It’s always important to be aware of the signs of a problem with your car so that you can get it fixed before it becomes a bigger issue.
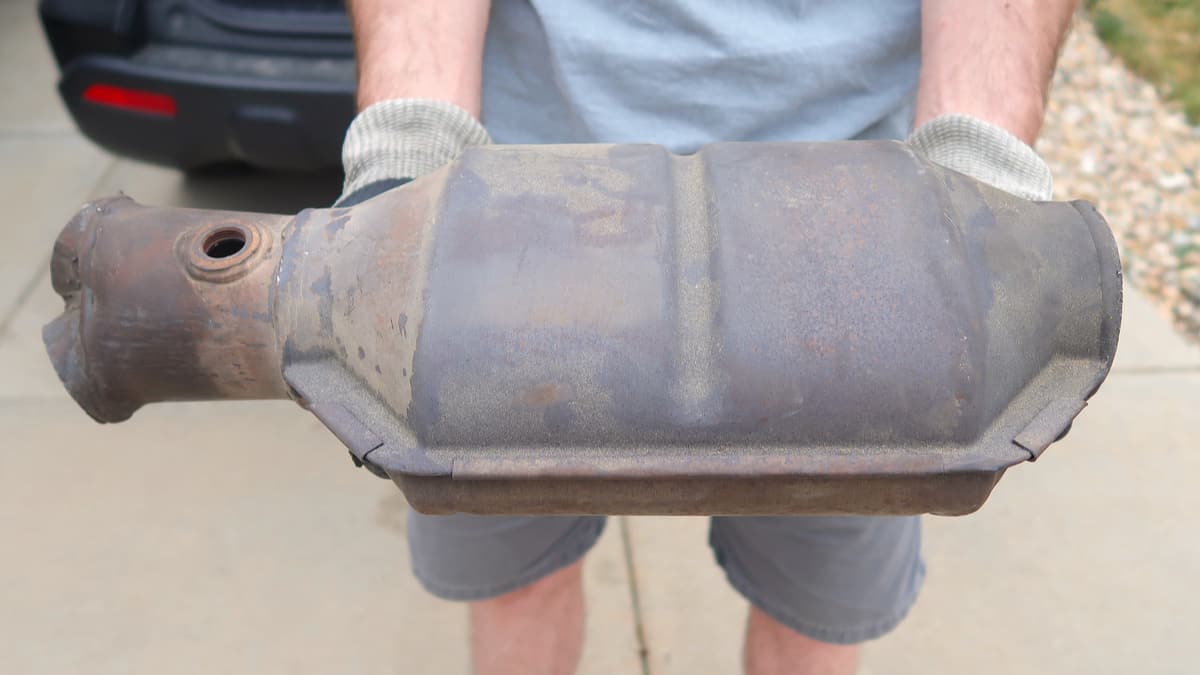
Catalytic converters are known to fail and are often very expensive to replace, especially if you are looking for a brand-new one.
Therefore, diagnosing a defective catalyst is crucial to ensure that you won’t replace a fully functioning catalytic converter. In this post, I’ll show you the most common bad catalytic converter symptoms, where the catalytic converter is located, and its function, and go through what makes it so attractive to thieves.
Symptoms Of A Bad or Clogged Catalytic Converter
The most common symptoms of a bad catalytic converter are a sulfur smell when the engine is warm and a check engine light on your dashboard. You may also notice engine performance issues like acceleration lag, higher or lower fuel consumption, and a misfiring engine.
While these are not all possible symptoms, they are the most common ones. Here is a more detailed list of the signs of a bad or clogged catalytic converter to look for:
1. Check Engine Light

The check engine light, one of the most obvious indicators of a malfunction with your car, is also one of the strongest indicators of a bad catalytic converter. When checked with a compatible OBD scanner, it will show you a catalytic converter-related trouble code that must be decoded with the help of the operating manual.
The most common trouble code when it comes to a bad catalytic converter is the P0420 code.
2. Acceleration Lag

If you observe delays when accelerating or a decrease in power when driving in steep areas while all other parts like spark plugs, filters, sensors, etc. are fine, then it could be the catalytic converter that’s bad.
Mechanics often misdiagnose the symptoms of a faulty catalytic converter as being caused by a bad oxygen sensor or any other sensor.
To check if your catalytic converter is clogged, keep your hand close to the exhaust pipe end and ask someone to push the accelerator pedal to increase your car’s RPM to 2000. If you get a meager amount of exhaust coming out, you might have a clogged catalytic converter. Compare the flow to a similar car if possible.
3. High or low fuel consumption

Better or worse gas mileage is one of the symptoms of a poor catalytic converter. While better gas mileage may sound like a good deal, it can damage your engine and may cause even more expensive repairs.
Due to improper combustion of the fuel when the exhaust is clogged, it will make your car engine to be much less efficient and it needs to work harder for the same amount of power. Therefore, a bad catalytic converter will most often cause a higher fuel consumption, even if lower is possible in some cases.
4. Smell of sulfur
When the catalytic converter is clogged, it will restrict the airflow of exhaust fumes so that the engine’s air-fuel mixture will get rich (too much fuel, leading to unburnt fuel)
The combustion of this excessive air-fuel mixture causes a smell like rotten eggs or burnt sulfur, which is an obvious indication of your catalytic converter’s malfunction.
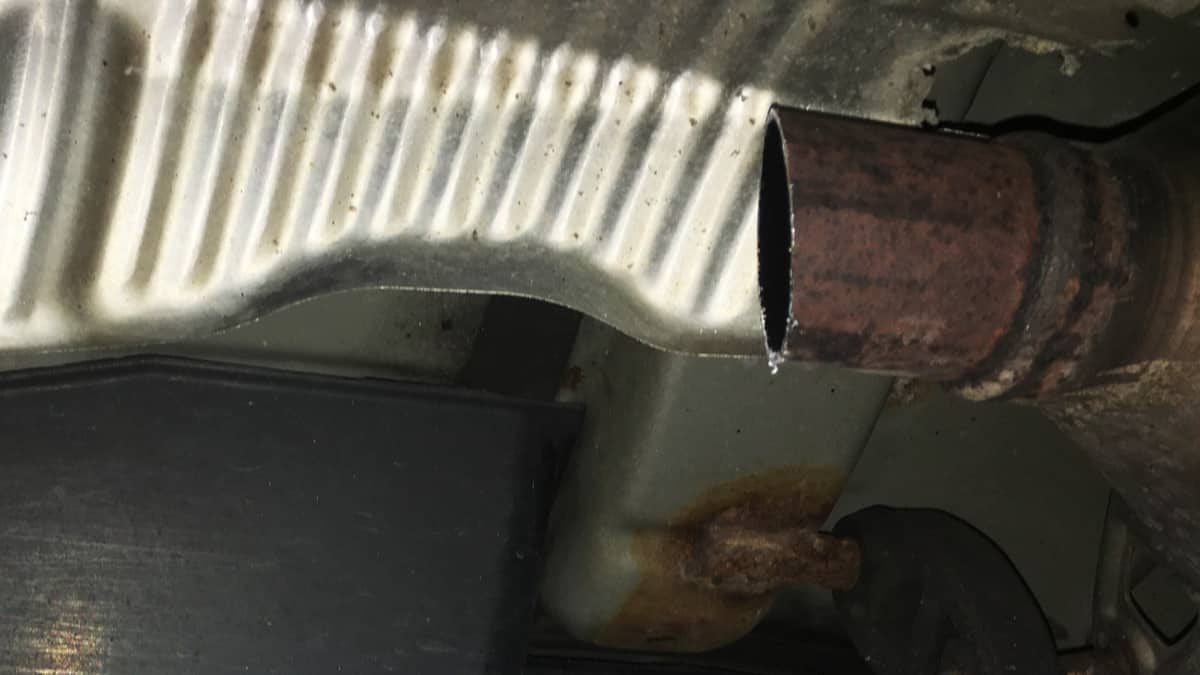
5. Discolored Housing
If you see that the catalytic converter’s housing has turned blue or some other color, it could mean that the catalytic converter is clogged and is creating excessive heat.
This could also happen if your engine is not running as it should and unburnt fuel is entering the catalyst. This mixture then ignites in the converter due to the heat and melts its inner material, causing even more blockages.
If your catalytic converter is clogged, it could also create excessive heat inside the engine, which could damage other parts quite quickly. Therefore, you should not drive your car if you suspect that the catalytic converter is bad.
6. Starting Issues
If the catalytic converter is clogged, the engine will get too much fuel that the engine cannot burn. It will also create back pressure which will cause the engine to struggle to get rid of the exhaust fumes.
If your car starts for 2-3 seconds and then dies, it could definitely be caused by a clogged converter. This is because it may take 2-3 seconds for the pressure to rise in the exhaust system until the engine is choked and shuts off.
7. Increased Emissions
If your catalytic converter is damaged or clogged, there is a risk that the catalytic converter is not doing its job properly anymore. This will cause an increase in the car engine’s emissions. The overall purpose of the catalytic converter is to remove bad emissions, so this is probably quite obvious.
You will often notice this by seeing dark exhaust smoke coming from your exhaust pipe during acceleration or at idle. If you have a yearly car inspection in the state or country you live in, your car will most likely fail an emission test or smog test.
8. Engine Misfires
When the catalytic converter is clogged, it restricts the flow of oxygen in engines, and engines require a lot of oxygen for proper fuel combustion. This reduced airflow leads to overheating due to an excessive amount of unburned gases and may also lead to a misfiring engine.
If your engine is misfiring, you should get it fixed as soon as possible, because it can lead to further expensive repairs if you just ignore it.
9. Rattles or other noises
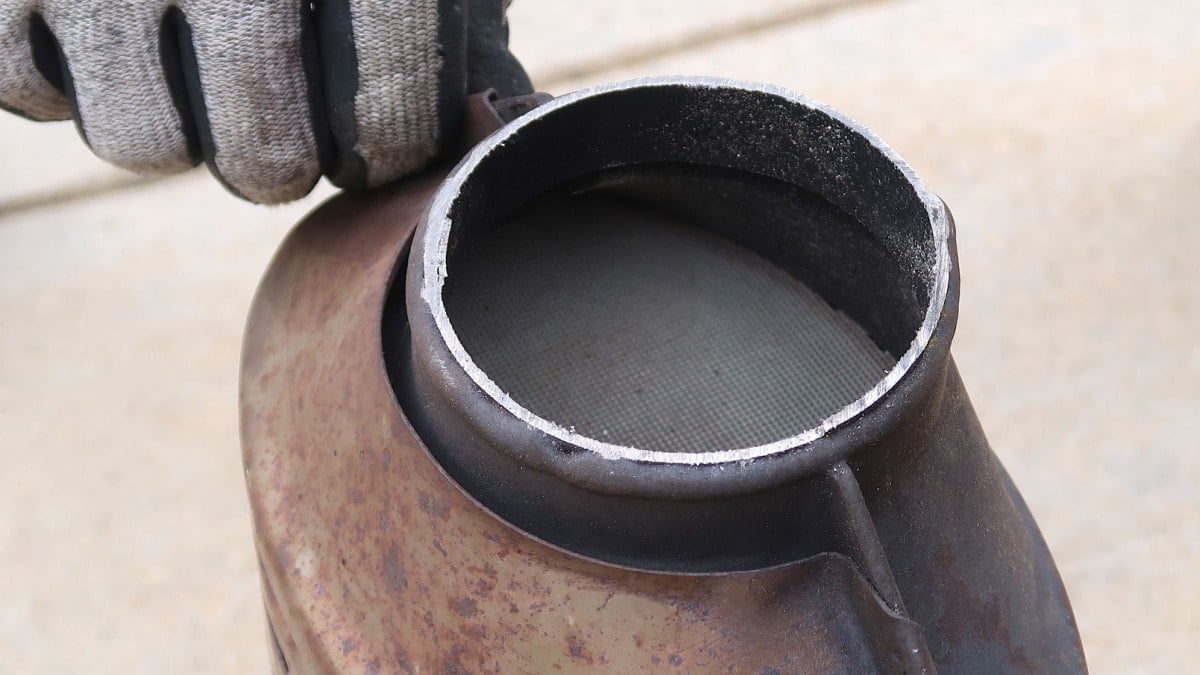
Inside the catalytic converter, there is a “honeycomb” that can get worn out and this can cause the honeycomb to break apart into pieces. This will cause a rattling noise from the catalytic converter when you rev your car engine.
You can ask a friend to press the accelerator pedal while you try to listen under the car if the rattling noises are coming from the catalytic converter or somewhere else.
What is a catalytic converter?
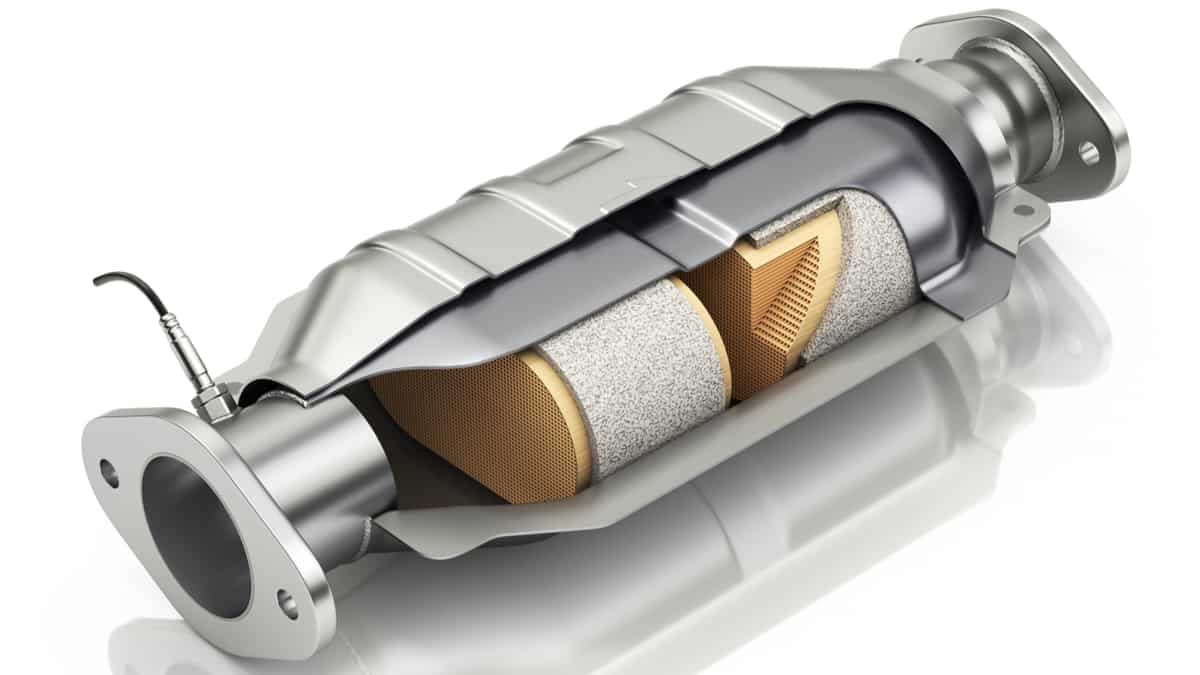
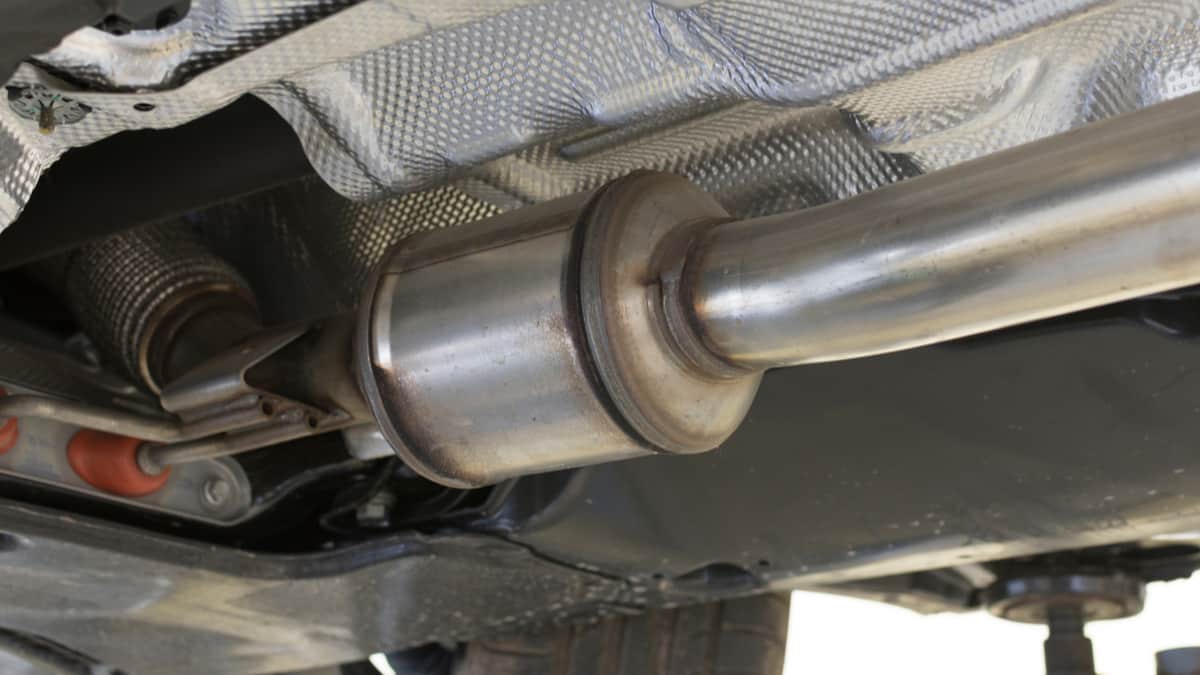
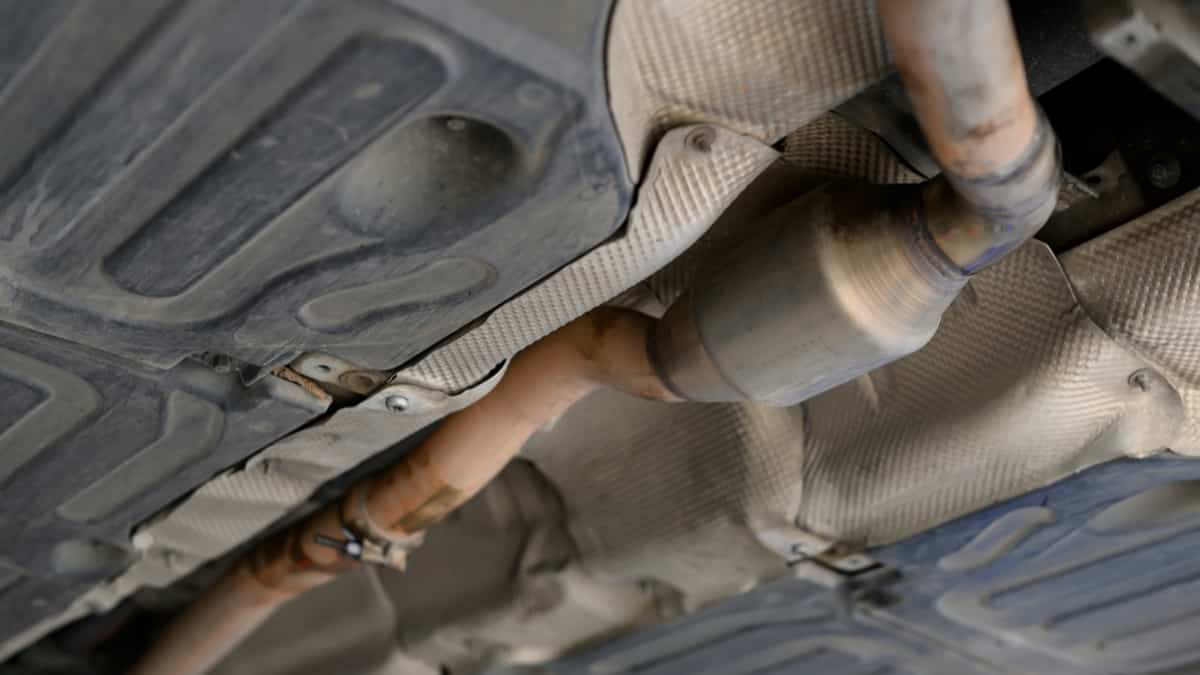
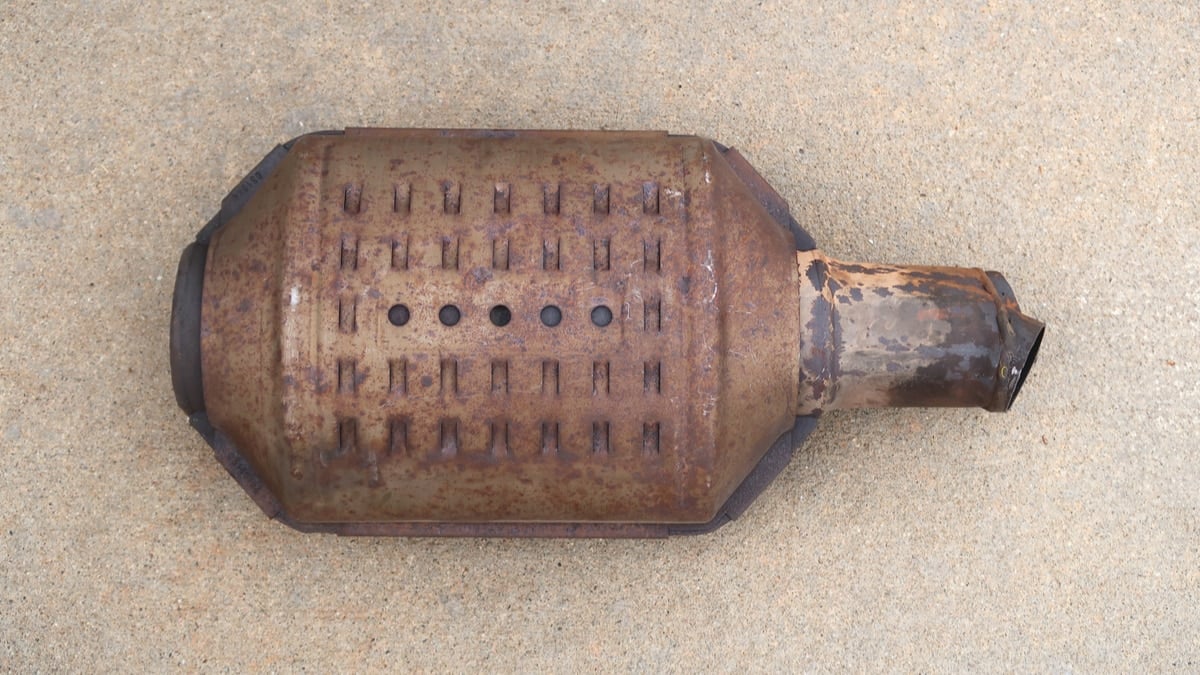
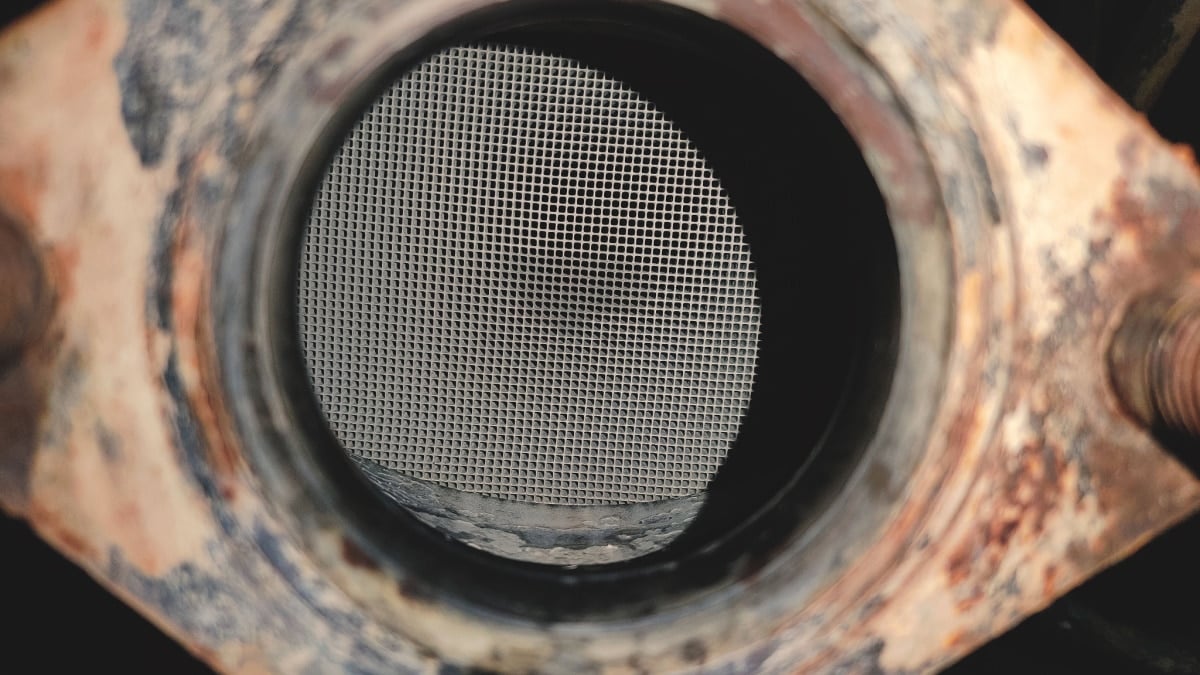
The catalytic converter is a device located in the exhaust system of a car. The catalytic converter consists of a catalyst that helps convert the car’s pollutant gases into less harmful pollutants. The structure of the catalytic converter has the look of a honeycomb.
The honeycomb shape aims to ensure that the pollutant gases flow through the more exposed surface and converts Nitrogen oxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons into safer elements like carbon dioxide . Despite being one of the most expensive products, Platinum is normally used as a catalyst in catalytic converters. However, in some cases, rhodium and palladium are also used.
Since combustion occurs in the engine, all the burnt gases flow at about 800 degrees through the exhaust pipe, which passes through the catalytic converter, thus affecting the engine’s exhaust gas flow. A perfect converter usually lasts up to 10 years. The honeycomb structure of the catalytic converter starts to suffocate slowly, which affects the engine’s performance.
What could damage a catalytic converter?
Catalytic converters are often getting worn with time and it most likely has to get replaced one or more times during your car’s lifetime. Some car models even have a service schedule of when it should be replaced (Even if most people don’t follow this because of the expensive replacement cost).
If your car engine is combusting motor oil, caused by worn piston rings or clogged crankcase ventilation, it could cause damages to the catalytic converter really fast. Other causes could be contaminants like unburned fuel caused by misfires. Coolant entering the combustion chamber by a blown head gasket could also cause damage to the honeycomb.
Catalytic Converter Theft
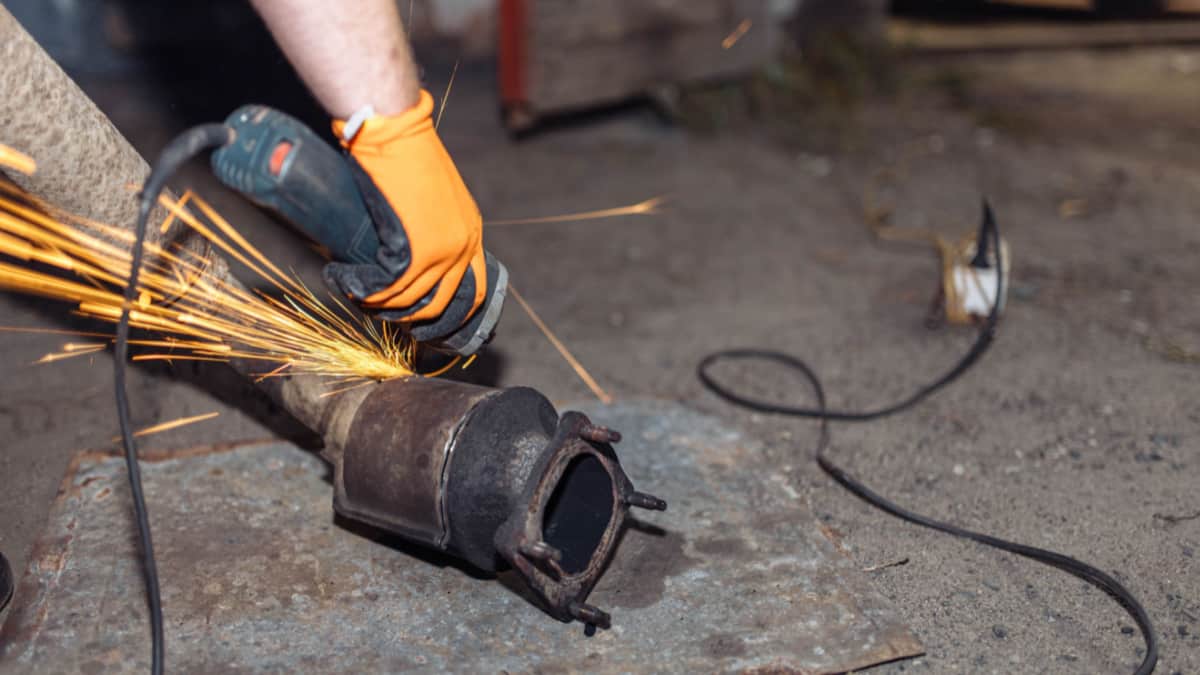
Catalytic converters contain precious metals like small amounts of platinum, rhodium, and palladium. These metals are very attractive to thieves since scrap yards will pay well for a used catalytic converter.
Catalytic converters are also relatively easy to steal because you just have to cut off the pipe with a tiger saw or something similar and it’s done in under 3 minutes. If you want to learn more about how to protect your catalytic converter from getting stolen you can check out our other article: How To Protect Your Car Against Catalytic Converter Theft
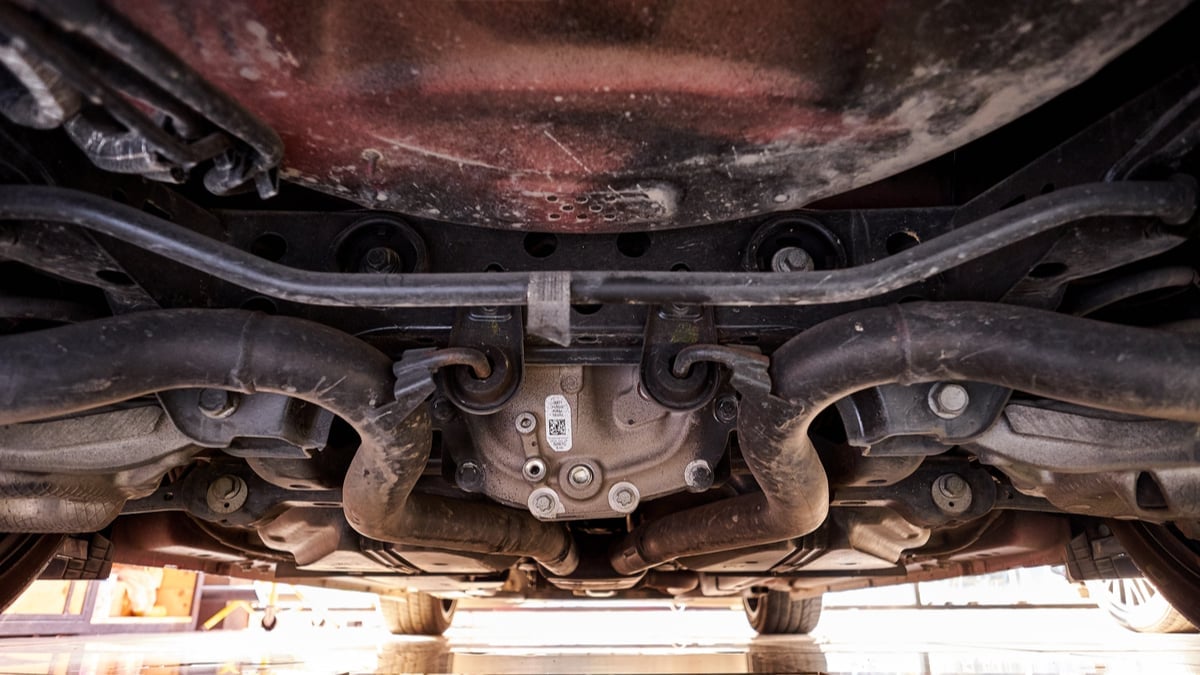
Catalytic Converter Location
The catalytic converter is located on the exhaust pipe system, between your muffler and the exhaust pipe manifold.
Depending on the car engine, the distance where it’s installed from the engine could differ a lot. On some engines, the catalytic converter is installed directly on the exhaust manifold, while on others it could be installed almost in the middle of the exhaust pipe.
Catalytic Converter Replacement
Replacing or repairing the catalytic converter is often very expensive and often not worth the cost, if your car is old. There are some workshops that replace the honeycomb inside the catalytic converter and keep the outer parts. This could be worth on some expensive catalytic converters, but in most cases, it’s easier and cheaper to just buy a new one.
The average catalytic converter replacement cost is between $400 and $2500. You can learn more about the replacement costs here: Catalytic converter replacement cost.
Can a bad catalytic converter ruin your engine?
Yes, it can but it is more likely that your engine will just shut off and not run until you fix the damaged catalytic converter. A clogged or damaged catalytic can create high backpressure into the engine which can damage other parts of your car’s engine or emission system, which could lead to severe engine failure.
What is the average life of a catalytic converter?
The average lifespan of a catalytic converter is roughly ten years or 100,000 miles. However, there are many factors that can affect the lifespan of a catalytic converter such as the quality of the converter, the type of vehicle it’s in, and how well the vehicle is maintained. Many catalytic converters will last the life of the car, while others have a scheduled service for when the catalytic converter is to be replaced.
What does a bad catalytic converter sound like?
If you can hear a rattling noise coming from the catalytic converter it can mean it’s bad. However, unfortunately, there isn’t necessarily one specific sound from the exhaust that indicates a problem with the catalytic converter.
How do you fix a catalytic converter without replacing it?
If there is severe damage to the catalytic converter, there is no other way than to replace it or remove the catalytic converter and reprogram the ECU. But if it is just clogged, you can clean the catalyst.