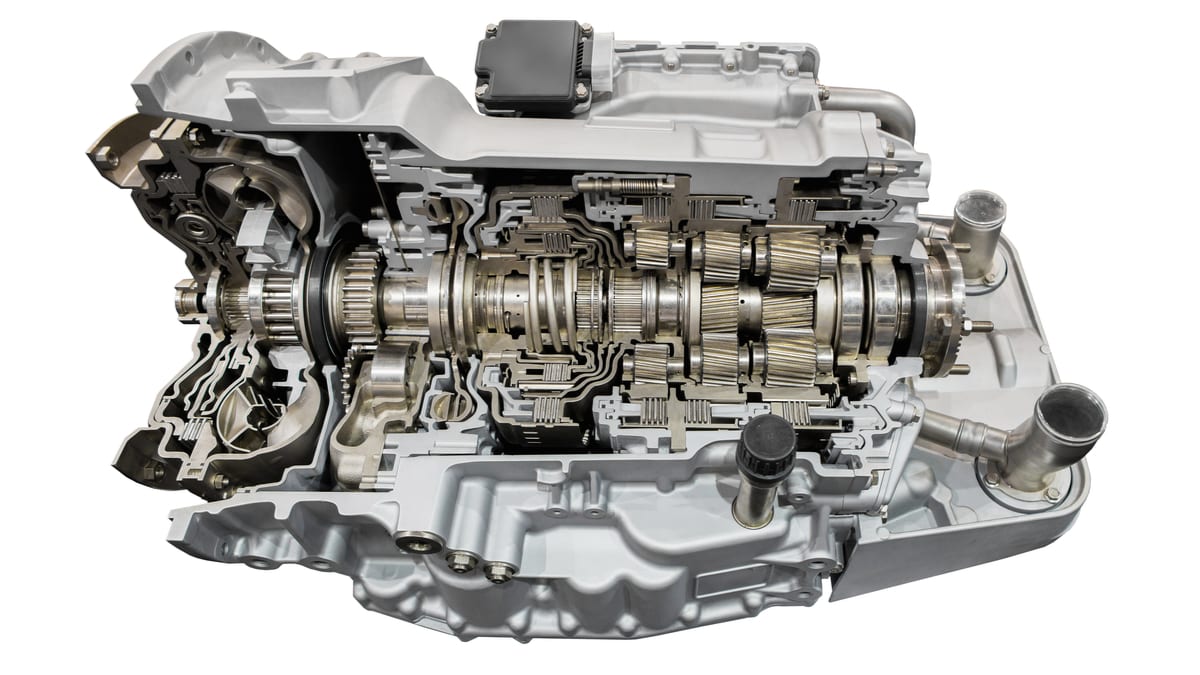
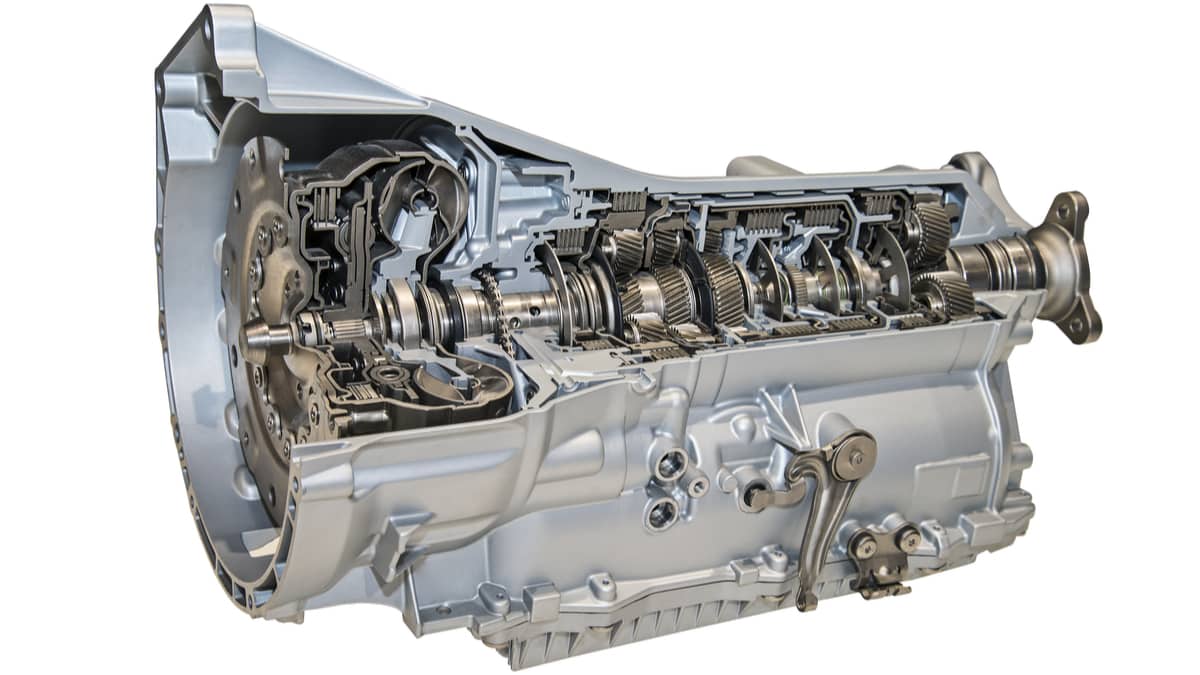
There are a lot of factors working together to ensure your vehicle runs as it should. One critical component is the automatic transmission, which transmits the power from the engine to the wheels. If the car doesn’t move in any gear of an automatic transmission, you have some issues that need to be dealt with.
In this guide, we look at the reasons you can’t get your car moving. We also give you a few tips to fix it and get back on the road.
Reasons Car Won’t Move in Any Gear (Automatic Transmission)
The most common reason is low transmission fluid or a leak. Otherwise, the car might not move because of a clogged filter, bad valve body, bad shift solenoid, failed torque converter, bad gear position sensor, defective transmission control unit, or due to worn-out clutches.
Here’s a more detailed list of why your automatic transmission may not move in gear:
1. Lack of Transmission Fluid

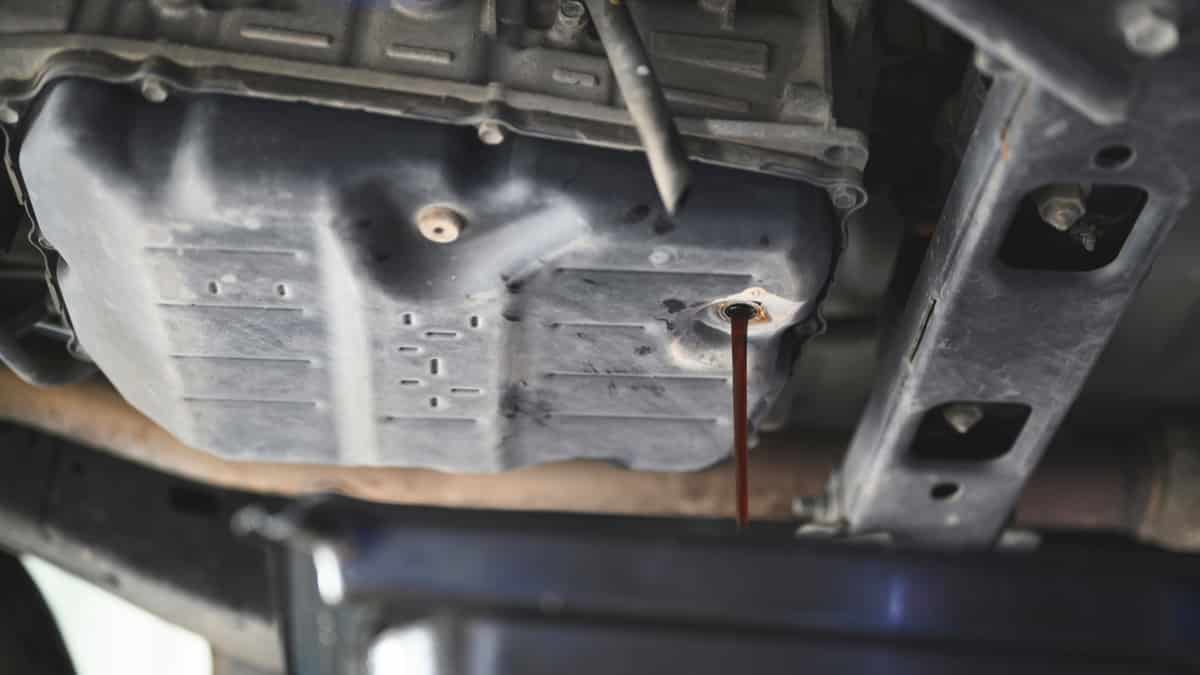
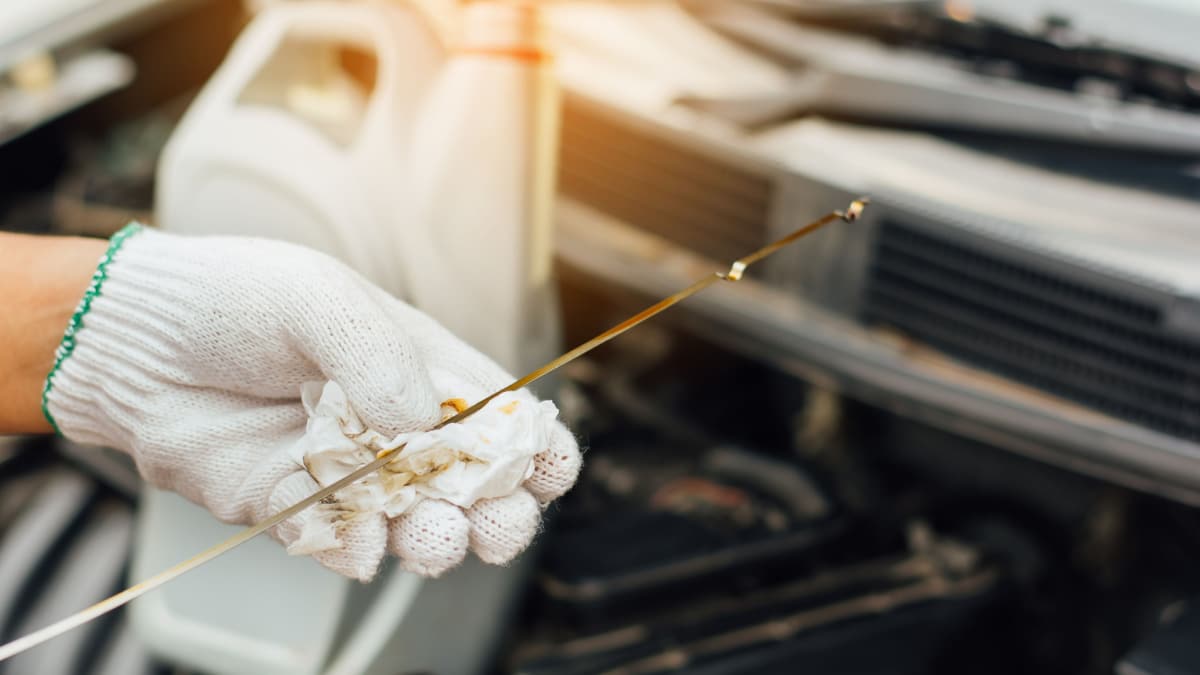
One of the most common reasons for transmission trouble is a low transmission fluid level. The transmission fluid is needed to keep the gears shifting and for the car to move forward.
It’s possible that there’s a transmission fluid leak that needs to be dealt with. You can check the fluid level on the transmission fluid dipstick and top it off if needed. Additionally, you want to repair any transmission leaks before you allow permanent damage to the transmission. In some ways, this would be the easiest and cheapest solution to your car problems.
RELATED: 6 Symptoms of Low Transmission Fluid (Check the Level)
2. Clogged Transmission Filter

The transmission also contains a filter responsible for keeping dangerous contaminants and dust from doing damage. If you aren’t changing the filter with your regular maintenance, you are allowing the debris to build up inside. Eventually, this practice will lead to a clogged transmission filter.
As the transmission filter becomes blocked, you can hear a whining sound. While it’s getting worse, you may be able to drive sporadically before it stops again. In general, you should replace the transmission filter every 30,000 miles or two years, whichever comes first. But check your owner’s manual for the correct intervals for your vehicle.
If you haven’t done this recently and are having transmission issues, this is a good place to start. You could also replace the fluid at the same time, helping to keep your transmission in optimal condition. Thankfully, the transmission fluid change doesn’t cost much.
READ MORE: How Much Does a Transmission Fluid Change Cost?
3. Bad Shift Solenoid or Valve Body
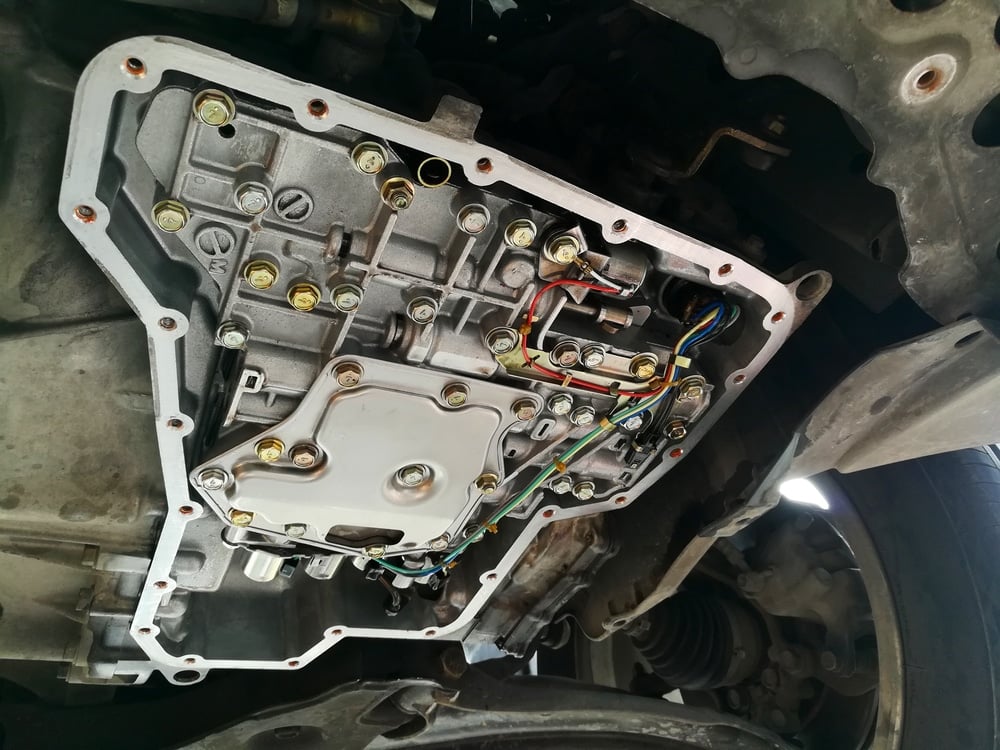

The transmission’s valve body contains hydraulic channels where the fluid flows through when the shift solenoids operate. The shift solenoids can become bad over time and the valve body channels can get clogged when the transmission fluid gets dirty. When the valve body goes bad, you will start to notice vibrations when the gears change. The car can also stall. Once it’s bad enough, the vehicle won’t move at all.
Sadly, replacing a shift solenoid or the valve body isn’t an easy fix. You need to drop the transmission pan to complete the job, so give yourself plenty of time.
READ MORE: 7 Symptoms of a Bad Shift Solenoid (& Replacement Cost)
4. Failed Torque Converter
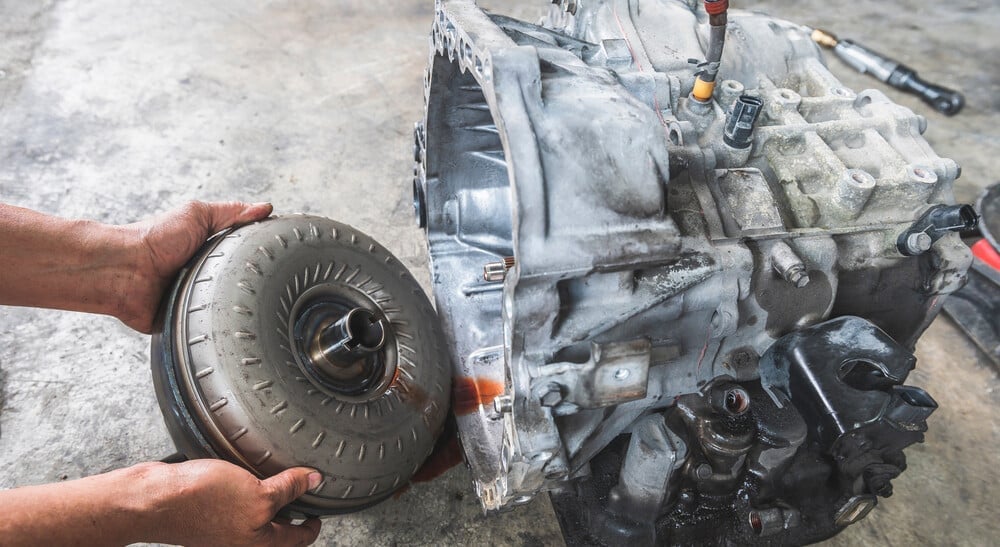

The torque converter often goes bad because the transmission hasn’t been maintained properly. If you are using junky transmission fluid, failing to make changes, leaving the dirty filter installed, and ignoring the signs it needs attention, you can end up with a bad torque converter.
As the converter begins to fail, you may notice some signs before the car stops driving. It can make strange noises first, especially at start up. The sounds might go away as the car gets warmed up. However, it will start to stall as the condition becomes worse.
The torque converter is usually an expensive part. Plus, it can take all day to repair because the transmission has to be removed. This might be another task for a transmission specialist.
5. Worn-Out Clutches
The automatic transmission contains clutches, similar to the manual transmission. When the clutches wear out, the automatic car will not move. The clutch discs are responsible for connecting the transmission to the engine, so they can cause a lot of problems when they fail. Before the car stops moving, there could be a blowing or a grinding noise during gear changes. You may also notice the changing of gears becomes rougher.
Changing the worn clutch discs isn’t an easy fix. As with many automatic transmission faults, you must remove the transmission and many components to complete the job. If you don’t know how to do this, it’s best to get some help.
6. Bad Gear Position Sensor or Shifter
If the gear position sensor or switch sends the wrong signal to the transmission control unit, it may cause problems. For example, if the gear is in D or first gear, but TCM thinks it is in neutral, your car will not move. However, this is often quite easy to recognize. Just look at your car’s dashboard and see if the gearbox matches the gear position.
RELATED: 8 Symptoms of a Bad Automatic Transmission (& Replacement Cost)
7. Defective Transmission Control Unit
In some cases, the faulty transmission control unit is easy to diagnose, because it may display the incorrect gear on the dashboard. When the transmission control unit isn’t working correctly, the car doesn’t seem like it changes gears, even when the RPMs are increasing. It can also fail to go anywhere at all.
However, a failing battery can also lead to this system not working right because it doesn’t have the correct amount of power. For starters, check your car battery to ensure it is adequately charged.
If that’s not the problem, you might need a new transmission control unit. These parts can be difficult to get to, requiring a skilled technician to work on them. If you are unsure, have a professional take a look.
Also, ensure your parking brake is not engaged, as it could be a silly but easy mistake to make!
How to Diagnose Automatic Transmission Problems
If you want to figure out the problem on your own, here are a few tips you can follow.
- Start by checking the transmission fluid. If it’s low, fill it up.
- If the fluid is low, you need to look for a leak. Leave a piece of cardboard under the car overnight to see where the leak is coming from.
- If you haven’t replaced the filter, it’s time to perform a transmission fluid and filter change. Check the filter to see if it was clogged.
- Check the shifter and ensure it says the right gear on the dashboard as the shifter position.
- Read the trouble codes in the transmission control module with an OBD2 scanner and look for any codes related to the valve body or shifter solenoid. Follow instructions and repair any codes related to the transmission.
- If nothing else has worked, check the battery voltage. If the battery isn’t charged, it can cause trouble with the control unit.
If, after these steps, you are unable to discover the problem, it might be time to take the vehicle to a qualified shop. Mechanics with specialized transmission diagnostic equipment can pinpoint the problems faster, and they have the skills to repair them. If your vehicle requires a transmission rebuild, this isn’t a task you want to take on at your home garage unless you have a transmission jack and other specialized tools.
RELATED: Should You Repair, Rebuild, or Replace Your Car’s Transmission?
How Does an Automatic transmission Work?
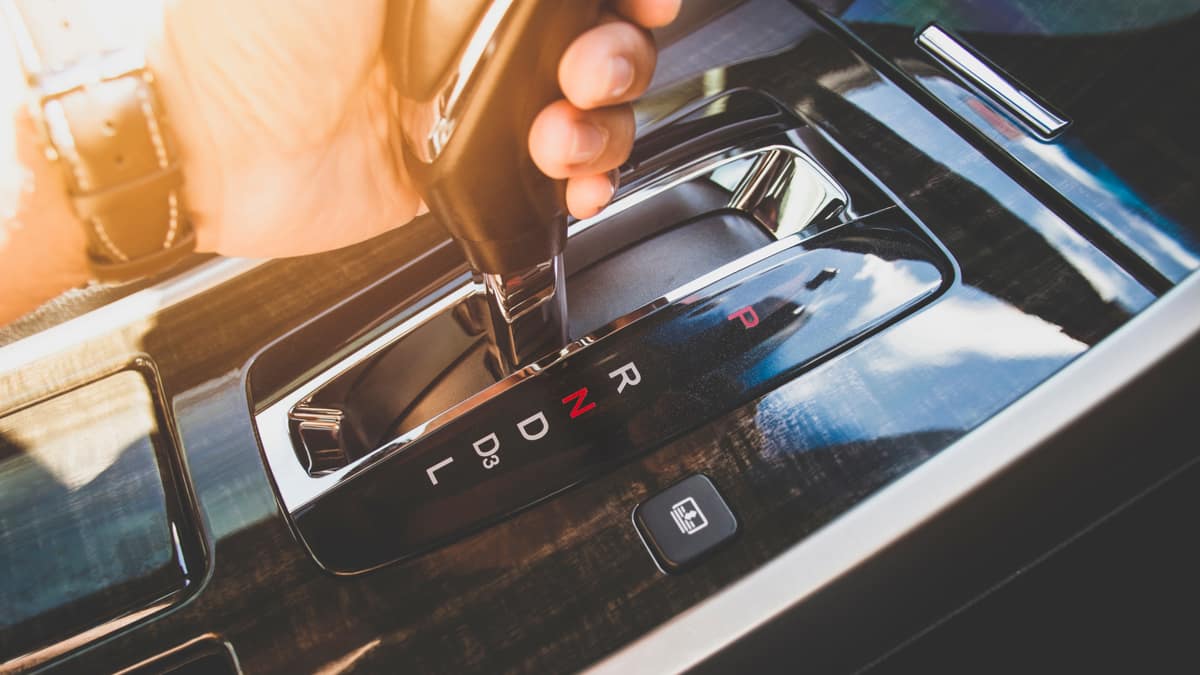
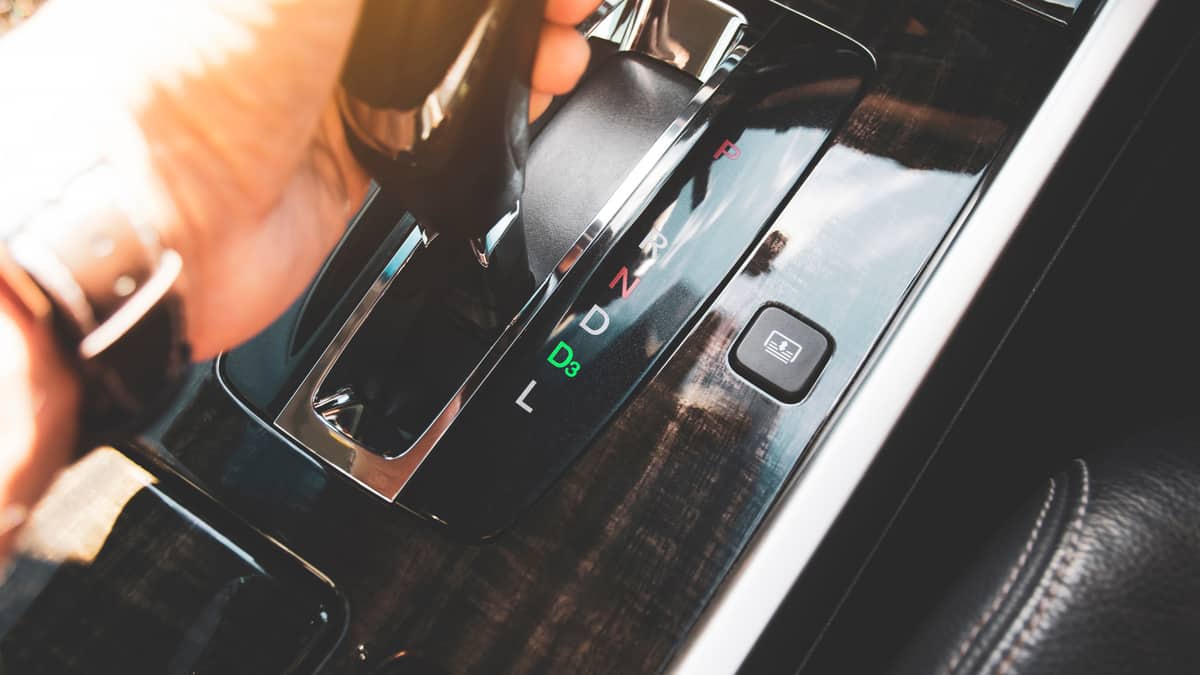
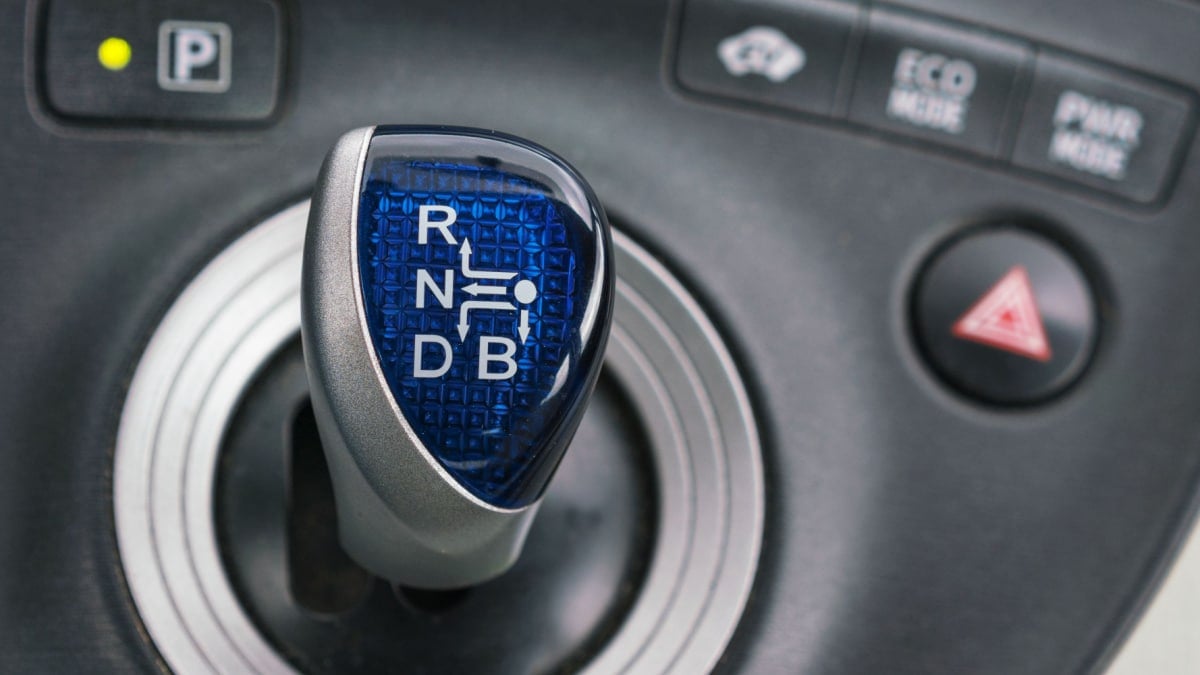
The automatic transmission system operates differently from the manual gearbox that forces you to shift between gears. The automatic utilizes sensors that indicate when the shifting should occur, and it performs the action for you. There’s no input required from you to keep the car moving.
Inside the automatic transmission, hydraulic fluid is used to keep the gears shifting. Most automatic cars contain the following selections.
- Park (P): The gears are locked and the wheels won’t spin.
- Reverse (R): The reverse gear is engaged, so you can drive backward.
- Neutral (N): This free-spinning mode releases all of the gears, allowing the wheels to spin without power.
- Drive (D): The car can move forward, progressing through all of the gears available.
- Low (L): The car remains in the lower gears, ideal for towing or getting up steep inclines.
Some cars remove the Low gear for a Manual (M) option. With this setting, you can manually gear shift your automatic transmission.
RELATED:
- Automatic Transmission Won’t Shift into the Third Gear (Causes)
- Transmission Shifting Hard – Causes & How to Fix it
Categories: Transmission, Troubleshooting