Many people don’t pay attention to the RPMs unless there is something wrong. As soon as there is RPM fluctuation while driving, it’s natural to take notice. What causes this condition and should you worry about it?
In this guide, we examine the most common causes of why your RPM is fluctuating while driving. We also look at how to diagnose the problem and fix it for a smoother ride.
Causes of RPM Fluctuation While Driving
Many RPM fluctuations are caused by transmission problems. It can also happen when the spark plugs are dirty or if there is a vacuum leak that causes misfires. In some cases, the crankshaft position sensor may send the wrong engine speed signal to the tachometer.
Here is a more detailed list of the causes of RPM fluctuation while driving.
1. Defective Transmission
The transmission handles all of the gear shifting. If there’s a problem with the automatic transmission, the shifting could become irregular or delayed. If you drive a manual transmission vehicle, the clutch could also be slipping.
It’s also possible that there’s a transmission leak. When the fluid levels fall below normal, the engine could rev at higher levels because the torque converter will not function properly.
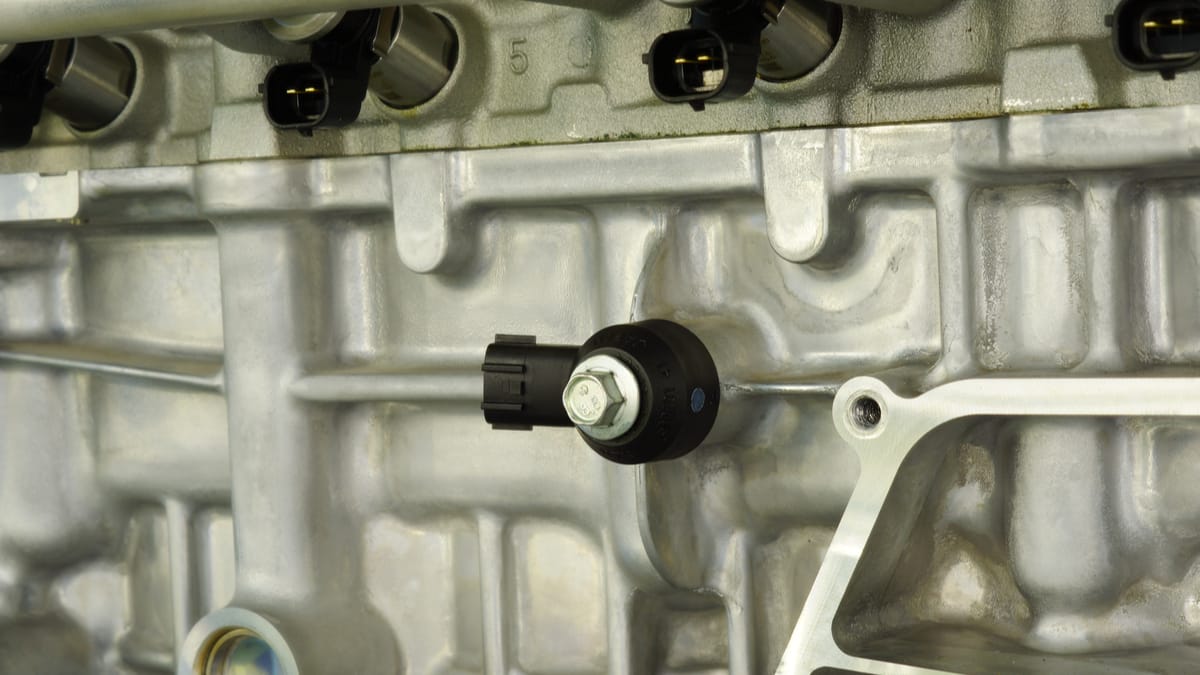
2. Malfunctioning Crankshaft Position Sensor
A faulty crankshaft sensor affects the engine timing negatively. As it controls the timing, the RPMs will fluctuate. Also, the engine control module and the tachometer (RPM) on your dashboard use the crankshaft position sensor to measure the engine speed. If there is something wrong with the engine crankshaft position sensor or the wirings, you can see a fluctuating RPM speed.
You might also notice that the bad crankshaft sensor causes stalling, trouble starting, and added vibration. Get this problem repaired before you are left stranded. Some car models use the camshaft position sensor, so it shouldn’t be overlooked. Use an OBD2 scanner and look for any related trouble codes.
3. Fouled Spark Plugs or Coils
The spark plugs are used to ignite the air and fuel mixture entering the combustion chamber. Once the plugs are worn, engine misfires can occur, leading to engine vibration.
This vibration can cause RPM fluctuations, and it will feel like the engine has a mind of its own. You may also notice poor acceleration, a drop in fuel economy, and jerking. Spark plugs may need to be replaced as early as 30,000 miles, depending on what type you choose.
You also want to take a look at the ignition coils, as these ignite the spark plugs and are known to fail quite often due to the engine heat. If you have an older car, you want to check the distributor cap and the spark plug wires instead.
4. Vacuum Leak
It’s always possible that the fluctuation has to do with an engine vacuum leak, especially if it occurs while accelerating. When there’s a vacuum leak, the engine’s air supply gets interrupted.
You might notice RPM fluctuation, as well as reduced fuel efficiency, the Check Engine Light, a rough idle and a hissing noise. A vacuum leak can cause the vehicle to stall, leaving you stranded, so don’t wait to get it looked at.
Vacuum leaks are normally found around the intake manifold and are often caused by cracked vacuum hoses. It can also be a leaking intake manifold gasket between the cylinder head and the intake manifold.
RELATED: How to find a Vacuum Leak & How to Fix It (8 Easy Steps)
5. Dirty Fuel Injectors
Fuel injectors allow the engine to receive the fuel needed to run properly. However, over time, debris and dirt can clog the injectors. When this happens, the fuel delivery is obstructed, leading to starvation of the engine.
Not only will clogged injectors cause fluctuating RPMs, but the car can also become jerky. It may also not accelerate the way you expect it to. However, bad spark plugs and vacuum leaks create many of the same symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose.
6. Bad Throttle Position Sensor
If you have a bad TPS, the car can accelerate on its own with an electric throttle body, whether you are pushing on the gas pedal or not. This creates an RPM fluctuation that becomes noticeable.
Additional symptoms include misfiring and trouble to start the engine. As the problem gets worse, you might not be able to get the car moving, so don’t overlook the problems.
It can also be the throttle body itself that is damaged. It might also just be dirty; it can often be cleaned without replacing it. Another reason may be the pedal position sensor, which sends electrical signals to the throttle control on how much acceleration to apply. This is not very common, but it should not be overlooked.
RELATED: How to Clean a Throttle Body (10 Steps DIY)
7. Dirty Air Filter
The fuel inside the combustion chamber must mix with the appropriate amount of air to create power. The air filter traps contaminants, ensuring that the air entering the engine is clean.
If the filter isn’t changed, it can become clogged, which stops air from entering the engine. Not only will this cause engine RPM fluctuations, but it can also lead to a delay in accelerating. Thankfully, it’s one of the easiest fixes to perform.
8. Bad tachometer (RPM meter)
Although it is quite rare for the tachometer to be damaged, it can happen on some car models, so it should not be overlooked. The tachometer is integrated into the instrument cluster of modern cars, so if it is damaged, you may need to replace the entire cluster.
But since it is so rare that the tachometer is bad and a new cluster is quite expensive, you should look at the wirings and look for other problems with a code scanner first.
How to Fix RPM Fluctuation
At the first sign of RPM fluctuation, you want to have the problem looked at. If you are mechanically inclined, there’s no need to visit a shop unless you can’t complete the repair. If the Check Engine Light is on, you want to start by reading the diagnostic trouble codes to see if that shows you the problem.
A quick tune-up might be in order to get the car running right again. You can change the spark plugs, swap out the air filter and possibly add a fuel injector cleaner to see what happens. However, some of the other problems are tough to diagnose and more difficult to repair. You will need special tools to diagnose and repair a vacuum leak, transmission problems and issues with the sensors. In these cases, it might be best to visit your local auto repair shop.
What are RPMs?
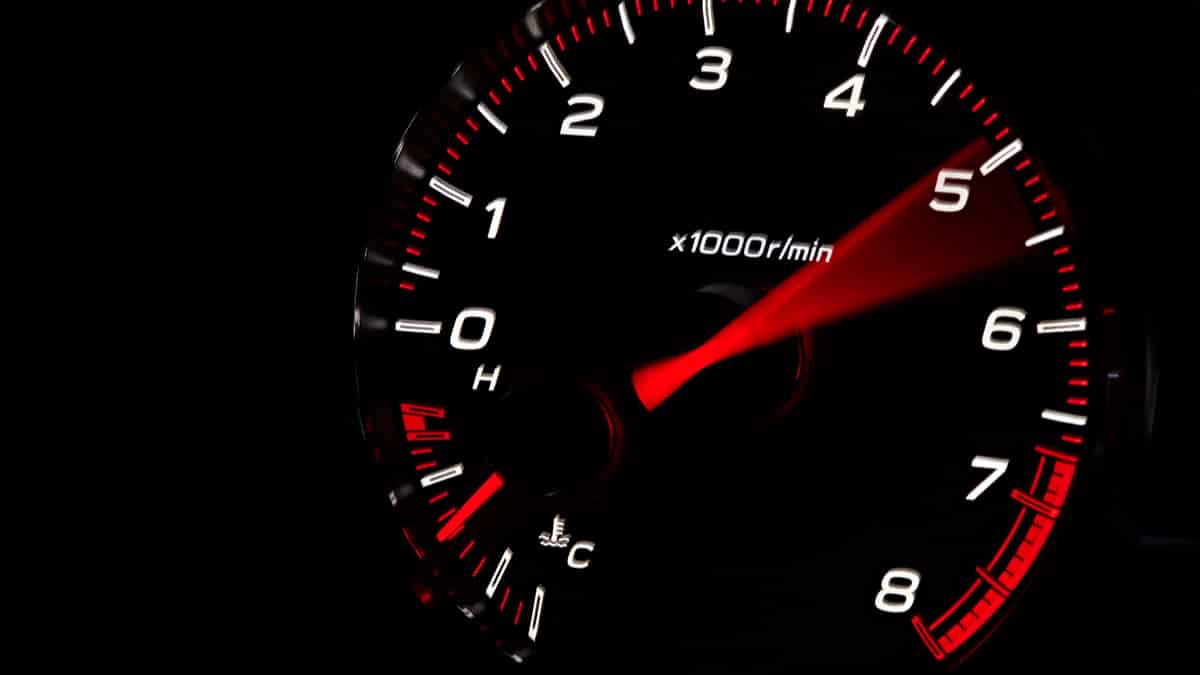
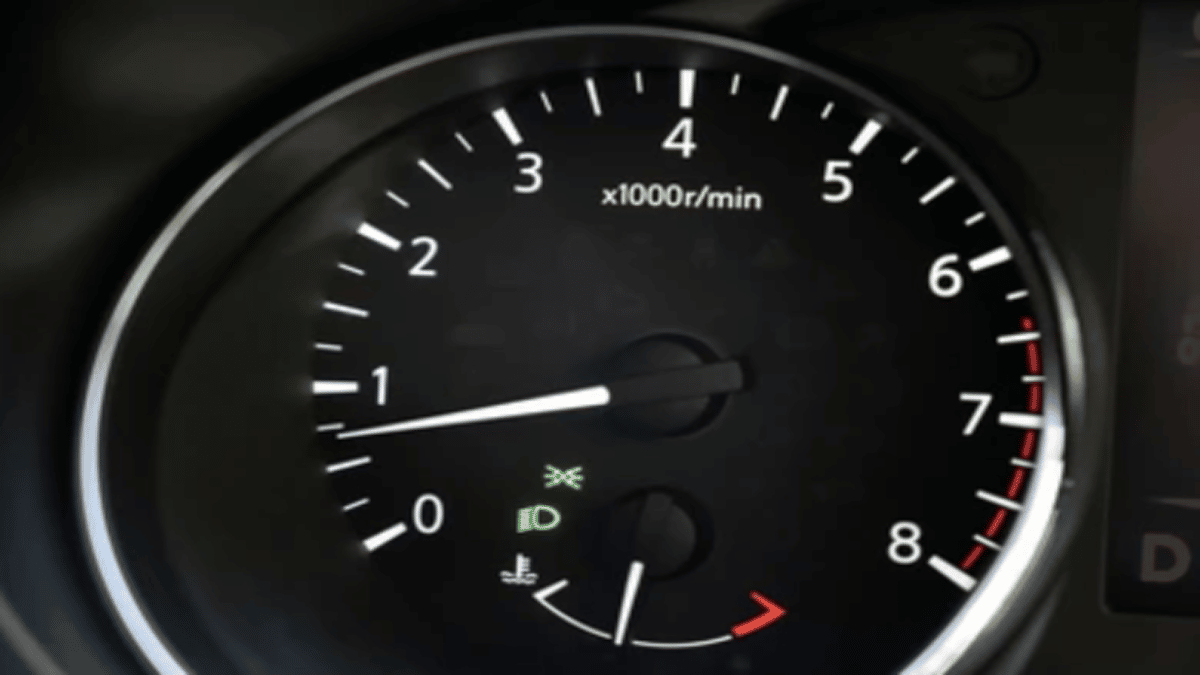
RPM means Revolutions Per Minute. When the car accelerates or decelerates, the engine’s crankshaft rotates. The RPMs measure these rotations in conjunction with how quickly the pistons are going up and down in the cylinders. You can view the RPMs on the car’s tachometer, usually sitting next to the speedometer.
When you are accelerating, the RPMs naturally increase. On the other hand, the RPMs decrease when you release the accelerator. The majority of engines rev up to 4,000 to 6,000 RPMs before shifting when operating normally, but this value depends on what type of vehicle and the motor that’s installed.
What are Normal Idle RPM Values?
When your car is idling, there shouldn’t be any surging or fluctuating, either. Normally, the idle speed should be somewhere between 500 and 1,000. If you are used to driving your car, you will get accustomed to what’s normal for your particular model.
If you are noticing a rough idle, it could be due to many of the problems listed above. However, it could also be due to a defective idle air control valve (IAC) valve that controls the airflow during idle.
What Causes Lower RPMs?
If the RPMs seem low and they are fluctuating, you might be looking at a dirty throttle body, defective spark plugs or a clogged air filter. It’s also possible that there’s a vacuum leak, which would create misfiring situations, too.
Go through the diagnostic steps listed above. You don’t want to ignore the low RPMs, because it can quickly cause engine stalling.
What Causes Higher RPMs?
If the RPMs are surging higher than normal or even to the red line, there could be multiple issues occurring. The most obvious thought is that there is a transmission problem, but you don’t want to overlook simpler issues.
We recommend performing a tune-up first to see if that resolves the problem. After that, you will have to start more extensive diagnostic procedures.
Cost to Repair Engine RPM Fluctuations
The repair cost varies depending on what you need to fix. You could spend $50 to $100 to perform a DIY tune-up that might resolve the problem.
On the other hand, there are some more expensive engine repairs you could be looking at. For example, replacing the throttle position sensor could cost $150 to $250, while the crankshaft position sensor replacement could be $175 to $275.
Additionally, finding and repairing a vacuum leak or having the transmission worked on could easily break the bank. If your car isn’t worth a lot of money, it might be time to get something newer.
RELATED: How Much Does a Tune Up Cost?
Categories: Driving, Engine, Troubleshooting