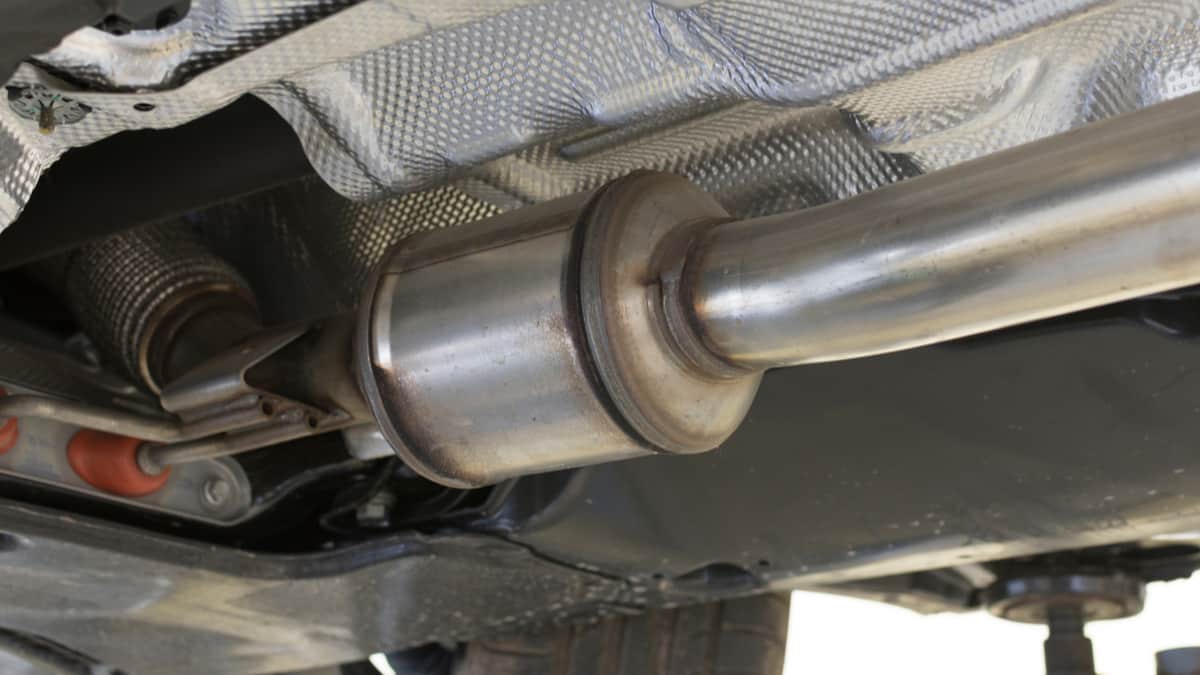
All of the ceramic blocks have a metal coating, such as platinum or palladium. The catalytic converter is located closer to the engine, with the converter heating up to catalyze the chemical reactions. These reactions convert toxic gases into harmless byproducts that can be released into the atmosphere.
The Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) is very similar in function to the equivalent part in a gas engine. Carbon monoxide is reduced to water and carbon with the help of metal catalysts. During this time, the volatile hydrocarbons and byproducts are broken down into less harmful substances, so the emissions of dangerous gases are reduced. However, this cat doesn’t contain rhodium like it would if it were in a gas engine. It also includes a diesel particulate filter (DPF) that eliminates particulate matter that isn’t found in a converter equipped to a gas-powered engine.
The SCR is responsible for breaking down the Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) into Nitrogen and Oxygen with the help of an ammonia-based catalyst. This open-loop system can reduce NOx emissions by 75 to 90 percent. SCR is also needed to reduce hydrocarbon emissions, but is only about eight percent effective. Using low sulfur fuel helps improve performance.
How Long Does A Diesel Catalytic Converter Last?
A diesel catalytic converter can last for 100,000 miles or about ten years. However, its health depends on how long your trips are and how the vehicle is treated. If you regularly take shorter trips, the catalytic converter could wear out prematurely.
During shorter trips, the engine gets turned off before the converter can obtain the appropriate operating temperature to catalyze the compounds. The more often this occurs, the more wear the converter deals with.
Signs of a Failed Diesel Catalytic Converter
If you recognize the signs that the converter is failing, you can have it replaced and not miss a beat. There are a couple of reasons the converter can fail early. A few of the most common causes for premature failure include:
- Free flow of exhaust gases is restricted
- Build-up of carbon deposits
- Physical damage
- Overheating
- Poor engine maintenance
Most modern cars use oxygen sensors that help determine if the catalytic converter is in need. When the oxygen sensors don’t receive the proper reading, they cause the Check Engine Light to come on. You can use a code scanner to figure out what’s causing the issue.
Aside from the Check Engine Light, you might also notice these symptoms that the catalytic converter is failing:
- Poor engine performance
- Trouble accelerating
- Rotten egg smell from the exhaust
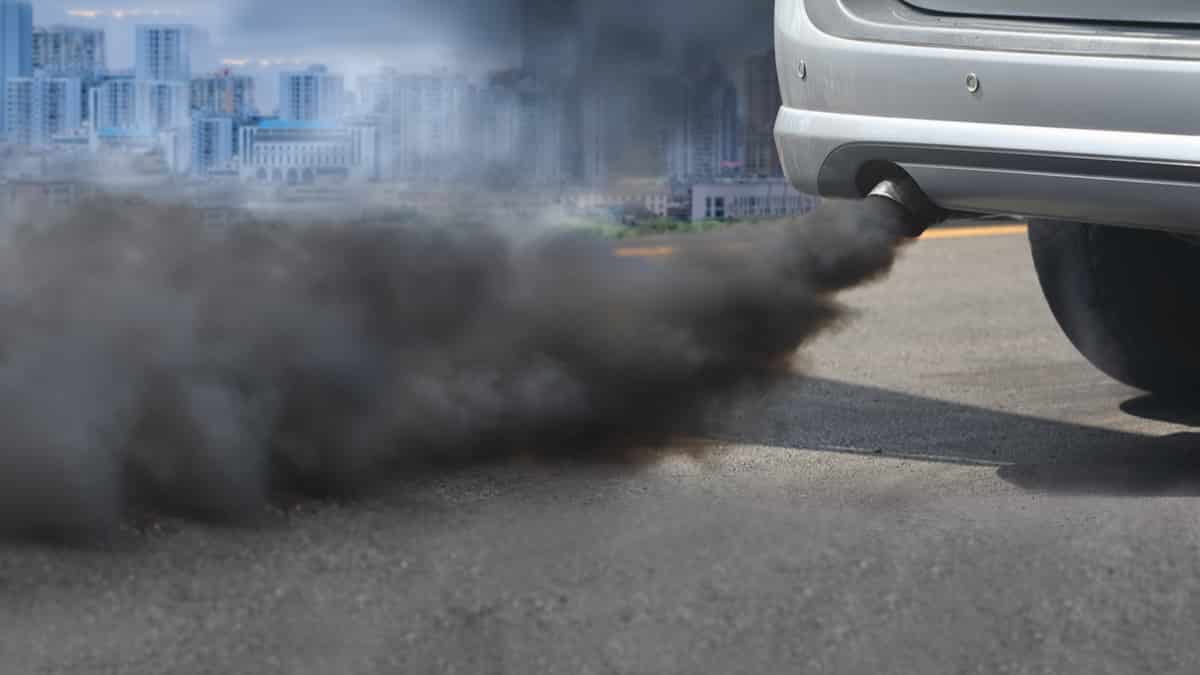
- Dark exhaust smoke
RELATED: 8 Symptoms of a Bad or Clogged Catalytic Converter
Diesel Catalytic Converter Replacement Cost
Having the catalytic converter replaced isn’t going to be an inexpensive job. It’s just as expensive or more expensive than with a gas-powered car. On average, you can expect to spend between $900 and $2,500, based on your car model and the material of the converter. This estimate includes both parts and labor.
If you are able to do the replacement yourself, you could save a small amount of money. However, the majority of the costs are made up of the part itself.
Because of how much it costs to get a new catalytic converter, some drivers choose to put theft-proof features on it to prevent it from being stolen. For $50 or less, you can easily keep the catalytic converter protected from thieves.
RELATED: How Much Does a Catalytic Converter Replacement Cost?
Can the Car Run Without a Diesel Catalytic Converter?
There’s nothing stopping the vehicle from driving with the catalytic converter missing. The engine is still going to work and you won’t be stranded without it. However, the emissions standards won’t be the same and you could notice some engine performance problems.
Additionally, catalytic converters are required by law. If you run your vehicle without one, you could face some stiff fines. You aren’t responsible for getting an emissions test, so that’s not the problem, but the safety inspection could flag it when you go to renew your registration.
Does Catalytic Converter Cleaning Work?
As carbon builds up inside the catalytic converter, it can become clogged. Some people assume this means that the only option is to replace the catalytic converter, but that’s not the case. There are products that claim to clean the catalytic converter.
While there’s a lot of controversy over whether these catalytic cleaner products work, most people agree that it’s worth trying. Paying a small amount for a simple cleaner could save you from needing to put on a new converter.
RELATED: How to Clean a Catalytic Converter (Without Removing it)
Additionally, some people find that using a catalytic converter cleaner can help maintain the life of this valuable part. While many of the products will recommend using a bottle every 3,000 to 4,000 miles, this guideline is overkill. You should be able to see results if you use it twice a year while driving the average amount of miles.