If your car is losing power, you might choose to scan it with your OBDII tool. What should you do when you see the P0299 code? This DTC points to the turbocharger or supercharger, but it could be caused by many problems.
In this guide, I cover the meaning of the P0299 trouble code. I also look at the causes, symptoms, and show you how to fix the issue.
Code Definition
P0299 – Turbocharger/Supercharger A Underboost Condition
What Does the P0299 Code Mean?
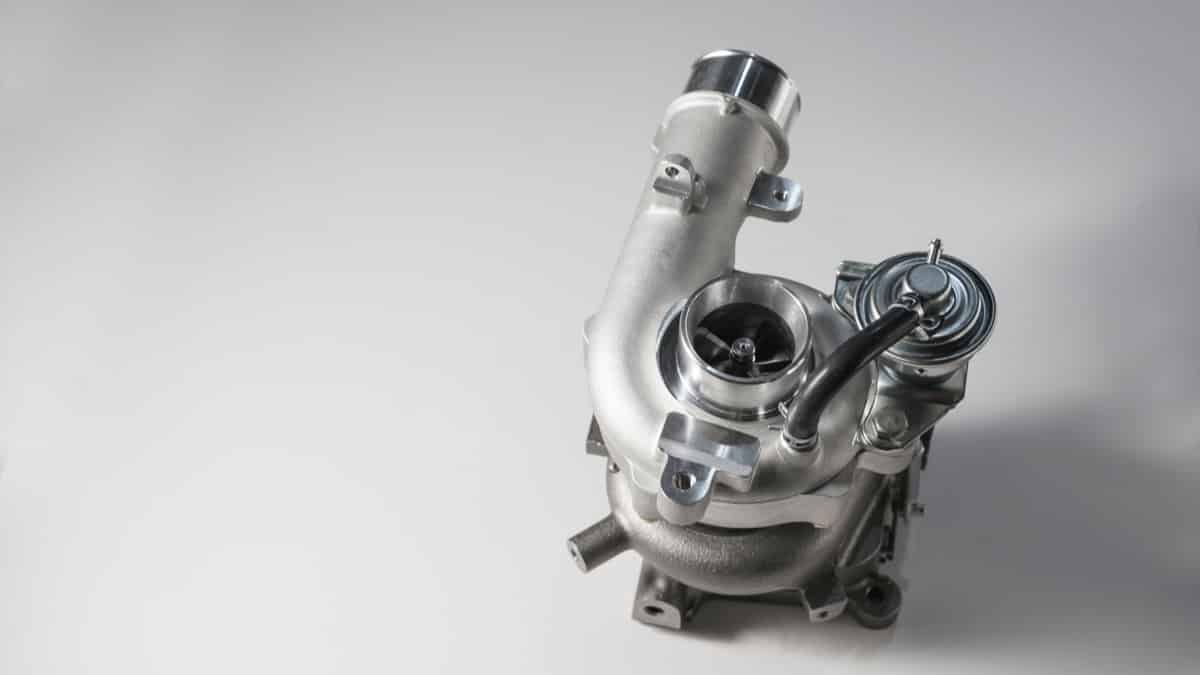
P0299 indicates that either the turbocharger or supercharger “A” shows an excessively low output. When the ECU detects a lower boost than what’s considered in the normal range, it will set the P0299 DTC. This code causes the Check Engine Light to come on, indicating that there’s a problem.
When a turbo or supercharger is operating normally, the air going to the motor is pressurized. It’s how the engine can output more power for its size. However, when this code gets set, it means the air can’t be pressurized the way it should be.
Turbochargers utilize the exhaust gases that come from the engine and a turbine that forces the air back to the intake. On the other hand, superchargers work from the intake side and are belt-driven, forcing more air into the motor.
P0299 Trouble Code Symptoms
When the P0299 trouble code sets, it will cause the Check Engine Light to come on. The car might also go into limp mode to protect the engine from damage. This should give you the time you need to drive home without causing more problems.
Here are the symptoms you might notice:
- Check Engine Light
- Car goes into limp mode
- Reduced engine power
- Mechanical noises from the failing supercharger or turbo
Causes of the P0299 Code
In general, you can expect that there’s a problem with the turbo, supercharger, or a boost pipe leak. However, there are other conditions that can reduce the output.
Some of the most common causes include:
- Defective supercharger or turbo
- Air intake leak or blockage
- Boost pipe leak
- Malfunctioning turbo boost pressure sensor
- Malfunctioning turbo pressure regulator or wastegate
- Faulty EGR system (with turbo setup)
- Low oil pressure
How Serious is the P0299 Code?
High – The P0299 trouble code indicates some form of mechanical failure. If the car goes into limp mode to protect itself, you won’t be able to drive more than a short distance before repairing the problem.
Even if it doesn’t go into limp mode, you will probably notice some drivability issues, such as slow acceleration or loss of power. You might even experience mechanical noise, showing that the car should be looked at right away.
If you allow a broken supercharger or turbo to continue running, you could be creating larger problems. Permanent engine damage can follow, which isn’t cheap to fix.
What Repairs Can Fix the P0299 Code?
It’s impossible to determine what needs to be repaired to make the P0299 code disappear unless you complete a full diagnostic walkthrough. While I can give you some ideas about the possible repairs, this list is not a replacement for proper examination.
Here are a few repairs that might be needed:
- Replace supercharger
- Replace turbocharger
- Boost pipe leak repair
- Air intake repair
- Replace turbo boost pressure sensor (Or check & repair wirings)
- Replace boost pressure regulator or wastegate
- Repair low engine oil pressure
- EGR replacement
Common P0299 Diagnosis Mistakes
The P0299 DTC can mean slightly different things on various car models. For example, with Volkswagen vehicles, the code could point to a faulty wastegate bypass regulator valve. In comparison, Isuzu uses the code for either a sticking turbocharger nozzle control solenoid or low fuel pressure issues.
When it comes to Ford, you could be looking at a malfunctioning injector control pressure sensor or trouble with the variable geometry turbo actuator. It could also mean the VGT vanes are sticking. Make sure you follow the proper diagnostics for your particular vehicle.
Recommended Tools for Diagnosis
- Diagnostic OBD Scan Tool
- Basic Hand Tools
- Multimeter
- Auto Repair Manual
How to Diagnose the P0299 Trouble Code
If you want to follow the same diagnostic steps as a professional mechanic, you will walk through this guide.
- Hook up the scan tool and check the trouble codes. If there are other codes present, you may want to fix these at the same time, especially if they are related.
- With the freeze-frame data, you can check the conditions when the code was set, allowing you to see what the supercharger or turbo was doing at the time.
- Reset the codes and take the vehicle for a test drive to see if it returns.
- Check the boost pipes and let someone rev the engine while you listen for any whistling sounds caused by a leak.
- Perform a visual inspection of the supercharger or turbocharger. You also want to look at the EGR system and air intake system to see if there is an obvious fault.
- If everything looks good visually, use your scan tool to check the boost pressure sensor readings. You can also rev the engine and try to regulate the boost pressure with the scan tool, if it’s a good one.
- Check the wastegate arm and try to move it. If it’s stuck, that could be the issue. If it’s a vacuum wastegate you can use a vacuum tool or air pressure tool to try to open and close it. Some turbochargers have an internal wastegate, which makes the test much more difficult.
- Check the air intake system for leaks or blockages.
- Check the oil pressure.
Estimated Cost of Repair
If you need to pay for parts and labor to repair the problem, here are some estimates you might be looking at.
- Replace supercharger – $2,500-$3,500
- Replace turbocharger – $1,500-$2,500
- Air intake repair – $250-$600
- Boost pipe leak repair – $0-$200
- Replace turbo boost pressure sensor – $150-$200
- Repair low engine oil pressure – $75-$250
- EGR valve replacement – $350-$500
Mechanics Tips about the P0299 Code
When the turbo fails, a part of the turbine can be sucked into the engine. This not only leads to a severe loss of power, but it can also cause loud mechanical noise. It can also eventually ruin the engine, making this problem even more severe than when it started.
Categories: OBD Codes