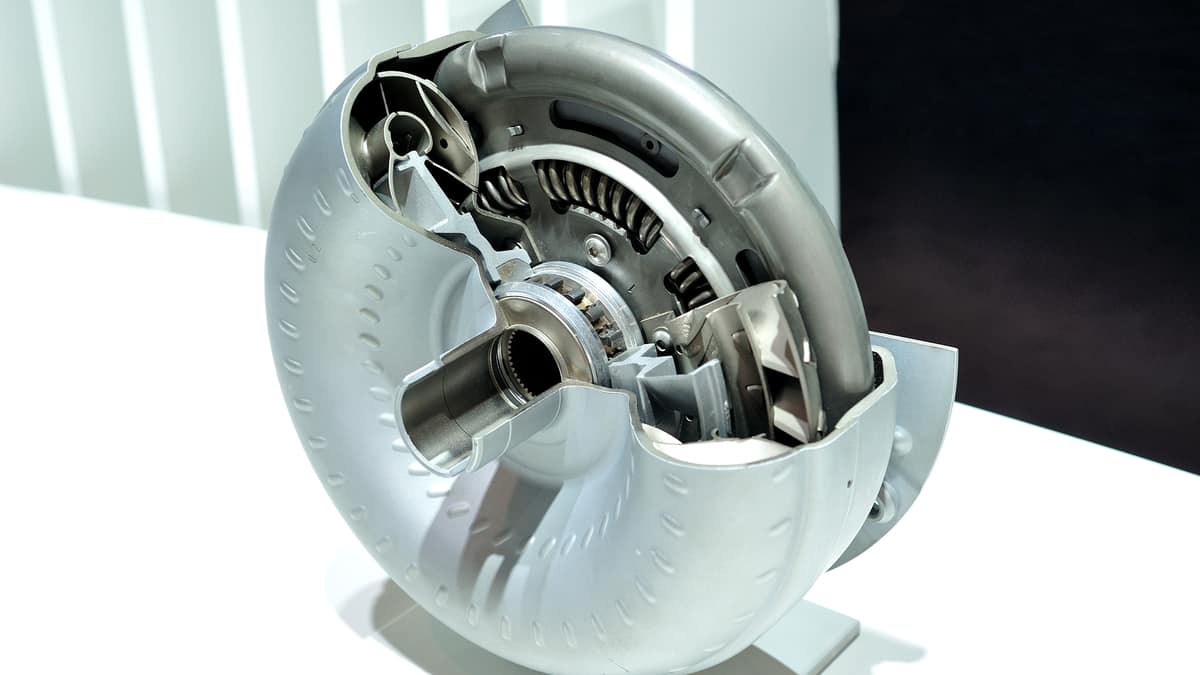
If you are into cars, you have probably heard about the torque converter before and the problems associated with it.
Torque converters can be found in almost all cars with automatic transmissions. This is probably one of the reasons why you have heard of so many failed torque converters.
In this article, you will find all the information you need about the torque converter. You will find information about how it works, the most common symptoms, problems, location, and how to test the torque converter. You will also find the replacement cost. First, let’s take a look at the signs you might be dealing with a bad torque converter.
Symptoms Of A Bad Torque Converter
The most common symptom of a bad torque converter is a slipping transmission during acceleration. You may also notice issues like a rough idle, rough acceleration, and noises from the transmission. Sometimes, your car won’t even move when the converter is bad.
While these are not all possible signs, they are the most common ones. Here is a more detailed list of the signs of a bad or failing torque converter to look for:
1. Transmission Slipping

A common symptom of a defective torque converter is that the transmission slips when accelerating.
You can feel this when the engine revs up when in gear, but the car does not accelerate. Often you need to have a good feel for your car to detect a slipping transmission.
The torque converter needs to build up pressure inside of it to move your car forward, and if it doesn’t, it may slip when accelerating.
2. Rough Idling

Rough idling is another common symptom of a bad torque converter. If you feel that your idle is a bit jumpy and sometimes too low and sometimes too high, it could be a torque converter problem.
If the torque converter is faulty, it might create unexpected pressures inside the torque converter, which can cause rough idling.
3. Rough Acceleration

Rough acceleration is also a known symptom when it comes to defective torque converters. Different pressure peaks can cause this in the torque converter, as well as the fact that the torque converter slips, as already mentioned.
If you feel that you are experiencing rough acceleration, check your RPM meter to see if it jumps a little when accelerating. If this is the case, a faulty torque converter is probably the cause.
4. Car won’t move in drive or reverse

If your car does not move at all in drive or reverse gear, a completely failed torque converter could be the cause.
However, a car that does not move in gear can be caused by many different things, and it should be properly diagnosed before replacing anything.
5. Transmission overheating

If the torque converter slips while driving, this can lead to unnecessary heating of the transmission fluid, which at some point can even become so hot that it boils.
A slipping torque converter will wear out the transmission very quickly. In some cases, you may have temperature sensors that cause the transmission control unit light on your dashboard to flash, which indicates that your torque converter is slipping and overheating the transmission.
6. Noises from the transmission

Check whether you can feel or hear strange noises from the torque converter both when idling and accelerating. Listen in the middle of the car under the gear stick to see if you can hear knocking or other strange sounds.
If you hear any noises, lift the car and check if other things could be causing the noises before replacing the torque converter.
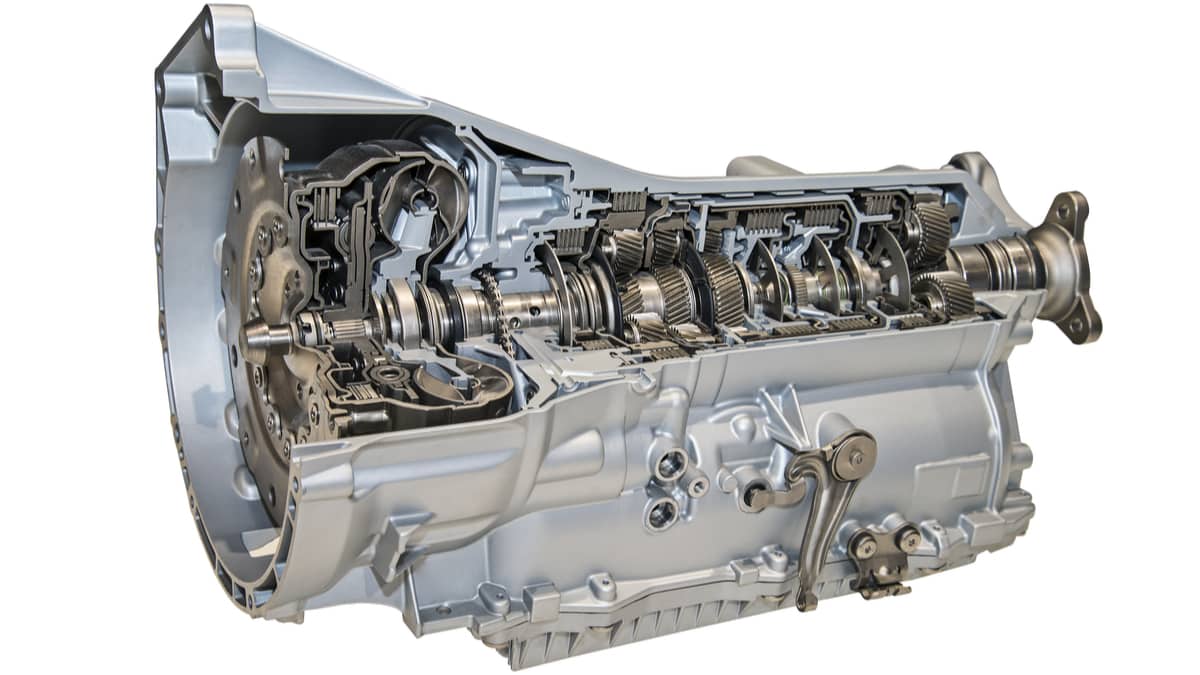
Torque Converter Function
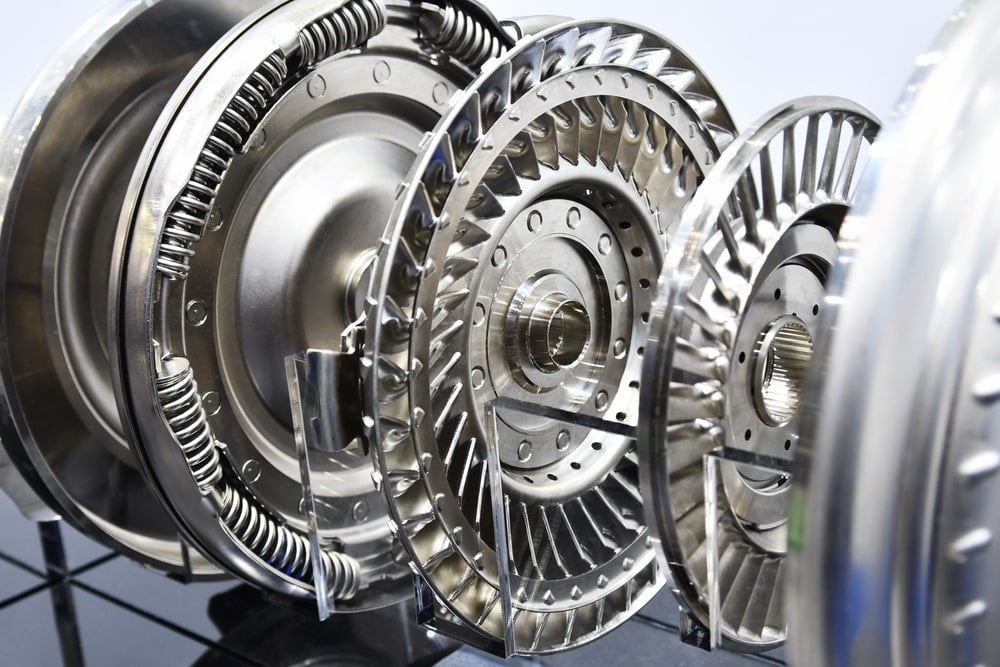

The torque converter is the unit that gently transmits power from the engine to the transmission gears. In short, the torque converter is filled with transmission fluid and has a “fan” or turbine-like unit inside. The more it rotates, the more pressure it creates inside the unit, and the more power is transferred from the engine to the transmission.
For example, if you run two fans against each other and start one of the fans, the other fan will also begin to rotate, but not directly at the speed the other fan has. This is precisely how a torque converter works.
As you can probably figure out, this gives you a very smooth power transmission between the engine and the wheels.
4 Common Torque Converter Problems
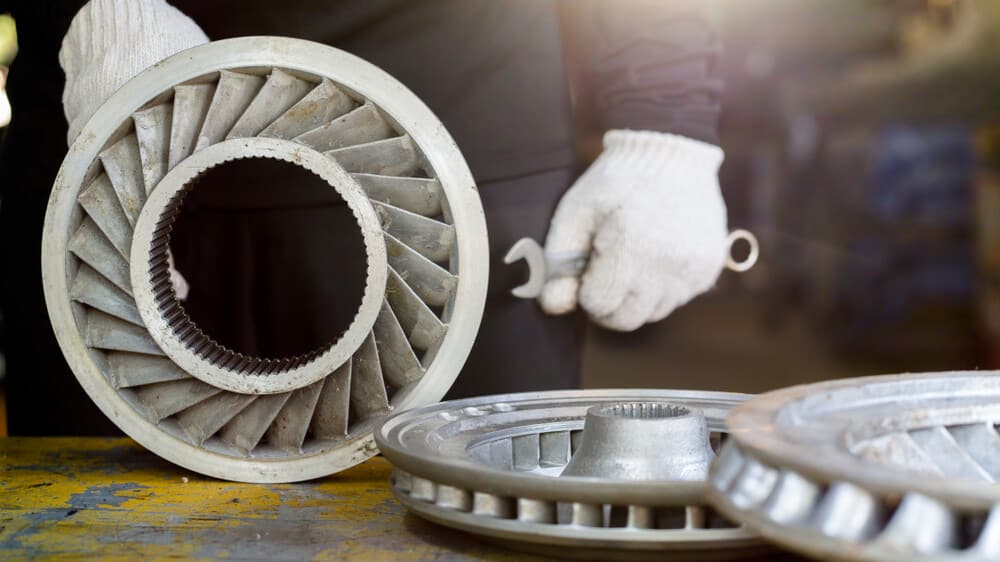

When it comes to torque converters, some common problems can be encountered. In general, the torque converter is not a very complicated piece of machinery, especially in older vehicles. There are not many parts that could fail.
Sometimes you can find cheap full replacements for torque converters, and in this case it is often not worth taking it apart and replacing different parts; rather, it’s cheaper and quicker to replace the whole thing.
1. Bad Torque Converter Bearings
A widespread problem is that the bearings in the torque converters are worn. This does not cause slippage or other transmission problems, but can cause bearing noises from the transmission.
If you hear bearing noises from the transmission, check the transmission fluid, and see if you can see metal parts inside the transmission fluid. If you find metal parts, they are probably from a defective torque converter bearing.
2. Damaged Torque Converter Seals
A faulty seal of the torque converter will cause the transmission fluid to leak out of the torque converter, and thus the pressure inside the converter will be lost.
Low pressure inside the torque converter will cause slippage, overheating, and other strange symptoms. This is actually one of the most common problems when it comes to a faulty torque converter.
3. Faulty Torque Converter Clutch Plate
There are several clutches in a torque converter. If the torque converter is locked in the drive or idling gear and does not release the transmission, you most likely have a problem with the converter clutch.
A faulty torque converter clutch can also cause other symptoms such as slipping and rough acceleration.
4. Faulty Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
The torque converter clutch solenoid is a common part that fails within the automatic transmission. The solenoid valve controls the fluid pressure of the hydraulic transmission, which enters the lock-up clutch.
This can cause various symptoms, such as slipping, overheating, and rough acceleration.
How to Test a Torque Converter

There are not many things you can do to test the torque converter without taking it apart, but there is a way to check the torque converter for signs of wear.
Here is a method I usually use to check for problems with the torque converter.
1. Start the engine and let it warm up
First, you should start the engine and let the transmission oil warm up to around 40 degrees.
This can take a long time. It is recommended to check the temperature of the transmission oil with a diagnostic scanner to make sure that the transmission oil is warm.
When the transmission oil is warm, it is time to move on to the next step.
2. Move shifter into gear
Now you can try to apply the drive gear. Listen carefully if you can hear any signs of noise from the torque converter.
The torque converter should move the car forward with just a light touch of the accelerator pedal. Shift between the other gears (Drive and Sport, if you have it) to see if you can hear any other sounds from it. If everything seems to be fine, you can go on to the next step.
3. Test drive
Now it’s time for you to drive the car at a higher speed. Keep an eye on the tachometer and speedometer. If the car revs up significantly without actually accelerating, the torque converter is slipping.
All older automatic transmissions slip a bit when accelerating, but if you have owned the car for a while, you probably know how much it should slip. If you are not sure, let a mechanic test drive your car and see if he hears any noise or can feel slipping.
Torque Converter Location
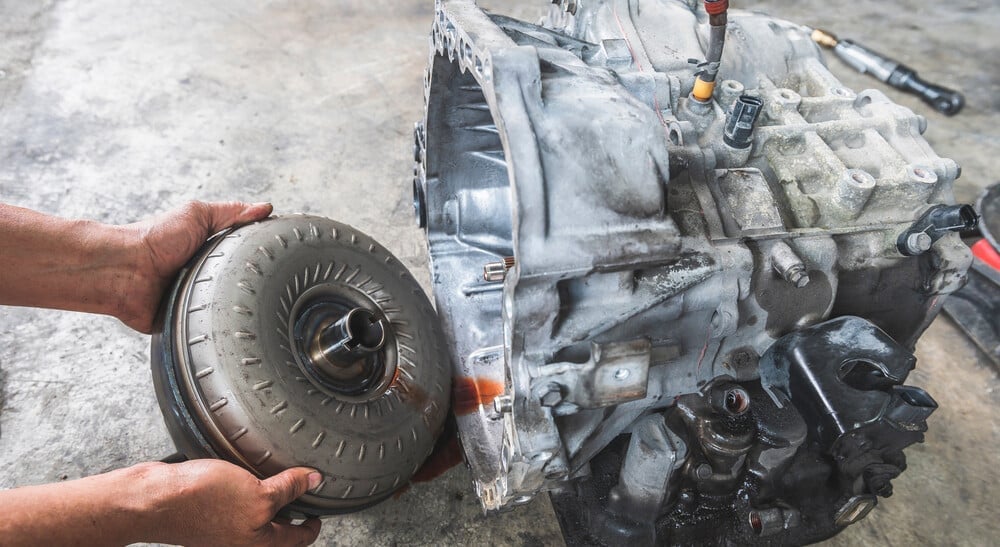

The torque converter is located between the engine and the automatic transmission.
To diagnose it correctly and carry out a visual inspection, you must remove the vehicle’s transmission and engine. Some older American cars have a cover plate that you can remove to inspect the torque converter, but even with them, you will not see much because the torque converter is a sealed unit.
I always recommend that you remove the torque converter from the transmission to diagnose it properly.
Torque Converter Replacement Cost
The average torque converter replacement cost is between $300 and $2500, depending on the car model and labor costs. A new replacement torque converter costs between $100 and $400. The labor cost to replace the torque converter is between $200 and $2000.
The transmission often must be removed to replace or inspect the torque converter for any problems.
Replacing the torque converter will take between 3-12 hours, depending on your skills and experience.
Categories: Transmission