If you’re like most car owners, you probably don’t think much about your car’s oxygen sensors until they are causing a problem. But did you know that a bad oxygen sensor can impact your car’s performance and even lead to decreased fuel efficiency?
In this guide, we cover the common symptoms of a bad O2 sensor, so you know what’s going on. We also show you where to find the oxygen sensor and discuss its function. We also talk about what you might spend to replace it and why you should get the repair performed right away.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Bad Oxygen Sensor?
The most common bad oxygen sensor symptoms are poor engine performance and rough idle, along with a check engine light on your dashboard. You may also notice reduced fuel economy, and the car may fail an emissions inspection.
Here is a more detailed list of the bad oxygen sensor symptoms:
1. Check Engine Light Illuminates

One of the most common bad oxygen sensor symptoms is a check engine light on your dashboard. In many cases, there can be a trouble code related to the oxygen sensor, and you don’t notice any other bad o2 sensor symptoms at all.
All of the trouble codes P0030, P0031, P0130, P0131, P0132, P0133 and P0134 have to do with the oxygen sensors. You might also see P0137, P0140, P0141, P0161 or P0172 on your code scanner. With this in mind, you can see any number of trouble codes relating to an air-fuel mixture imbalance that could ultimately be caused by the oxygen sensor.
2. Decreased Fuel Economy

Inside the combustion chambers, there must be the right amount of air and fuel mixing. If there’s more fuel than air, your defective oxygen sensor might not be able to detect it.
As more fuel burns in the engine, your gas mileage decreases. What you are left with is more money spent at the pump and more frequent trips to the gas station.
3. Rough Idle

If you’ve noticed that the car runs roughly when it’s stopped or parked, the idle is off. Usually, a car should idle at around 1,000 or fewer RPMs. If it shoots up, that’s one of the bad o2 sensor symptoms.
However, a rough idle isn’t always indicative of a bad oxygen sensor. It could mean any component that’s responsible for the air-fuel ratio is defective. That’s why you need to compare this symptom with the others.
READ MORE: 10 Causes of Car Engine has Rough Idle (How to Fix it)
4. Stalling Engine
When the engine idle gets too rough, the motor could stall. This problem normally starts out as a misfire and doesn’t normally occur until the problem has been left unresolved.
If the engine is unable to sustain the right amount of power to remain working, it will shut down. You should still be able to get it started again, but there are no guarantees.
5. Poor Motor Performance
If the normal combustion process is interrupted, you can expect to notice trouble with the performance of the engine. It’s going to be weaker than normal, especially when you try to push on the gas pedal. At first, this problem can be so subtle that you don’t notice it’s occurring.
The problems could continue getting worse until driving becomes cumbersome. That’s why it’s important to have the fault looked at as soon as you notice it, especially before the lack of acceleration leads to an accident on the road. If you notice that your engine performance has decreased, that’s a strong indicator that you may have a bad O2 sensor.
RELATED: Car Losing Power When Accelerating? (Here’re the Causes)
6. Failed Emissions Test
The oxygen sensors are part of the emission control system in the vehicle. If they aren’t working, there could be an imbalance in the exhaust, which would be read through an emissions test.
While there are numerous reasons you might fail these mandatory tests, the oxygen sensors tend to be a major culprit. If you have failed an emissions test, have the computer checked for codes that show you what the problem might be.
7. Strange Sounds
When an oxygen sensor fails to monitor the air-fuel mixture, an abundance of carbon could build up in the combustion chamber. This problem could cause a lean-running mixture in the motor.
With a lean mixture, you are left with pre-ignition that leads to pinging or knocking noises. However, these noises can also occur for other reasons, such as a clogged fuel injector, bad fuel, or engine damage. Most often, these noises are heard under engine load.
RELATED: 7 Engine Noises You Should Not Ignore (& What They Mean)
8. Catalytic Converter Failure
What happens if you continue running the system with a bad oxygen sensor? Eventually, the catalytic converter will fail because of the imbalance of air and fuel. The oxygen sensors must be in optimal working order to prevent damage to the catalytic converter.
It’s never cheap to replace a catalytic converter. For this reason alone, you want to fix the defective oxygen sensor because it causes bigger problems.
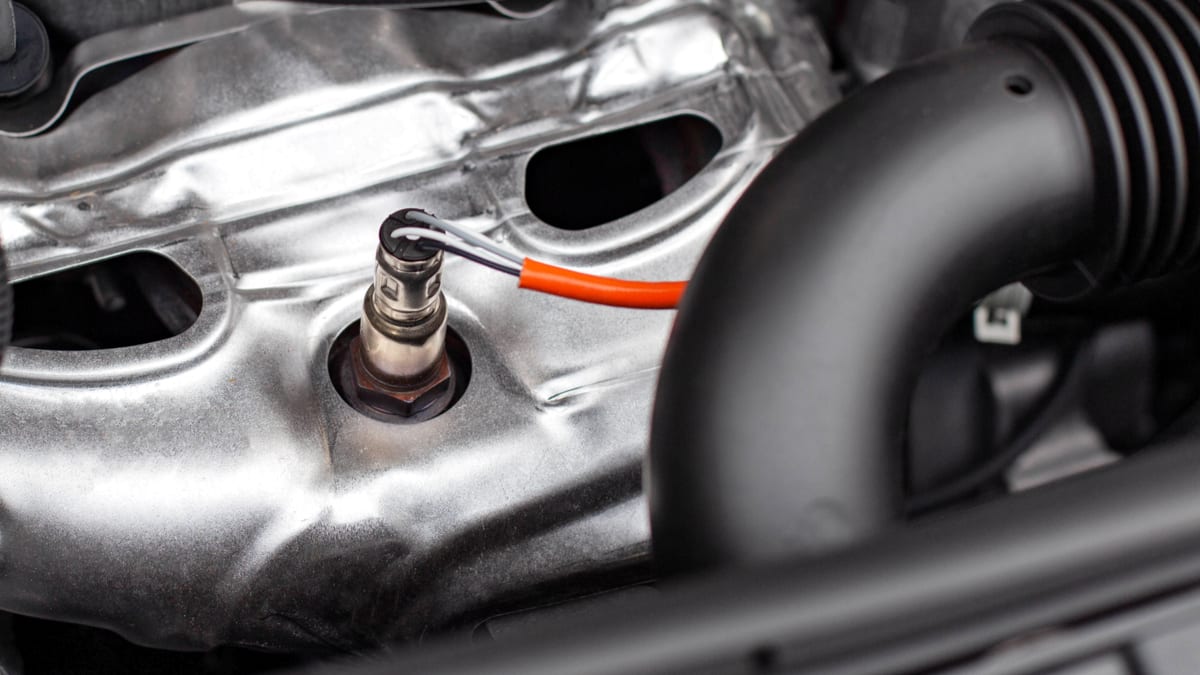
Oxygen Sensor Location
The oxygen sensor is found in the exhaust system. It can be found near the engine or on the exhaust manifold. Many cars have several oxygen sensors, but they are all monitoring the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
If the car has more than one oxygen sensor, the other will be located behind the catalytic converter. This sensor monitors the performance of the converter by comparing the readings occurring before and after.
RELATED: How to Bypass Oxygen Sensors – Can & Should You Do it?
Oxygen Sensor Function
The car engine uses a combustion process that produces exhaust gases once the fuel and air have ignited in the cylinders. These exhaust gases contain several components, such as oxygen and carbon. The oxygen sensors monitor the level of these gases in the exhaust as it’s leaving the motor. Whatever oxygen is flowing through the combustion process is measured by this sensor.
The information received from the oxygen sensor is sent back to the engine control module (ECM). This computer is in charge of processing all of the information so adjustments can be made to the air and fuel ratio. If the ECM reads that there’s too much oxygen, it will adjust other sensors to add more fuel and vice versa. Otherwise, you are left with either a lean- or rich-running condition that creates engine problems.
Not only will the bad oxygen sensor cause engine troubles, but it can also lead to further damage to other components. For example, as the imbalanced exhaust continues to flow through the catalytic converter, you are allowing additional wear to this expensive part. That’s why repair should be performed as soon as possible.
Oxygen Sensor Replacement Cost
On average, you might spend $50 to $450 to replace a bad oxygen sensor. However, this price is based on several factors. The type of car and engine you drive has a lot to do with the cost.
If you are driving a small economy car, your cost is probably going to be much less than the larger SUV or truck. Luxury cars also have more expensive parts that increase the overall total. Additionally, you might need a specialty mechanic to work on your luxury brand, which you wouldn’t need if you were driving a small Chevy.
The other major factor has to do with the labor rate. If you can replace the oxygen sensor yourself, there’s no reason to pay a professional mechanic. Considering the oxygen sensor might only cost you $20 to $175, you can save a lot of money figuring this out on your own. The service manual or a repair manual is quite helpful when it comes to these fixes.
The trouble comes in when you wait to change the oxygen sensors. By procrastinating with this repair, you can allow other damage to occur. For this reason, what would have been a simple repair can quickly turn into something more costly. That’s why we always recommend changing the defective oxygen sensor at the first sign of trouble.
Compare the costs of replacing an oxygen sensor with swapping out the catalytic converter. For a typical catalytic converter replacement, you are looking at an average of $1,000 to $2,500 to have it worked on by a professional. However, most of this cost isn’t related to the labor costs but how expensive the part is. That’s why it’s best to spend the money upfront and get the oxygen sensors working right than deal with what’s coming down the road as a result of neglect.
What happens if you don’t replace the oxygen sensor?
If the oxygen sensor isn’t replaced, the car’s computer won’t be able to monitor the air/fuel mixture accurately. As a result, the car’s engine will run either too rich (with too much fuel) or too lean (with not enough fuel). This can cause all sorts of problems, including excessive emissions, poor fuel economy. In the long run, it will cause excessive wear on the engine, which can damage expensive parts like the catalytic converter or internal engine parts.
Can I drive with a bad oxygen sensor?
While you can drive your car with a bad oxygen sensor in most cases, it is not recommended, as it can cause the car to run lean or rich and potentially damage the engine. However, if you are on your way to the mechanic, you can still drive the car as long as you are aware of the potential risks.
Can I replace the oxygen sensor myself?
Yes. Replacing an oxygen sensor is in most cases a fairly simple job. However, it depends on the make and model of your car. In some cases, if the car is older, the oxygen sensor can get stuck because of rust, and it can be difficult to remove it without special tools.
Will check engine light reset after replacing the O2 sensor?
It depends on the make and model of your car. For most cars, the answer is ‘yes.’ The check engine light will reset after replacing the O2 sensor, but it can take a while. Every time you start the engine and warm it up, the car checks the emissions. It may take 10-20 successful cycles before the engine control module understands that the oxygen sensor is working and removes the light. So it’s definitely easier to clear the error code with a scanner.
There are a few symptoms that can point to a bad oxygen sensor, but the best way to know for sure is by using an OBD-II scanner or letting a professional mechanic diagnose the car. If you notice any of these problems with your vehicle, be sure to take it in for service as soon as possible.
Learn more: