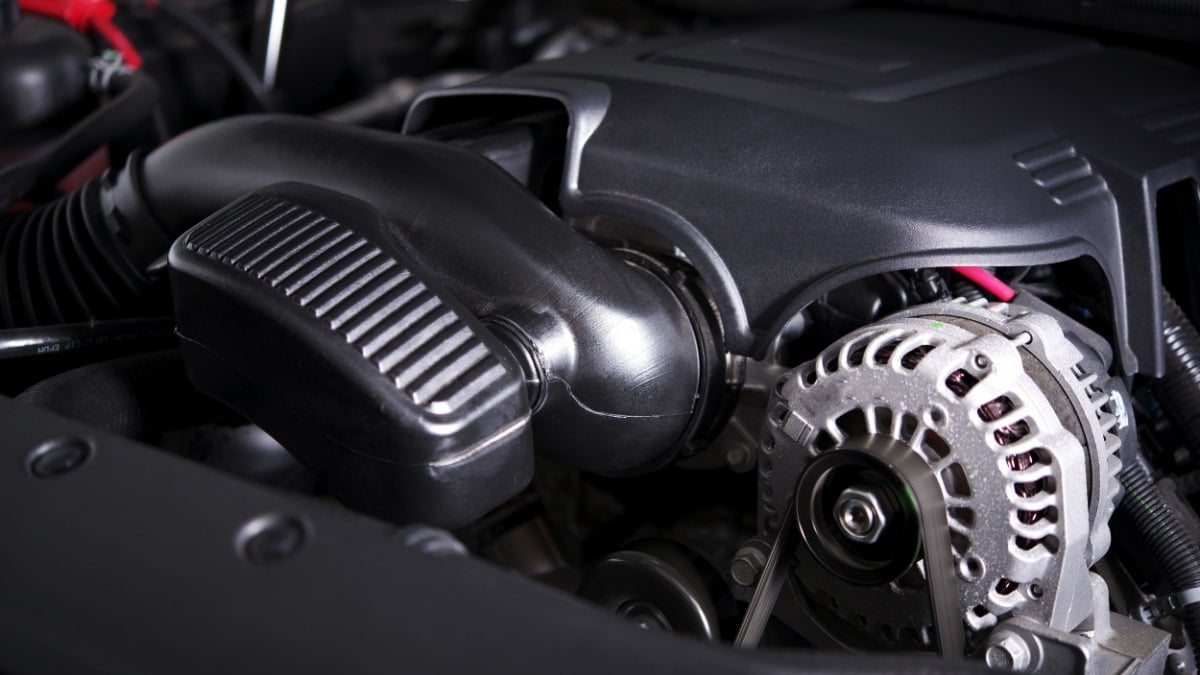
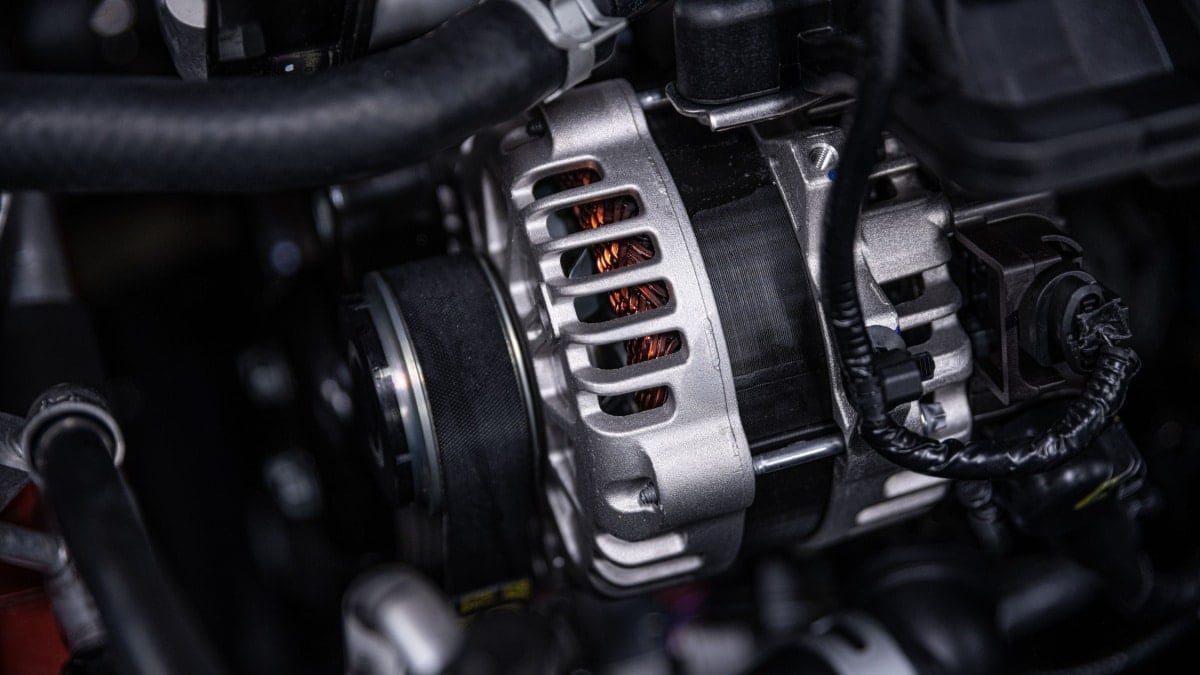
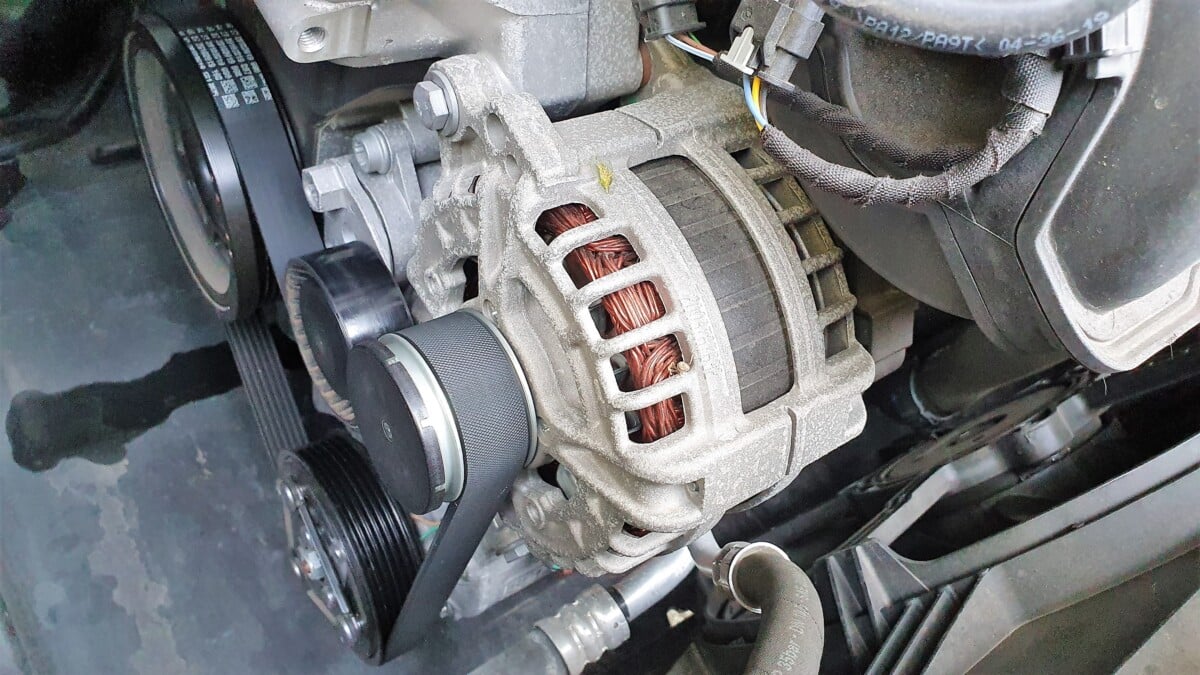
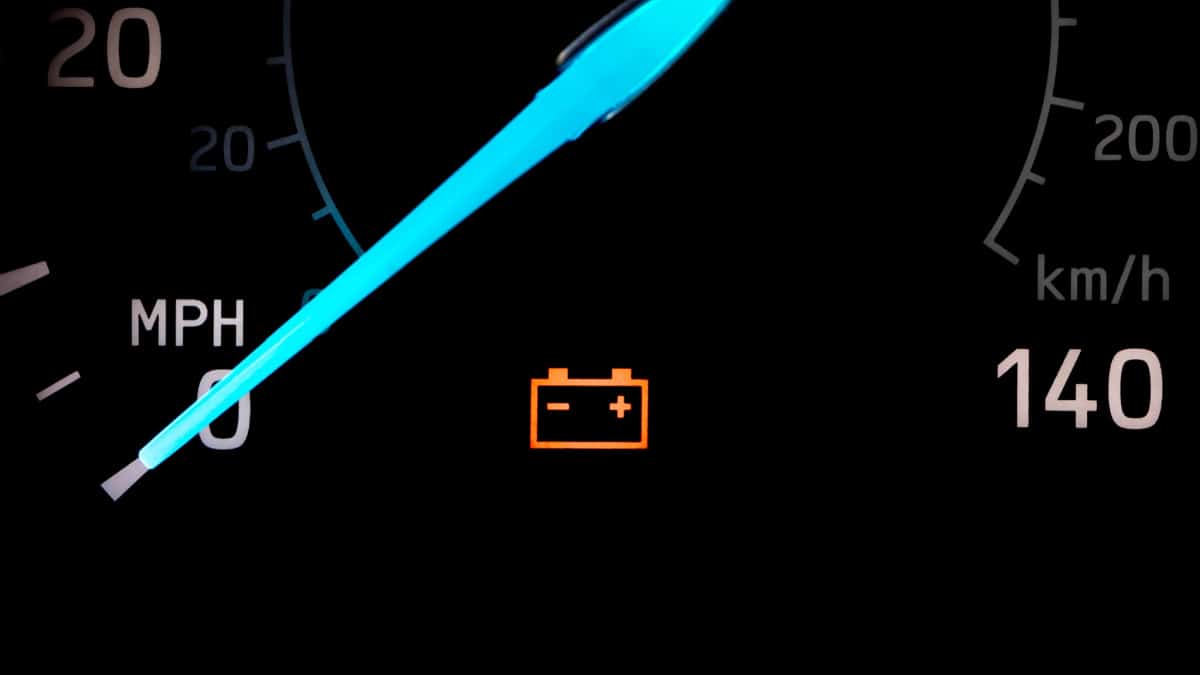
Many people assume that the car’s battery is the only thing that powers all electrical components in the car, but this is not true. The alternator plays a vital role in supplying power to the car’s AC, recharging the battery, and ignition.
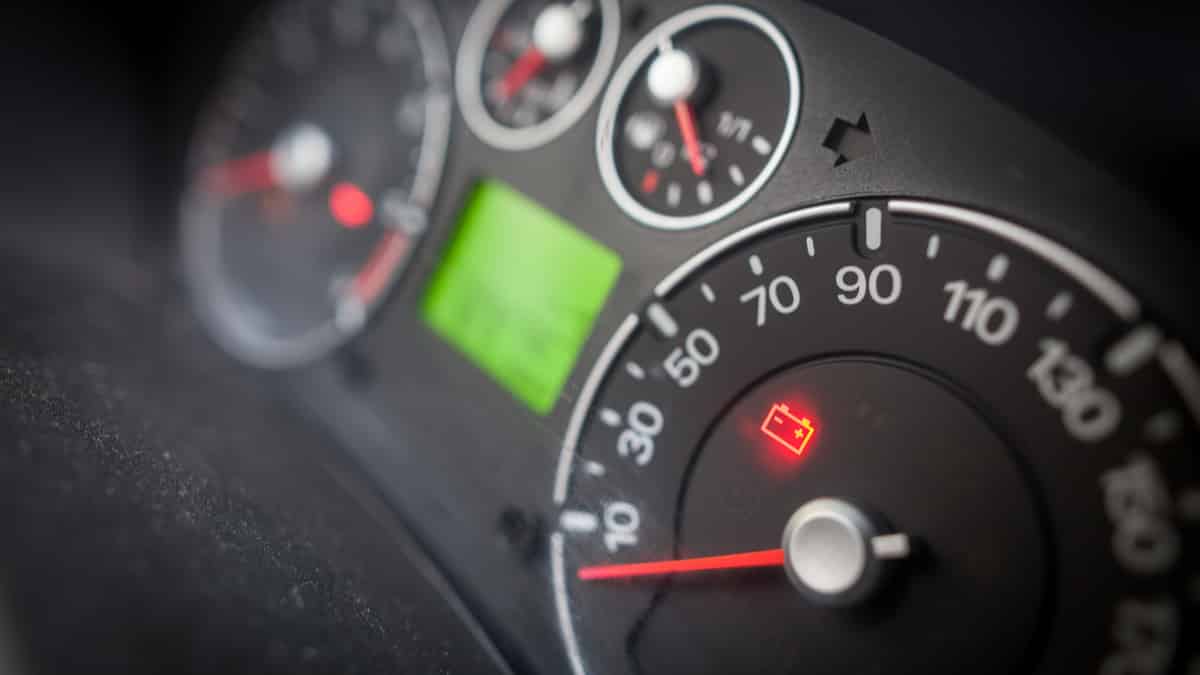
When your alternator is faulty, the battery power drains very quickly, and you will find yourself with a stalled car. But what can cause the alternator to go bad and stop charging the battery?
Reasons Why Your Alternator Is Not Charging
The most common reason why an alternator is not charging the battery is due to worn carbon brushes or a damaged alternator itself. It can also be caused by a blown fuse or bad wiring. Your alternator will also not charge the battery if the serpentine belt has snapped off.
Now that you know the most common reasons in brief, you’ll probably want to read about them in greater detail. Here is a list of the 5 most common reasons why your alternator is not charging the battery.
1. Worn out carbon brushes or damaged alternator
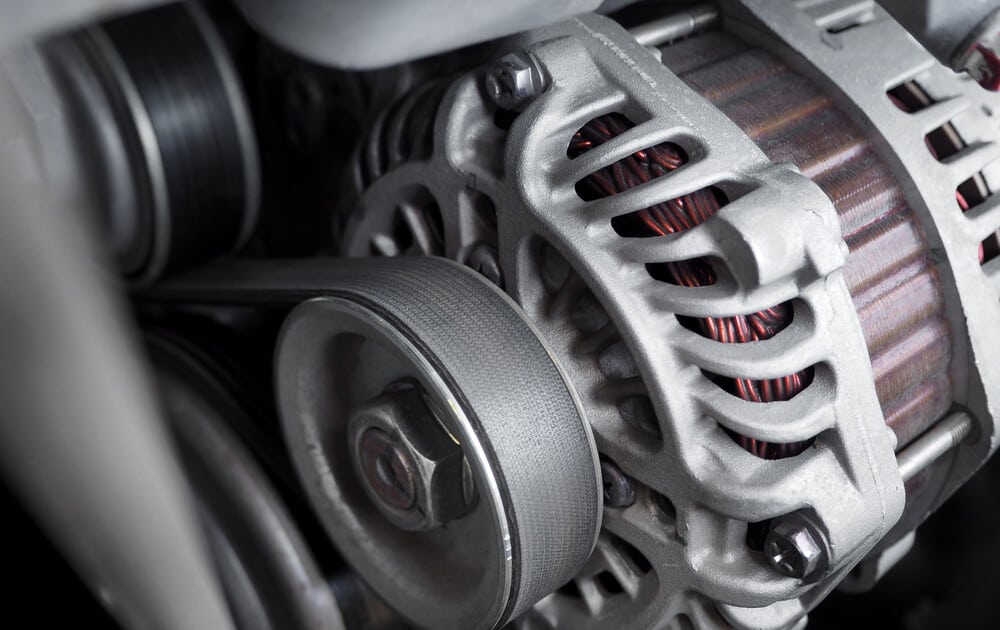
The most common reason why your car is not charging the battery is actually because of a worn-out or damaged alternator.
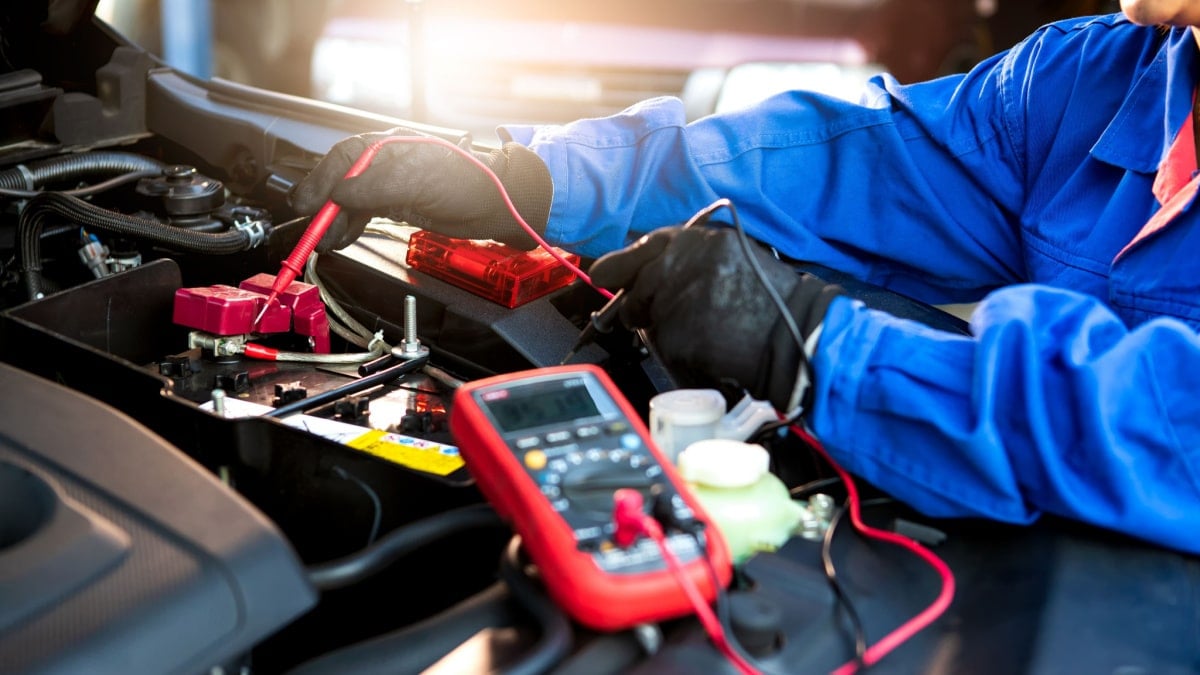
You can carefully tap it with a hammer while the car engine is running while checking it with a multimeter on the car battery to see if the voltage is within the charging range.
If the voltage changes and go back to normal when you tap it lightly with a hammer while the car is running, that means the carbon brushes are worn out and need to be replaced in the alternator. Alternatively, you could replace the entire alternator.
Sometimes there is an electrical problem in the alternator, and even if the voltage does not change, it might be damaged.
Another common cause is bad diodes or a voltage regulator. Replacing either of these generally requires you to have more advanced knowledge about alternators.
Replacing parts inside the alternator, such as carbon brushes, the diode plate, or the voltage regulator, was more common on older cars. These days, alternators are quite cheap, so it is usually cheaper to replace the whole thing than it is to fix a problem internal to the alternator.
If you have already replaced it with a brand new alternator, but it’s still not charging the battery, you should keep reading this list.
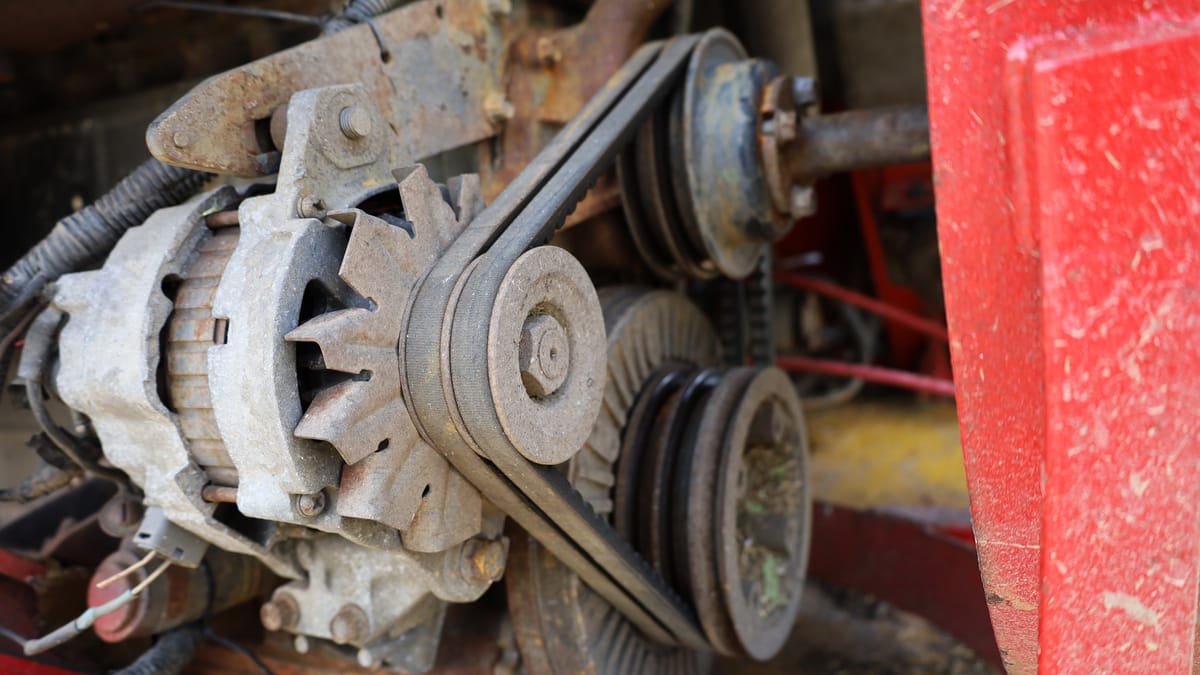
2. Broken Serpentine belt
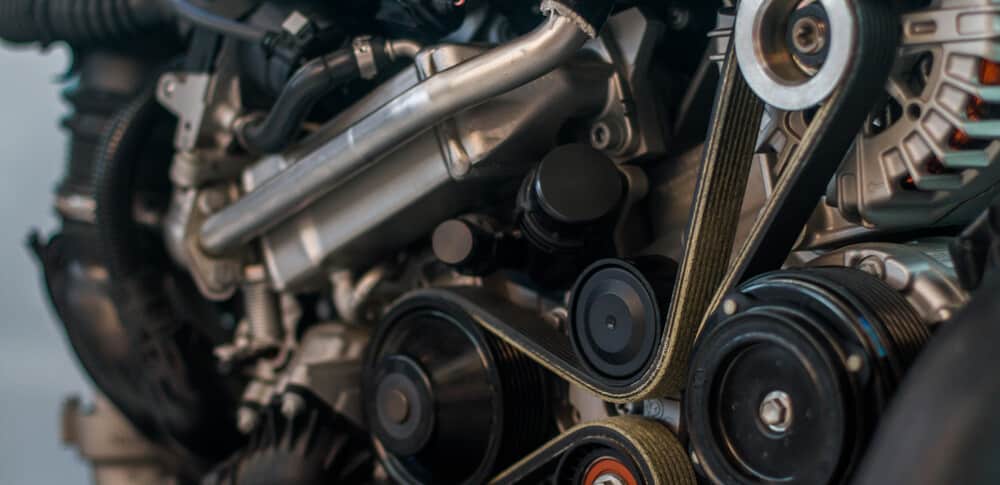

A closer observation of the alternator will reveal a pulley and belt system that works to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The serpentine belt powers the alternator. If it fails, the alternator will stop working the moment your belt wears out and breaks, or the pulley becomes damaged.
This can also happen if the serpentine belt is not tightened correctly. Most cars have automatic tensioners, but these can fail, so it is better to double-check.
Some older cars have manual tensioners, and in this case, you might have to tighten the serpentine belt. The serpentine belt and pulleys are often pretty easy and cheap to replace.
3. Faulty fuse
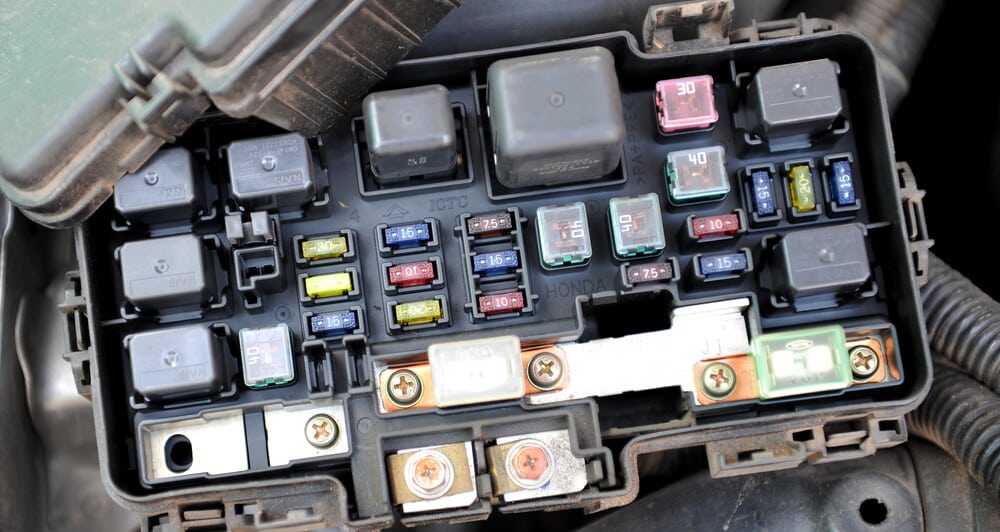

There is often a huge fuse connected to the alternator’s big power cable. It is often an 80A fuse or more, and is most often found in your car’s fuse box in the engine bay.
Fuses blow due to a power surge, or they wear out. When this happens, the current will stop flowing from the alternator. The solution is to check your car’s manual for the particular fuse that controls the alternator, and replace it.
In some cars, you might also find another small fuse to the alternator’s control—usually a 15A to 20A fuse.
4. Wiring issues or connectors
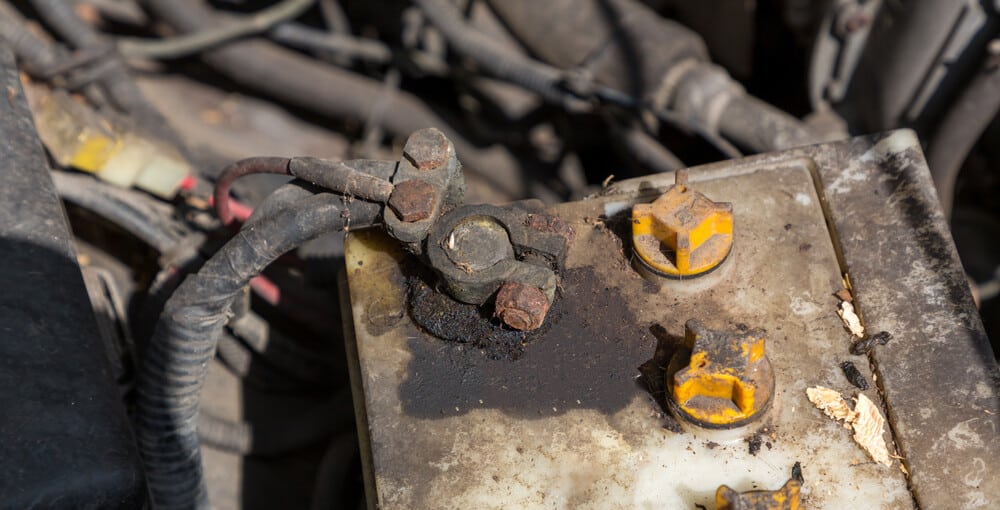

A properly functioning alternator usually has three or four wires to it. You will find one big main cable together with two or three small ones.
All of these wires are important for the alternator’s function, and if one breaks off, you might lose the charging function.
Check the big power cable connectors between the alternator and the car battery to ensure there is no corrosion there. The cable will usually get warm if there is a bad connection somewhere.
Check or measure these wires with a multimeter. Remember that measuring them is not always correct, because you have to load test wires that are half broken or have a bad connection.
You should usually have 12 volts on one of these wires, and the other one goes to the battery light on the dashboard. If you have a third one, it does often go to the engine control unit. To measure this properly, you need a wiring diagram of your specific car model.
5. Damaged car battery

The alternator and the car’s battery work hand in hand. A really bad car battery might not take charge from the alternator at all. In this case, it is the battery – not the alternator – which is the source of your problem.
In theory, a car can run only with the alternator power, but this can cause heavy voltage spikes and other strange symptoms, so this means that a bad car battery can cause an alternator to not charge also.
6. Engine control module error

Cars are increasingly being equipped with modern electronics. In this regard, the engine control unit (ECU) controls most of the car’s electrical components.
Modern cars also control the alternator. In some rare cases, there might be a problem with the engine control module not controlling the alternator’s charging.
Check for any trouble codes with an OBD2 scanner to determine if anything is any other damaged part that prevents it from charging.
In some rare cases, there might actually be a faulty engine control unit, but you should always check all other possible causes first.
Diagnosing an alternator that won’t charge
There are some easy steps you can go through to check the function of your alternator.
- Tap the alternator carefully with a hammer while the engine is running; if the charging goes back to normal, the carbon brushes inside it are worn out and need a replacement.
- Check the large power cable to the alternator and the fuse – usually, a large 40-60 amp fuse near the battery.
- Check the ground cable between the engine and the body.
- Check the serpentine belt and make sure the alternator is spinning with the engine.
- Check the small power supply wire and the charging light wire. You can measure it with a multimeter, but you might need a wiring diagram and some car electronic skills to do this correctly.
- You can measure the diode assembly and the voltage regulator to make sure they are not damaged. You can replace these with some alternators, but it is often the same price to buy a new alternator nowadays. It is up to you what you think is more worth it.
Is there a fuse for the alternator?
In most car models, there is a high-amperage fuse between the alternator’s terminal and the battery. You may also find low amperage fuses for the alternator ignition terminal. It is not very common for these fuses to blow, but it is definitely worth checking.
Can I test my alternator without removing it?
You most certainly can test your alternator without removing it! A basic voltmeter will do the trick for a basic check. For more advanced tests, it depends on the car model and how accessible the alternator is. In some car models, you cannot reach the alternator well for testing without removing it.
How can I test my alternator without a meter?
Assuming you don’t have access to a multimeter, there are still a few ways you can test your alternator at home. Start the engine and let it run for a few minutes. Turn on all the lights in your car (headlights, taillights, interior lights, etc.) and observe whether they seem dimmer than usual. If they do, it’s possible that your alternator isn’t charging the battery correctly. If your alternator is not charging the battery at all, your car will eventually die.
How long will a car run with a faulty alternator?
It depends on how bad the generator is, how many electrical consumers you use, and what car model you drive. If your car battery is fully charged and the alternator is not charging at all, you can expect to drive about 15 miles or 15 minutes until the car stops.
There are many possible reasons why an alternator won’t charge. However, the most likely cause is a problem with the alternator itself, the drive belt, or the connection between the battery and the alternator. If your alternator is not charging, your car will stall when the battery is drained, so it is important to fix the problem as soon as possible.
If your alternator is not charging, there are a few things you can check before taking it in for service. First, make sure all connections are secure, and there is no corrosion between the alternator and battery. Next, check the drive belt to see if it is loose or broken. If everything looks good there and you feel you don’t have enough knowledge to make a proper diagnosis, it’s time to take it in for service.
Learn more:
- 7 Symptoms of a Bad Serpentine Belt
- 6 Symptoms of a Loose Alternator Belt (& Replacement Cost)
- How to Disconnect a Car Battery (7 Easy Steps)
Categories: Engine, Troubleshooting