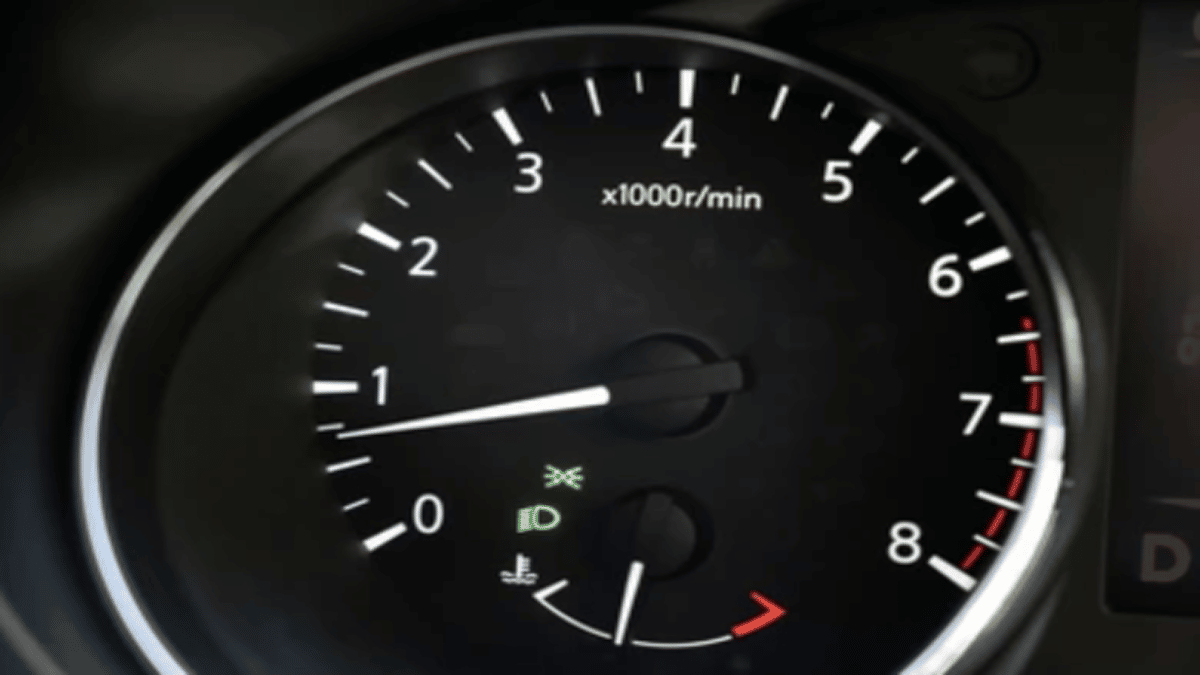
When your car engine runs as it should, everything should be smooth without any noise. When something thing goes wrong, the engine can start running rough, especially while idling.
By understanding the causes of a car engine that has a rough idle, you can resolve the issue easily. Here are ten of the most common causes of a rough engine idle.
In this article, I will go through all the possible rough idle causes together with an explanation of how you can test them. Let’s begin with a quick look at the reasons.
What Causes Rough Idle?
The most common cause of rough idle is a vacuum leak or a failed PCV valve. It could also be caused by other air-fuel mixture related issues like bad fuel injectors, EGR valves, or low compression. In rare cases, it is caused by misfires from a bad spark plug or coil.
While these are not all of the signs, it’s a great place to start. Here’s a more detailed list of the most common causes of rough idle:
1. Defective PCV Valve

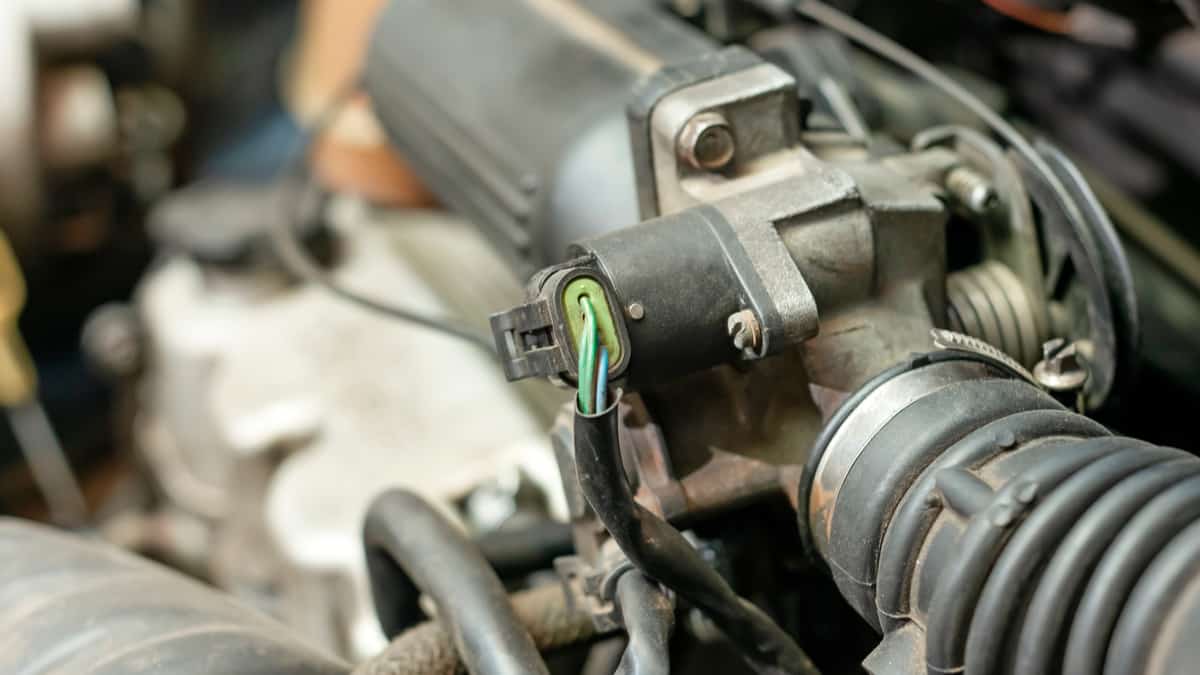
Your car engine’s Positive Crankcase Ventilation takes the unburned gases escaping from the cylinders and moves them from the crankcase, allowing them to go back to the engine for a complete burn. Because the PCV valve is working in the engine, it endures a lot of stress and is often filled with contaminants, such as dirt or sludge.
Over time, the valve can become blocked, rendering it useless. This blockage can also create a leak that forces the air/fuel mixture to become lean, leading to a rough idle.
To prevent this, you can periodically service the PCV valve. Once it is clogged, you might be able to clean it. Otherwise, it needs to be replaced.
RELATED: 7 Symptoms of a Bad PCV Valve
2. Vacuum Leak
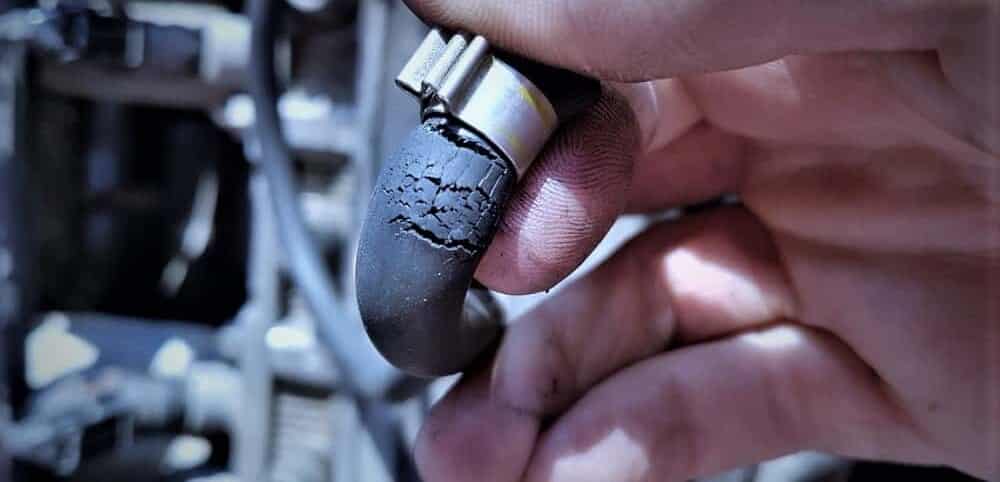

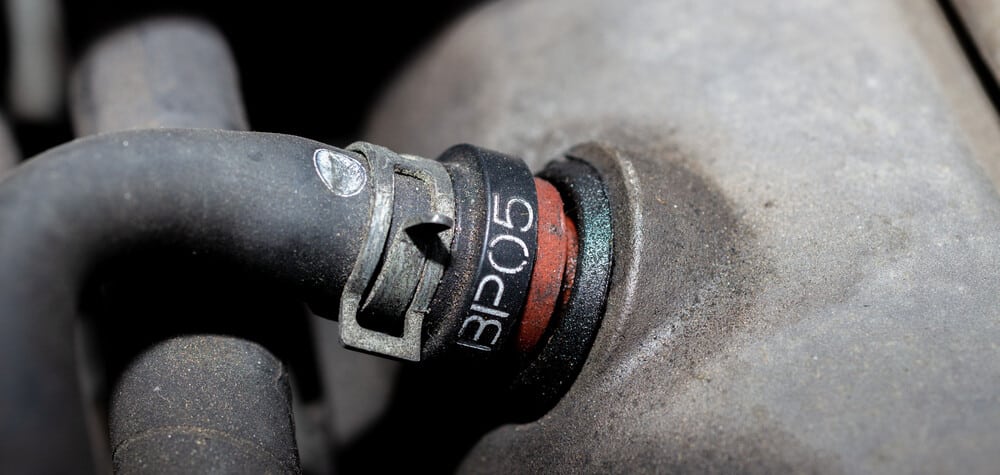
The engine compartment is filled with vacuum hoses, all of which can wear out at any point. Over time, these hoses become brittle and crack. If one gets a leak, it causes a lean air/fuel mixture, which leads to a rough idle. It can also turn into an engine misfire because of the combustion fault inside one or more cylinders.
Vacuum leaks can also occur from leaking vacuum supply tanks, vacuum brake boosters, and intake manifold gaskets. When you drive a car with a vacuum leak, you will notice that everything seems fine when the RPMs and speed are up, but idling causes it to run rough.
Checking the codes of the computer should indicate a vacuum leak. The air/fuel mixture is going to be lean, and the engine won’t be able to correct it.
RELATED: 6 Symptoms of a Vacuum Leak & Causes
3. Dirty Fuel Injectors
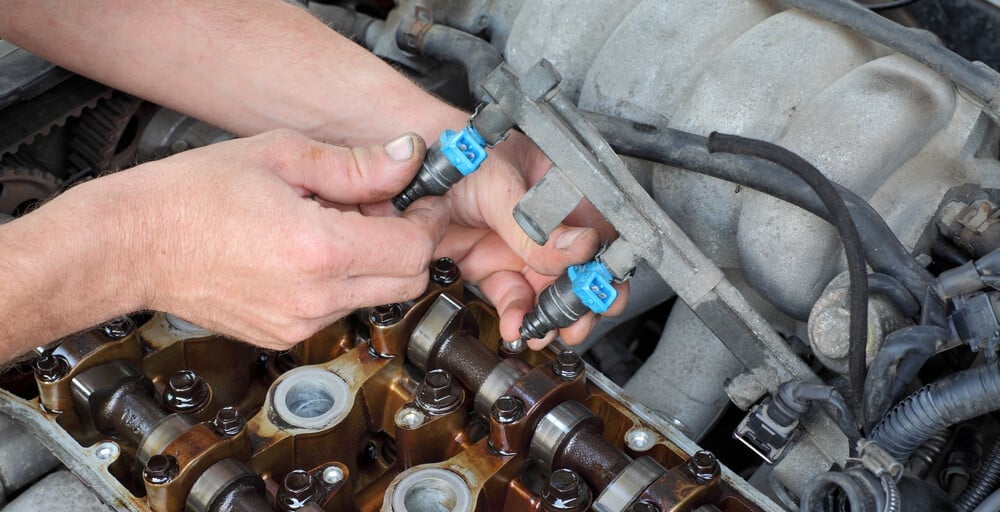

When the fuel injectors become dirty, a rough idle is just one problem you will experience. You will also notice a sharp decrease in fuel economy.
When the injectors get restricted, there’s a significant lack of performance, especially during acceleration. Dirty fuel injectors can be diagnosed through an exhaust gas analyzer because restricted injectors create higher hydrocarbon and carbon monoxide readings.
By using an injector cleaner additive regularly, you prevent this situation. Once the injectors are clogged or restricted, an injectable solution will need to be introduced into the system.
Fuel injectors often contain a small filter which is easy to replace if the injectors have become clogged, and this is much cheaper than replacing them.
RELATED: 8 Symptoms of a Bad Fuel Injector
4. Carburetor Issues
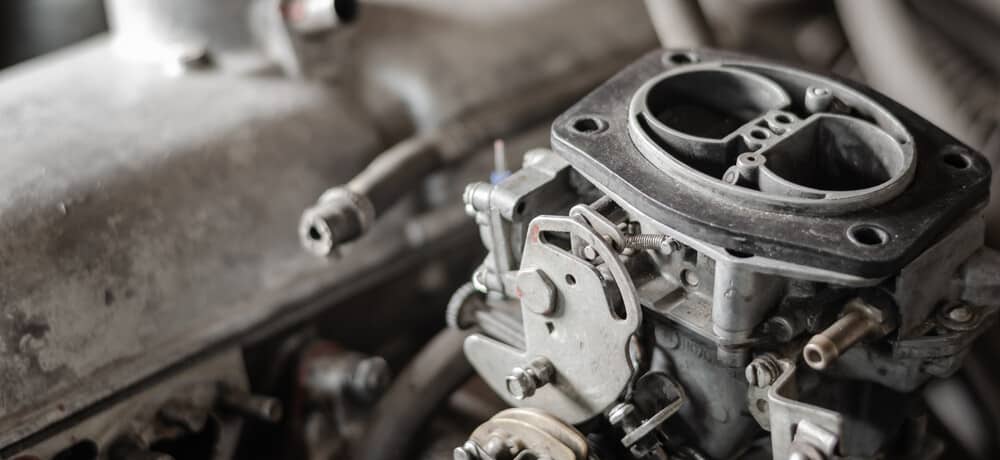

Older vehicles with high miles are the only ones on the road with a carburetor. However, there are still enough of them for this to be a problem.
Carburetor issues produce signature black smoke from the exhaust. Normally, this smoke only occurs once the vehicle has been warmed up.
The first thing to check is the choke. It should be completely open once the car is warm. If the choke is open, there’s likely an internal carburetor issue that requires a rebuild. Sometimes, it’s just the ethanol in gasoline that causes the carburetor to go bad.
However, you might also experience a problem with the throttle shaft at the carburetor base. This can wear out over time, leading to a vacuum leak.
5. Bad EGR Valve
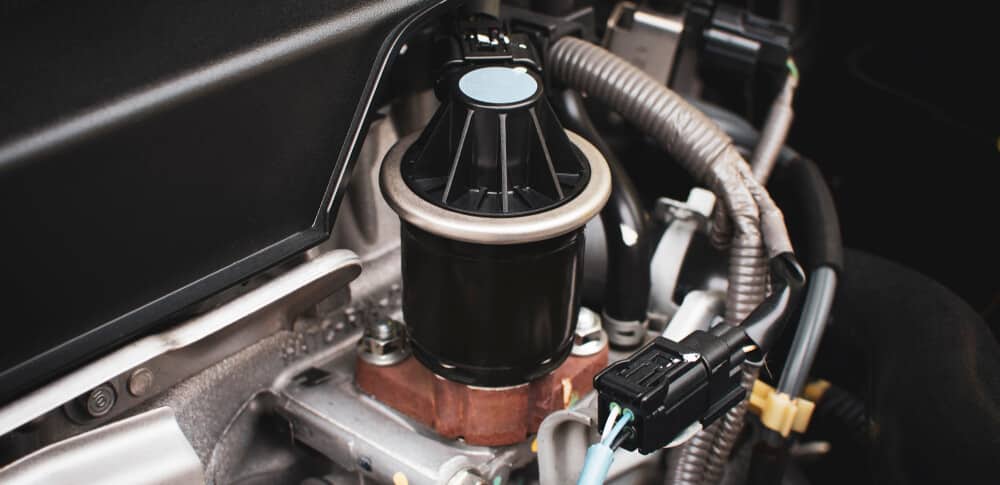

The Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve is a vital emission control device. It allows the exhaust gas to enter into the intake manifold, with the sole purpose of reducing emissions from the motor.
However, this EGR valve isn’t supposed to operate during idle, at wide open throttle, or before the engine is warmed up. If it runs at any of these times, the performance of the engine is affected.
When the EGR valve malfunctions, it doesn’t follow the rules. Instead, it sticks open and leads to a rough idle, or even worse, a stalling engine.
The car’s computer should set a code indicating that this component has gone bad. You can also try tapping it to see if you can free the stuck position. Cleaning the dirty EGR valve might be enough to resolve the situation. Otherwise, a low-cost replacement is all that’s needed.
RELATED: 6 Symptoms of a Bad EGR Valve
6. Faulty Ignition Coil
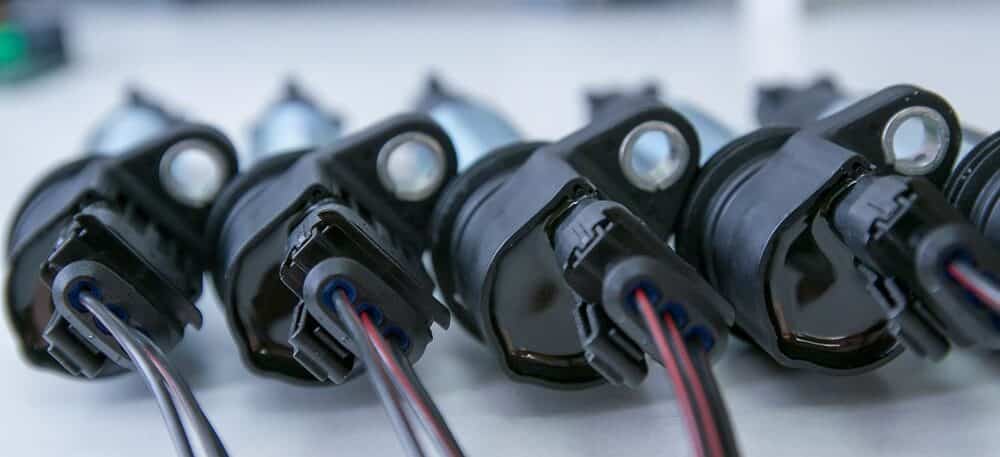

The ignition coil is essential to maintaining proper engine performance. It works in conjunction with the spark plugs to ignite the fuel/air mixture.
When the car has a faulty coil, it will experience a rough idle, misfire, loss of power, trouble accelerating, and poor fuel economy. As the situation becomes worse, it can also cause the vehicle to stall.
7. Defective Spark Plugs/Wires
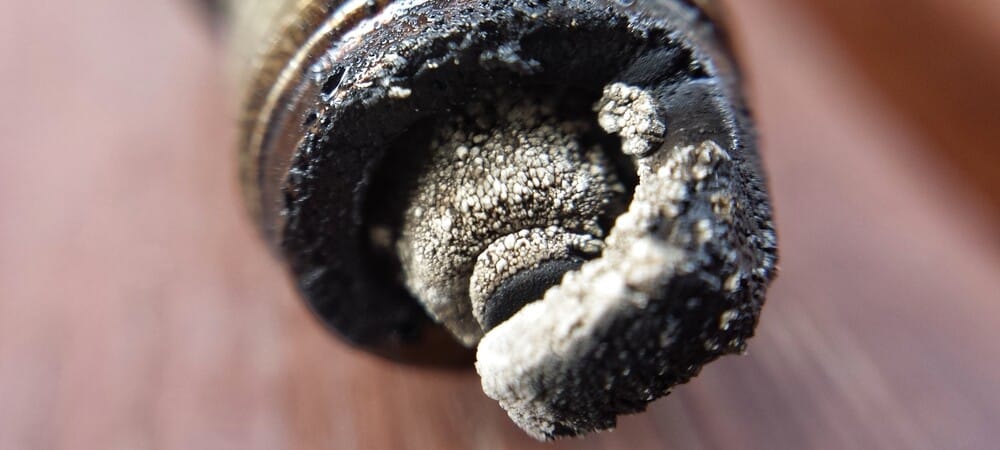

The spark plugs and wires are also critical to the ignition system. Over time, these parts will wear out, especially if contaminants get into the cylinders.
However, you can prevent this by regularly changing the spark plugs and wires. Because this is considered a maintenance task, you can find the recommended service interval in your owner’s manual.
8. Low Compression
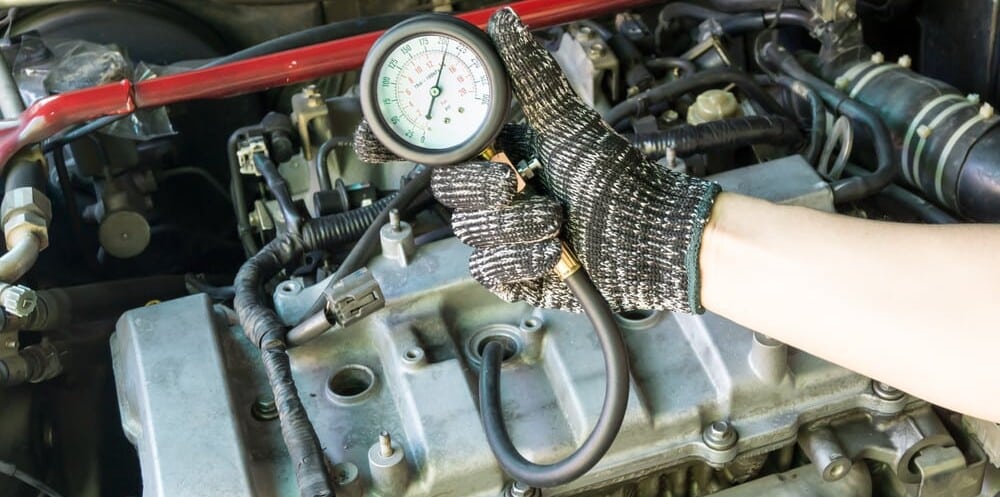

Low compression in your car engine is most noticeable at idle and, therefore, the place where you will notice it first. You can often notice low compression as a “miss” or misfire on idle.
The most common cars to experience a miss caused by low compression are those with more than 100,000 miles. Typically, the miss occurs when compression is low in one of the cylinders. To determine if this is the cause, a compression test needs to be performed.
To solve the problem, the engine will need to be disassembled for repair. The valves might need to be replaced for proper compression or the camshaft lobes might be worn out. Either way, it’s not a cheap fix.
Luckily, low compression does not happen as often as with older cars and is starting to get quite rare in newer car models.
9. Clogged Air Filter
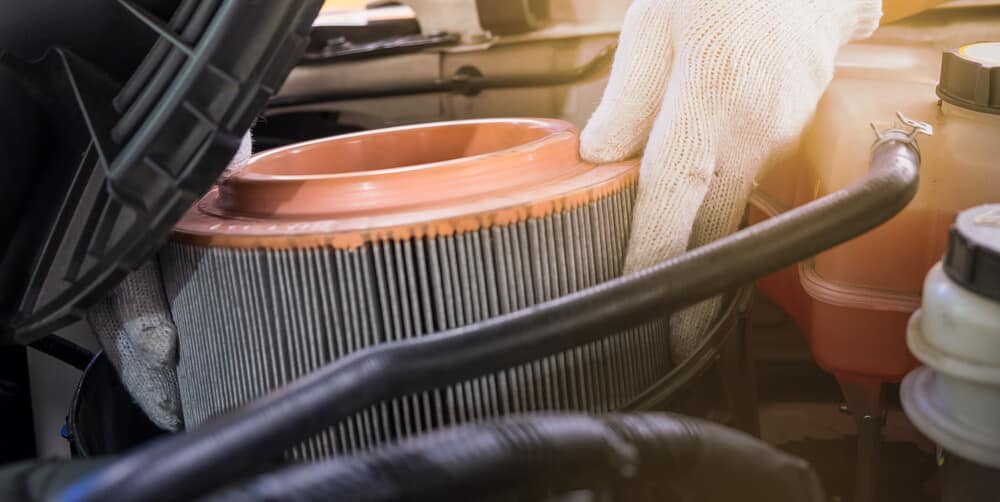

The engine air filter is critical for proper operation. It’s meant to keep dust, dirt, and other contaminants from getting into the engine. The paper element can easily become clogged, thereby restricting the airflow into the engine.
However, this is another maintenance task that should be performed regularly to keep the engine running the way it should. Ideally, you want to choose a high-quality air filter that isn’t easily clogged. For the small expense, it’s worth protecting your engine.
10. Bad Oxygen Sensors
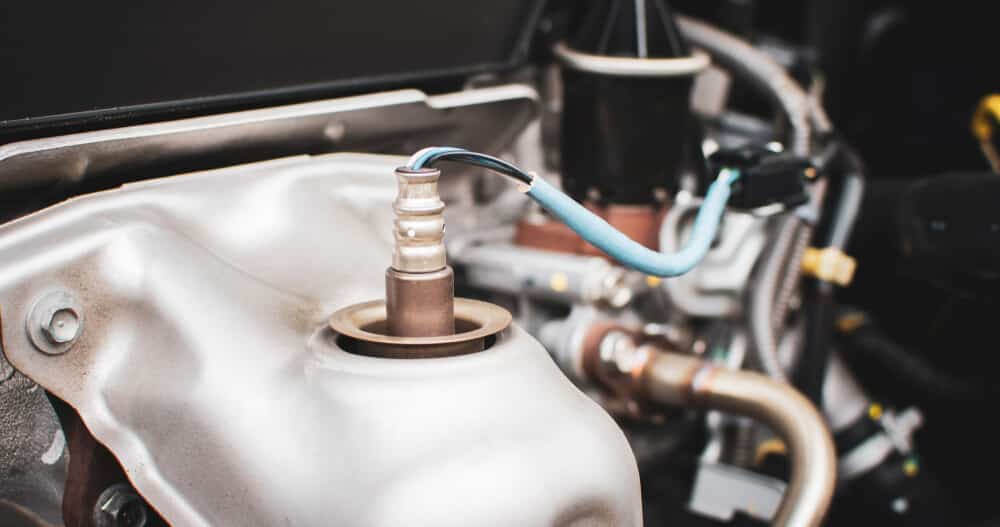

The oxygen sensors are vital to the emissions system of your car. They are located in the exhaust system, constantly monitoring the oxygen content of the gases. The information is sent to the engine computer, where it is used to maintain a proper air/fuel mixture.
However, oxygen sensors go bad because of the high temperature they are subjected to. Over time, they wear out or suffer from carbon deposit contamination. When this happens, the wrong information is sent to the computer, leading to an improper air/fuel ratio. If the ratio becomes too lean, a rough idle occurs.
This fault will create a trouble code that can be read with your scanner. A digital multimeter can also help you pinpoint which oxygen sensor has failed.
Whatever is causing your engine to idle rough, it’s important to diagnose the issue quickly and repair it. Ignoring poor engine performance issues only leads to more extensive and costly repairs down the road.
Categories: Engine, Troubleshooting