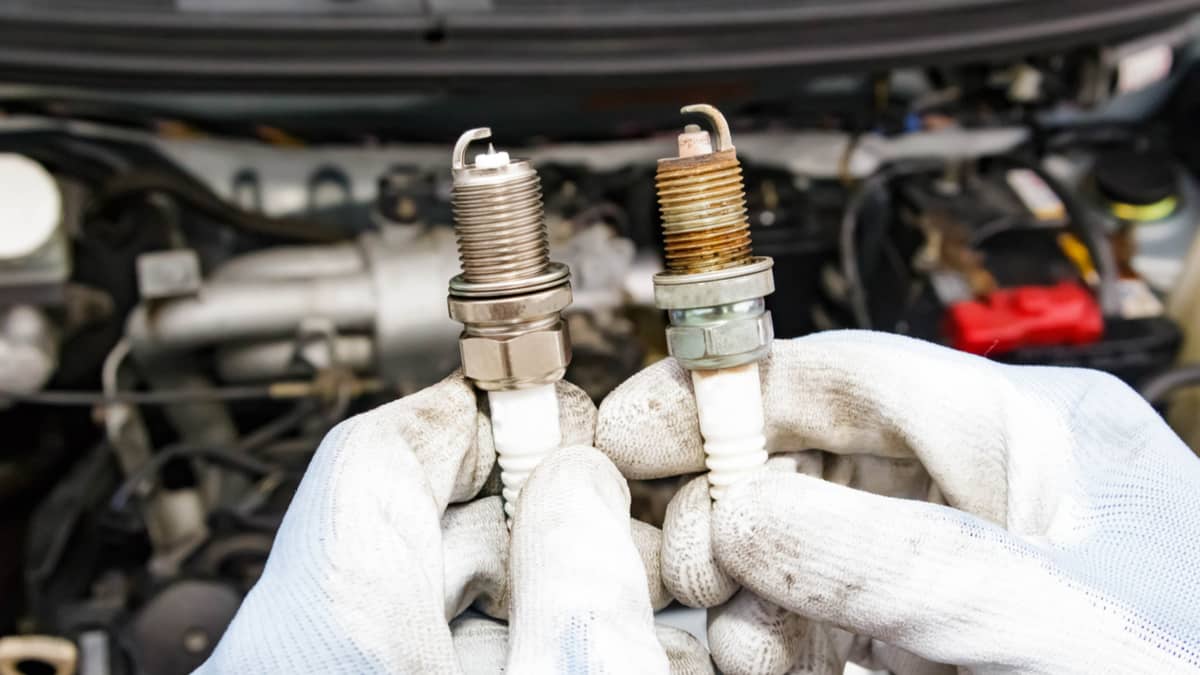
For the car engine to work properly, the perfect mixture of air and fuel is required, along with a clear and strong spark. If any of these things fail, it will not ignite the combustion chamber properly and a misfire will occur.
If your car engine is misfiring, it is important to find out the cause and fix it as soon as possible. Misfires can cause all sorts of problems, from reduced fuel efficiency to complete engine failure. But how do you tell if your engine is misfiring, and what could be causing it?
In today’s article, we will discuss the meaning of engine misfires and what possible issues can cause them. We’ll also look at how to determine if your engine is misfiring and answer some common questions about misfires.
What is an Engine Misfire?
An engine misfire is an event that occurs when one or more of the engine’s cylinders fail to ignite the air/fuel mixture during the combustion cycle. This can lead to a variety of engine performance issues and can even lead to serious engine damage if left untreated.
For complete cylinder combustion to occur, the engine needs three important things, and that is the correct air/fuel mixture, compression, and spark. If any of these are missing or incorrect, the cylinder combustion will not be done correctly, and no power will be created.
The engine control module monitors the crankshaft rotation speed with the crankshaft position sensor, and if the speed does not increase slightly on a cylinder after the combustion, it means that the engine is misfiring, and a trouble code will be stored.
The most common code you will see is the P0300 code, along with a code like P030X. The X is replaced with the cylinder number where the cylinder misfire occurs; for example P0301 is a cylinder 1 misfire.
What Are The Causes Of An Engine Misfire?
The most common causes of engine misfires are bad ignition coils or failed spark plugs. It can also be caused by fuel-related issues such as a faulty fuel injector or a bad fuel pump. In rare cases, it can also happen because of low engine compression.
Here is a more detailed list of the most common cause of engine misfires:
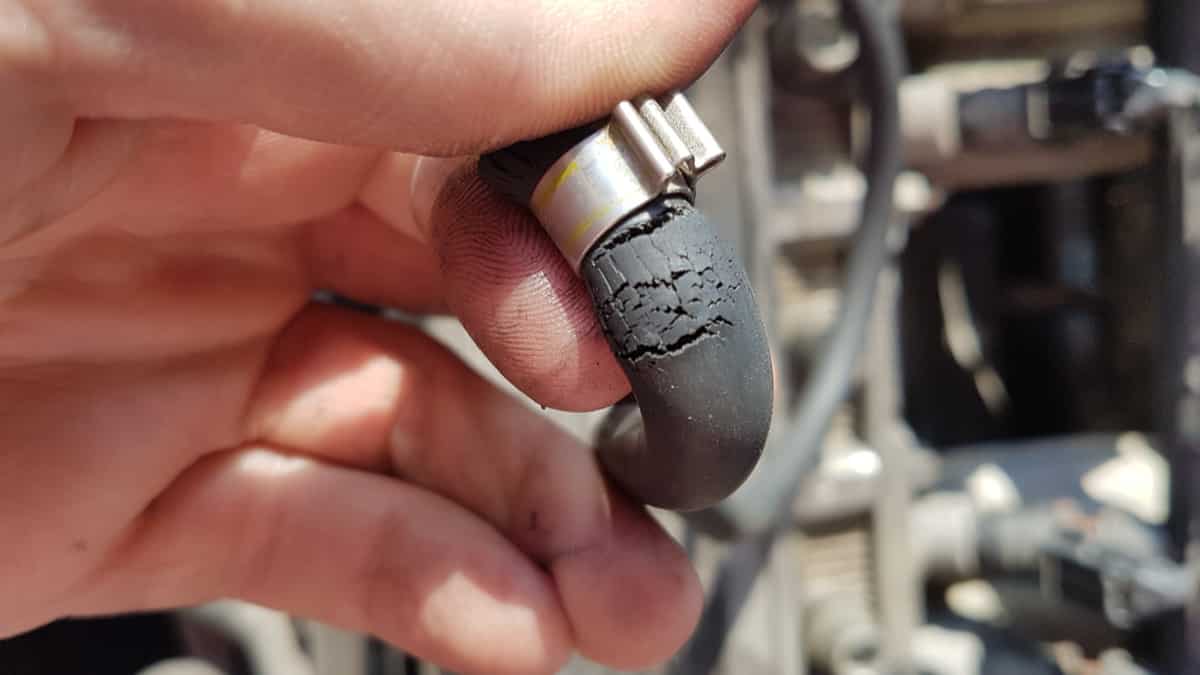
1. Bad Ignition Coil
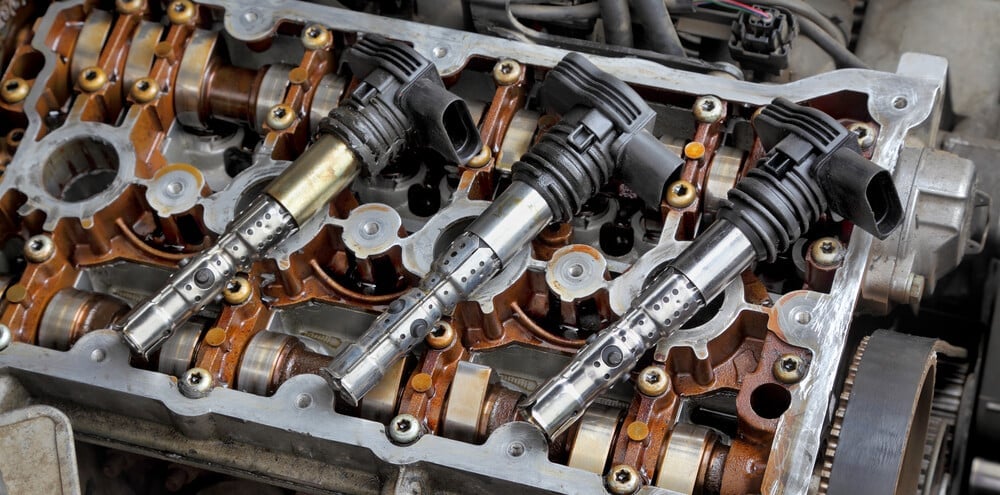

The most common cause of an engine misfire is a bad or failing ignition coil. Some vehicles have a separate ignition coil on every spark plug, while some cars have one coil pack with an ignition wire to each spark plug.
Older cars use a distributor to distribute the spark to all the spark plugs, which are powered by an ignition coil. If either the distributor or the ignition coil creates a weak spark, it can cause misfires.
READ MORE: 6 Symptoms of a Bad Ignition Coil (& Replacement Cost)
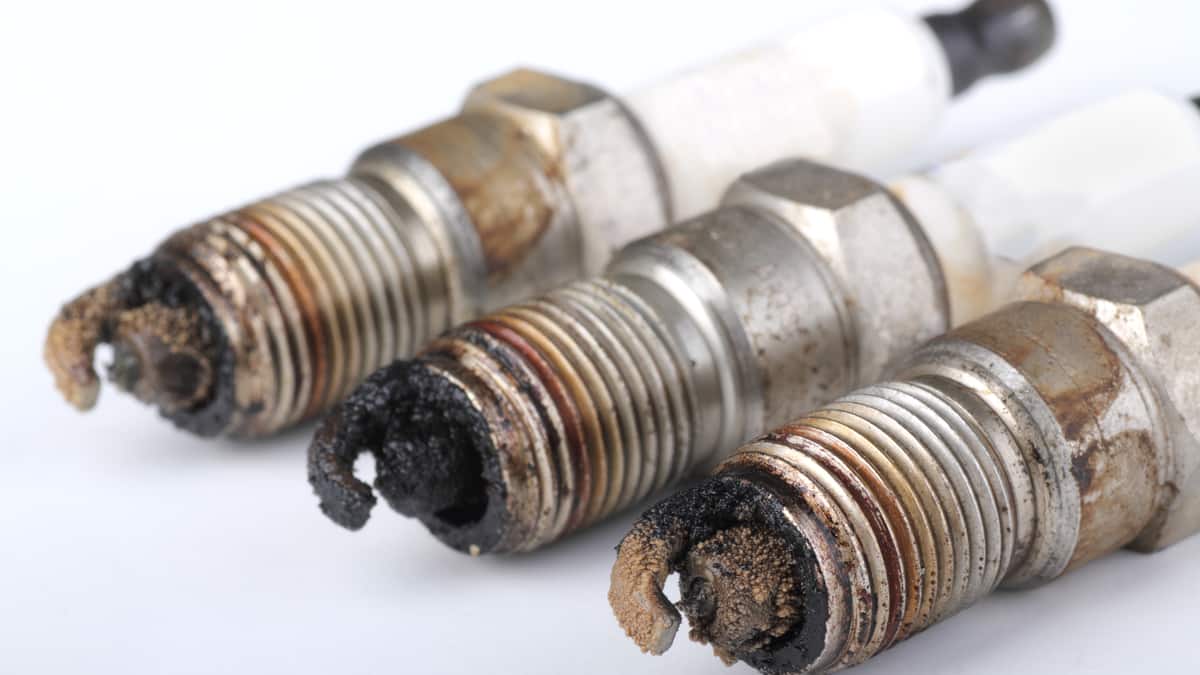
2. Failed Spark Plug
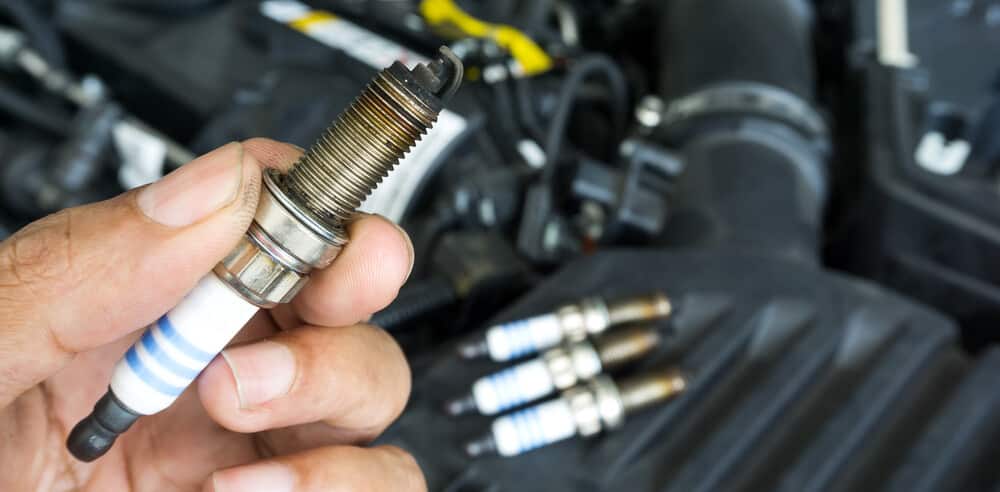

The second most common cause of a misfiring engine is bad or failing spark plugs. The function of the spark plug is to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber, and if there is something wrong with the spark plug, it will not ignite, and a misfire will occur.
Spark plugs should be replaced on a schedule for all car models, and not replacing them on time can cause fouled spark plugs, which can cause misfires. If you don’t know when you last changed the spark plugs, you need to check your service manual and replace them if necessary.
Read more: How Long Do Spark Plugs Last?
3. Intake Manifold Gasket Leaks
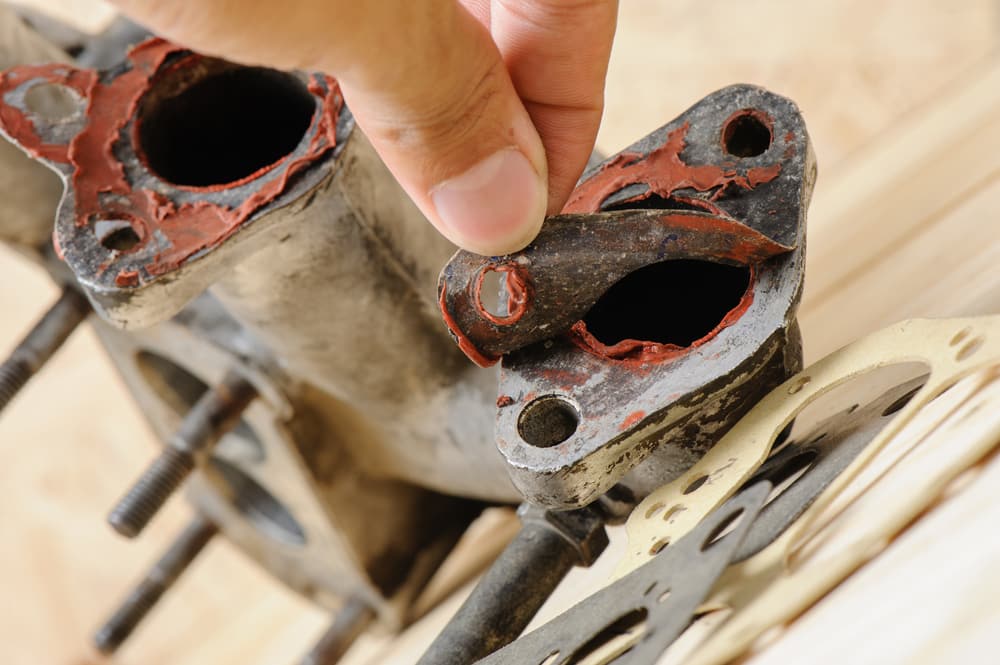

There is a gasket located between the cylinder head and the intake manifold called the intake manifold gasket. If this gasket leaks, it will draw air into the combustion chamber, causing the air-fuel mixture to become too lean, and this can cause misfires.
There are also many vacuum lines on the intake manifold that can leak, giving the same symptoms as a bad intake manifold gasket. However, finding these vacuum leaks is often quite easy and we will talk about that further down in the article.
RELATED: 5 Signs of a Bad Intake Manifold Gasket (& Replacement Cost)
4. Low Fuel Pressure
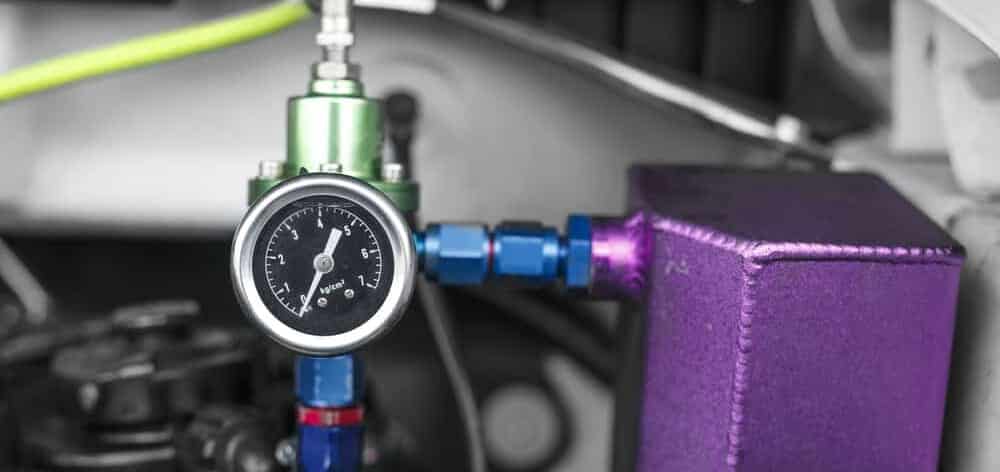

Low fuel pressure is another thing that can cause misfires. Low fuel pressure causes less fuel to enter the engine’s combustion chambers, resulting in a lean air-fuel mixture that can cause misfires on all cylinders. Low fuel pressure can be caused by a faulty fuel pressure regulator, a faulty fuel pump, or a clogged fuel filter.
Fortunately, checking the fuel pressure in your car is fairly easy with a manual fuel pressure gauge, and worth doing if you suspect low fuel pressure.
Read more: Low Fuel Pressure – Symptoms, Causes (& How To Fix it)
5. Faulty Injector
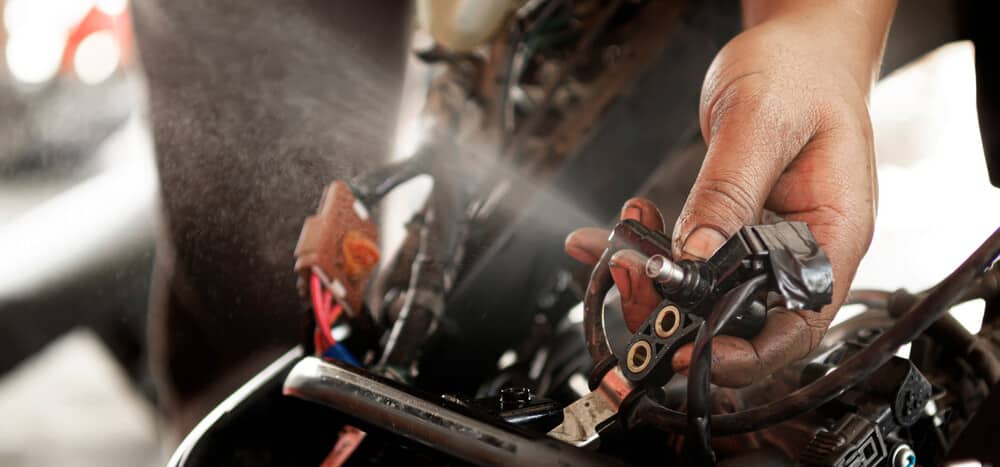

The fuel injectors supply the combustion chamber with the correct amount of fuel for each cylinder, and there is usually a separate fuel injector for each cylinder. If the fuel injector injects the wrong amount of fuel, it will cause the engine to run rich or lean, which can lead to engine misfires.
Failed injectors aren’t very common on most modern car models, and because of this, you’ll want to check out the other possible causes first. If you can’t find the issue elsewhere, it’s definitely worth taking a look at your fuel injectors.
Read more: 8 Symptoms of a Bad Fuel Injector (& Replacement Cost)
6. Bad Engine Sensor
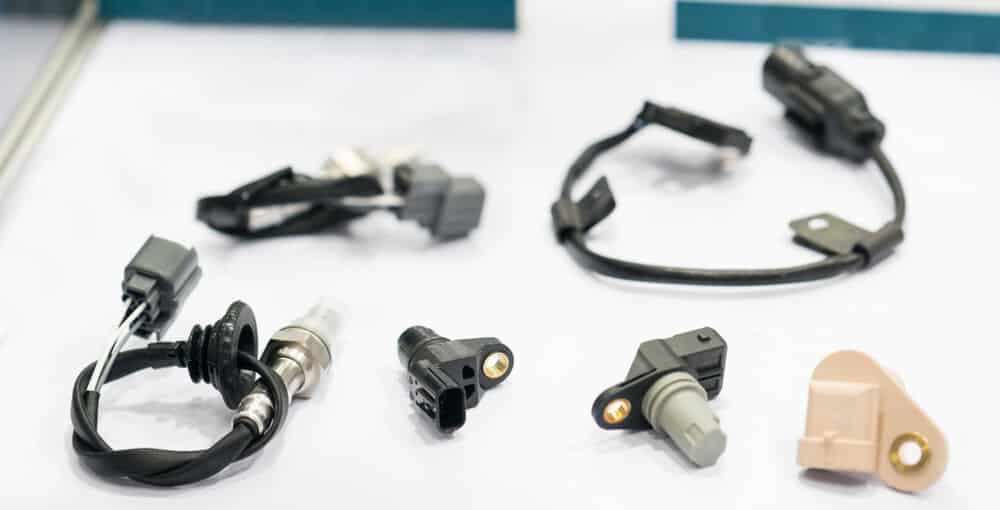

The engine in modern cars uses many sensors to measure everything in the engine to make them as efficient as possible. Failure of any of these sensors can cause an incorrect air-fuel mixture to enter the engine, which can cause the engine to misfire.
The most common car sensors that cause an incorrect air-fuel mixture are the MAF sensor, the MAP sensor, the oxygen sensor, and the coolant temperature sensor.
READ MORE: 15 Types of Car Sensors (& What They Do)
7. Low Compression
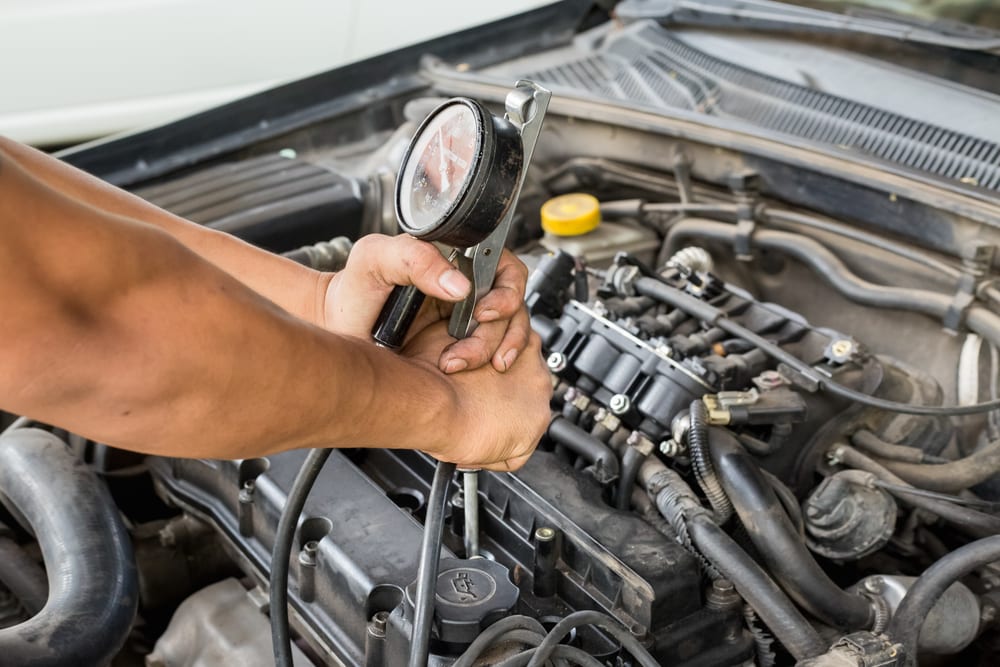

As we talked about earlier, the engine needs the right air-fuel mixture, spark, and compression to fire properly. If you already checked the fuel supply and the spark and couldn’t find any problems with it, there is a risk of low compression in your engine.
To find out if your engine has low compression, you need to do a compression test and compare the results to the manufacturer’s specifications. Unfortunately, low compression problems are often caused by worn parts inside the engine, which can be very expensive to fix, so you’ll want to inspect the other possible causes first.
RELATED: 8 Causes of Low Compression in a Car Engine (& How to Fix)
What Are The Symptoms Of Engine Misfires?
The main symptoms of an engine misfire include:
- Rough Acceleration
- Rough Idle
- Vibrations
- Check Engine Light
- Engine Sound Changed
Here is a more detailed list of the most common signs of engine misfires:
1. Rough Acceleration
When an engine misfire occurs, you may feel a strong or light jerk coming from the engine. These misfires often occur under load from the engine, such as when you accelerate quickly.
The most common situation where you will feel misfires is in high gear, low RPM, and with the gas pedal to the floor. Rough acceleration is a typical sign that your engine is misfiring.
You may also notice other performance issues, like slower acceleration than usual or a stalling engine while accelerating.
2. Rough Idle
The car engine is most sensitive to small air-fuel mixture problems at idle, so this is probably one of the first places you will notice misfires.
Therefore, if you notice that your car engine idles rougher than usual, it could be a sign of a misfiring engine. You may also notice problems such as the engine stalling at idle or an uneven idle that jumps up and down.
3. Vibrations
A car engine is very balanced when it is manufactured and often has balance shafts and various tricks to get as little vibration out of it as possible.
When one or more cylinders do not fire properly, the engine will become unbalanced, and this can cause severe vibrations inside your car when accelerating or idling. You can also open the hood of your car and watch the engine idle. If you notice that it vibrates more than usual, it could be a sign that the engine is misfiring.
4. Check Engine Light
Modern cars have good monitoring systems for all the different car sensors on the engine. If a sensor is failing or a sensor detects that something is wrong with the engine, it sends the information to the engine control module.
When the engine control module receives the data, it will determine if the problem is serious or not. If the problem occurs repeatedly, the engine control module will illuminate the check engine light to let you know that something is wrong so that you can have it repaired.
If you see a blinking or flashing check engine light, that’s another strong sign that your engine is misfiring.
5. Engine Sound Changed
If you know a little about cars, you’ve probably noticed a difference in sounds from different engines. V8 engines have a completely different tone than a four-cylinder engine, for example.
Therefore, if your 4-cylinder engine misfires on one cylinder, it will sound like a 3-cylinder engine. If your car engine sounds unusual, it’s possible that your engine is misfiring on every cycle.
How To Fix Engine Misfires?
To fix engine misfires, you need to read the trouble codes from the engine control module and continue troubleshooting from there. You’ll also want to inspect the spark plugs and ignition coils. Then, you want to look for vacuum leaks and cylinder compression.
Here is a more detailed list of how to diagnose and fix engine misfires:
1. Check Trouble Codes
Modern car engines have a system that monitors all the sensors in the car engine, and if there is something wrong with a sensor, it will store it as a trouble code in the engine control module.
Therefore, the first thing you want to do when diagnosing misfires is to check the trouble codes with an OBD2 scanner. You can either get one yourself, or go to a mechanic and borrow their diagnostic tool to read the trouble codes from the ECM.
This will give you important information. For example, if you see a trouble code like P0300 or P030X, it means that the ECM is detecting a misfire on a specific cylinder, and you may want to start checking the spark plug or ignition coil on that cylinder.
If you find trouble codes on an engine sensor or low fuel pressure, you’ll want to start the diagnosis from there. It is important to start by reading the error codes to know where to start troubleshooting.
2. Check Spark Plugs and Coils
If you have a misfire trouble code on a specific cylinder, you’ll want to start by looking at the spark plugs and ignition coil on that cylinder. Remove the spark plug and ignition coil from that cylinder and visually inspect them and replace them if they look bad or dirty.
An old trick that mechanics often use on car engines with separate ignition coils is to switch the spark plug and ignition coil to another cylinder. Then, clear the codes and drive for a while to see if the problem has moved to another cylinder. If it did, you know it’s a problem with either the spark plugs or the ignition coil, and you will want to replace all the spark plugs and the ignition coil on that cylinder.
3. Check vacuum leaks
If you can’t find any problems on the spark side, it’s time to look at the air-fuel mixture. Vacuum leaks are a common cause of an incorrect air-fuel mixture and are fairly easy to check, so you want to start there.
You can check for vacuum leaks by gently spraying a flammable spray around the engine’s intake manifold while the engine is idling. If the engine speed increases, it means there is a leak and the engine is injecting the flammable spray. However, be very careful when doing this and have a fire extinguisher ready.
You can also use an EVAP smoke machine to easily find vacuum leaks, but these are often quite expensive and probably not something most people have in their garages.
Learn more here: How to find a Vacuum Leak & How to Fix It (8 Easy Steps)
4. Check fuel pressure
The next thing you want to check is the fuel pressure. Although most modern cars use an electric fuel pressure sensor, you’ll want to confirm the results with a manual fuel pressure gauge, because an electronic sensor can fail.
Connect a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel rail and start the engine. Check the fuel pressure and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications. If it is too high or too low, you need to inspect the components of the fuel system such as the fuel pump, fuel filter, and fuel pressure regulator.
5. Check Compression
You also want to ensure that the engine’s compression is correct, so you must do a compression test on all cylinders. You can do this with either a compression tester or a leak-down tester.
Compare the results with the manufacturer’s specifications, and if the compression is low on a cylinder, you need to inspect the engine parts such as the timing belt, piston rings, valves, or pistons. All of these parts are often very expensive to replace, so you want to make sure you do a proper diagnosis before replacing them.
6. Take it to a mechanic
If you’ve checked all the things above, but still can’t figure out what’s causing the misfires in your engine, it might be worth taking the car to a professional mechanic instead. Engine misfires can actually be quite difficult to diagnose even for us experts in the field.
Even if you think it will be very expensive to take the car to a mechanic, it can actually sometimes be cheaper to get a proper diagnosis rather than replacing fully functional parts.
Is Engine Misfire Serious?
Yes. Engine misfires are serious. When an engine misfires, it can cause reduced fuel economy, engine damage, and a loss of power. In some cases, it can also lead to dangerous situations where the car stalls and becomes difficult to steer due to the loss of power steering. It can also seriously damage your engine.
What Does An Engine Misfire Feel Like?
If your engine misfires, it will feel like the engine is shaking or vibrating, and it may make a knocking noise. You may also notice that the engine does not sound like it used to, and that your car has reduced power and fuel efficiency. If you think you may have a problem with engine misfires, the best thing to do is take it to a mechanic to have it checked out.
How Much Does It Cost to Fix Engine Misfires?
You can expect a cost of $200 to $500 to fix a misfiring engine in most cases. However, it depends on how serious the fault is and what specific repairs need to be made. Some of the most common causes of engine misfires are bad spark plugs or a bad ignition coil, which can be relatively cheap to repair. If you’re unlucky, it could be due to poor compression, which can be very expensive to repair.
How long can you drive with a misfiring engine?
It is not recommended to drive your car at all with a misfiring car engine. If you suspect that your engine is misfiring, it is important to take care of the problem as soon as possible. Continuing to drive with a misfiring engine can cause serious damage to your car’s engine.
Can I drive with a misfiring engine?
No. It’s not recommended to drive with engine misfires. Misfires can cause serious damage to your engine’s internal parts and the catalytic converter, which can be very costly to repair. It’s best to diagnose and repair the issue as soon as possible.
A misfiring engine can be a serious problem that should be fixed as soon as possible. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and how to fix it, you can keep your car running smoothly and avoid expensive repair costs.
Fixing a misfiring engine can sometimes be difficult without the right knowledge and tools, due to the multitude of possible causes. Therefore, if you have checked the basics, it may be worth taking your car to a qualified mechanic for expert advice.
I hope you enjoyed this article and now have the expertise to diagnose engine problems like misfires and fix the problem with your car yourself to save some money.
Learn more:
- Car Jerking When Accelerating? (Here’s How To Fix it)
- 7 Best Spark Plugs – Review & Buyer’s Guide
- Car Losing Power When Accelerating? Causes & How To Fix It
Categories: Engine, Troubleshooting