The coil pack is an essential part of the ignition system. It works hand in hand with the spark plugs to combust the air-fuel mixture in the engine. When a coil pack goes bad, you are going to know it, even if you aren’t a professional technician. The symptoms will be impossible to ignore.
In this guide, we examine the top symptoms of a bad coil pack. We also explain its function and show you where to find it. Finally, we look at how much a coil pack replacement might cost you and answer your top questions about this system.
Symptoms Of A Bad Coil Pack
When the coil pack goes bad, you can expect the Check Engine Light to come on, and it will probably be blinking. The engine may also misfire, and the fuel consumption increases. With that comes a rough idle, trouble accelerating, a changed sound to the engine and a possible fuel smell.
Many of these symptoms occur whenever there’s an issue with the engine. For that reason, you can’t use one symptom alone to determine there’s a problem with the coil pack. Let’s examine these bad coil pack symptoms closer to see what you might be dealing with.
1. Misfiring Engine

The air-fuel mixture in a gasoline engine must be properly ignited for the engine to run smoothly. When the ignition pack doesn’t operate as it should, this mixture can’t ignite.
The result is a misfiring engine that feels like it sputters or jerks when in Drive. As you stop at lights, the misfire can be so bad that it causes the engine to shake and vibrate.
2. Blinking Check Engine Light

The Check Engine Light is designed to tell you when something’s wrong with the motor. All modern cars are equipped with a self-diagnostic system known as OBD-II. When an engine sensor notices something operating outside of normal parameters, the Check Engine Light comes on and a code is set in the system. If there’s a severe problem, the light will blink, telling you to stop driving before engine damage occurs.
With a compatible scanner, you can read the trouble codes coming from the engine sensors to determine what’s wrong. It’s possible that your vehicle is throwing a P0351 code, indicating trouble with the ignition system. You could also see a code related to the engine misfire.
3. Increased Fuel Consumption

Ignition coils can fail spontaneously or go bad over time. As they wear, the fuel economy of your car gradually decreases. By using a gas mileage calculator, you can keep a close eye on your car’s fuel economy, so you’ll notice when there’s a problem.
Even if you find the drop in fuel economy to be related to another mechanical issue, you’ll be happy you noticed it. After all, no one wants to waste money on gas.
4. Rough Idle

Any mechanical malfunction that fails to ignite the air-fuel mixture can lead to rough idling. For that reason, the coil packs must be considered.
Along with the coil packs, clogged air filters, failing spark plugs and dirty fuel injectors could also be to blame. That’s why you can’t diagnose the problem on this symptom alone.
5. Rough Acceleration
The same can be said about trouble with acceleration. While it is a symptom of a bad coil pack, it can also be the root of most engine malfunctions.
If there’s a drop in power when you step on the accelerator, something is wrong that should be dealt with immediately. If you allow the problem to continue, the vehicle may begin to stall.
6. Changed Engine Sound

Earlier, we talked about a misfiring engine. This symptom also comes with some strange noises you may not be used to hearing. As the engine jerks and bucks, you are going to hear a louder sound.
If the coil pack is bad, it can cause the engine to run on one or more cylinders less than normal, and this will cause your engine sound to change.
In extreme cases, the car could also backfire. This loud banging noise occurs whenever there’s unburned fuel escaping from the exhaust. You want to have this fixed not only to prevent further damage but also to avoid embarrassment from the sounds.
7. Fuel Smell
If the fuel mixture isn’t being burnt properly, you could smell a hint of gasoline. However, ignition problems aren’t the only reason for this symptom either.
In fact, most often when there’s a gasoline smell, it’s related to the fuel or exhaust system. If this symptom is occurring with some of the others we mentioned, it could be caused by the coil packs or spark plugs.
What Is The Function Of A Coil Pack?
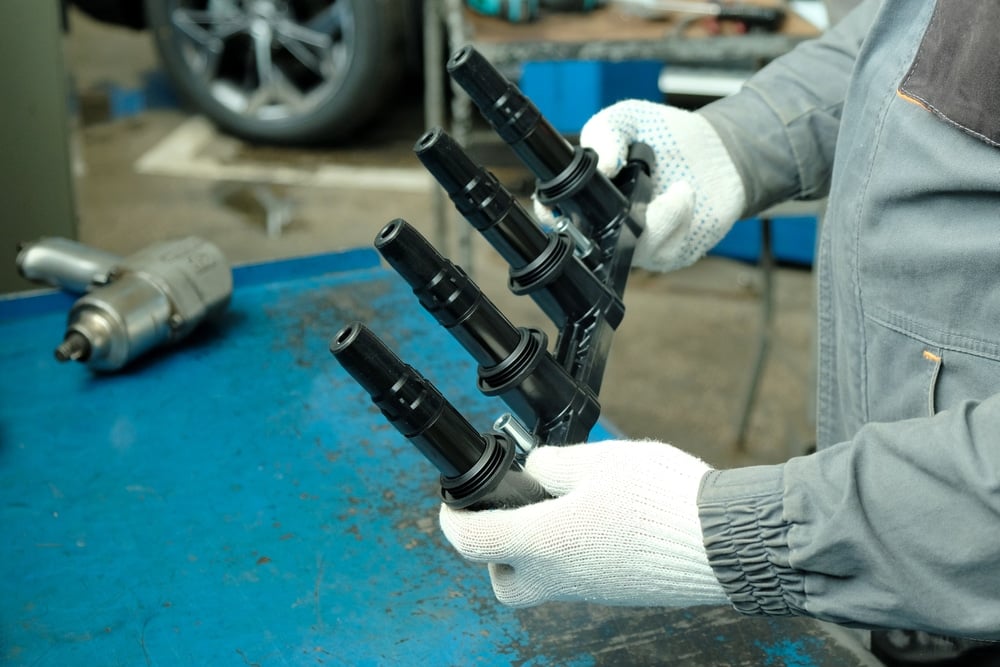

The coil packs work in conjunction with the spark plugs. To create a spark, there must be a high-voltage supply to ensure the fuel burns in the cylinder. As combustion begins, the coil pack is responsible for building up the appropriate amount of energy. In some cases, that is between 50,000 and 75,000 volts.
The electronic control module, or computer, then sends the signal to the ignition control to release voltage from the coil pack. This voltage travels to the spark plugs, where the spark can jump the gap and ignite the fuel-air mixture in the cylinder chamber.
Where Is The Coil Pack Located?
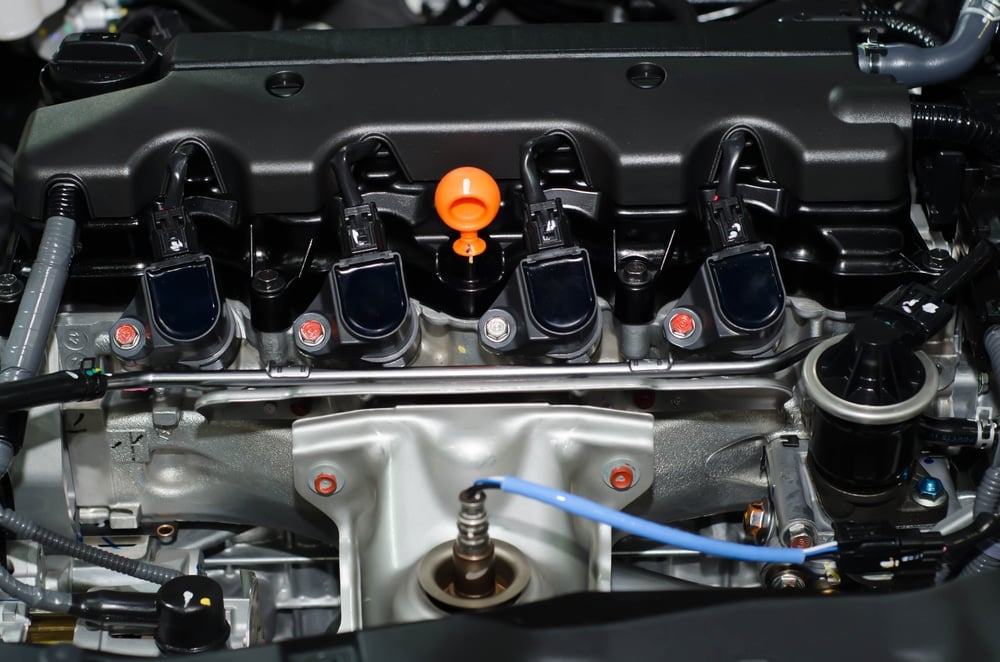

Today’s gas-powered motors usually use independent coil systems known as coil on plug. This coil is fitted over each spark plug individually. So, if you have an eight-cylinder engine with eight spark plugs, you also probably have eight coils too.
However, older engines used a different coil design fitted with coil packs. Instead of one coil for every spark plug, there would be a coil pack for multiple plugs. For example, an eight-cylinder engine may have four coil packs, one for every two spark plugs.
Coil packs can be located anywhere on the engine. Every model does it differently. Often, these coil packs are in a different location from the spark plugs, requiring a wire to connect the two together. If you trace the wire coming from the spark plug, you can find the coil pack attached to it.
The downside to the coil packs is that if one coil fails, the entire pack needs to be replaced. The packs are molded together and cannot be separated.
How Much Does a Coil Pack Replacement Cost?
On average, expect to spend between $250 and $450 for a coil pack replacement. This estimate includes the parts and labor for a standard car. Prices may be different based on where you live, the type of vehicle you drive and how many coil packs need to be replaced.
Additionally, you may want to have the spark plugs replaced at the same time. If it’s almost time to replace them as part of your regular maintenance, you may as well do it while you are already working on the car.
If you can perform any of this work on your own, you will also save some money. In some vehicles, it’s simple to replace the coil packs with some basic mechanic tools.
Interestingly, the price to replace a coil pack is often more than replacing the coil over plug in newer models. Because this system handles multiple spark plugs, it is naturally more expensive. Additionally, they can be harder to find since they are on older vehicles. You may need to order your coil packs online if your local auto parts store doesn’t carry them.
Coil Pack Testing
You can test the coil packs yourself to see if they are failing. We recommend getting a service manual for your vehicle, so you can check the readings against the manufacturer’s specifications. The specifications differ depending on the coil pack type, but here are some general recommendations.
Follow these steps.
- Find the coil pack. We showed you the location above.
- Remove the spark plug wires from the terminal. Take out the pack with a ratchet and socket or a wrench.
- Use a multimeter to read Ohms. Set it to 200 Ohms.
- Hook the multimeter up to the appropriate terminals.
- Test the coil pack for continuity. Most coils have continuity between 0.3 Ohms and 1.0 Ohms.
Next, you want to check the coil pack for secondary resistance.
- Set your multimeter to the 20,000 Ohms range.
- Put the probes on the appropriate terminals. There’s a protruding tower connecting the secondary winding in the ignition coil.
- You should see a reading between 5,000 and 12,000 Ohms. The value may read 5.0 to 12.0.
- A reading of O.L suggests that there is an open loop in the circuit.
If the readings don’t match what’s in the manual, you should replace the coil pack. Additionally, you can scan the engine for codes to see what faults have been discovered. You may find multiple problems occurring at once.
Can you drive with a faulty coil pack?
You may still be able to operate the vehicle, but we don’t recommend driving it. Not only will there be performance issues that can cause an accident due to the unpredictability, but it’s also possible to ruin other vital parts. As an example, the catalytic converter will eventually fail after driving your car this way.
How often do coil packs need to be replaced?
Most manufacturers don’t have a recommended service interval for the coil packs. This older technology isn’t used in today’s vehicles, so you should only replace them when necessary. It’s expected that most coil packs will last at least 100,000 miles without any trouble.
What causes coil pack damage?
Wear and tear is the most common reason for failure. Many years of abuse will take a toll on the ignition coil packs. Additionally, the vibration from the engine and driving can cause the insulation to break, leading to a short in the electrical connection.
Are coil packs the same as spark plugs?
Many online sources tell you that spark plugs and coil packs are the same things, but it’s not true. The coil packs supply the voltage to the spark plugs. On modern engines, there’s a coil on plug for every spark plug, while older vehicles often use a coil pack for multiple plugs.
The car’s ignition system is fascinating and we still marvel at it today after many years of working on vehicles. If everything is running as it should, it’s like a well-oiled machine with everything in its place performing its job. On the flip side, the second something malfunctions during the operation, everything seems to go downhill.
The coil packs may not be a large part of the car, but they have a big purpose. Without them doing their job, the whole performance of the engine suffers. If you notice problems with the coil packs, whether fuel economy has dropped or the engine is misfiring, it’s time to have it looked at before bigger problems occur.
Categories: Engine