The exhaust system is made up of several parts working together to route the gases from the engine away from the vehicle. If you want to know how hot an exhaust pipe and muffler get, you must look at all aspects of the system.
To give you a better understanding, I look at the various parts of the exhaust system and determine the temperature of each. I also examine the factors that affect exhaust temperatures.
How Hot Does A Car Exhaust System Get?
The temperature within the exhaust system can range from 300 to 1,600 degrees Fahrenheit, depending on which part you are looking at. However, the average temperature of the muffler or exhaust pipe is usually between 300 and 500 degrees Fahrenheit.
Here is a more detailed list of the temperatures of the different exhaust parts:
1. Exhaust Manifold
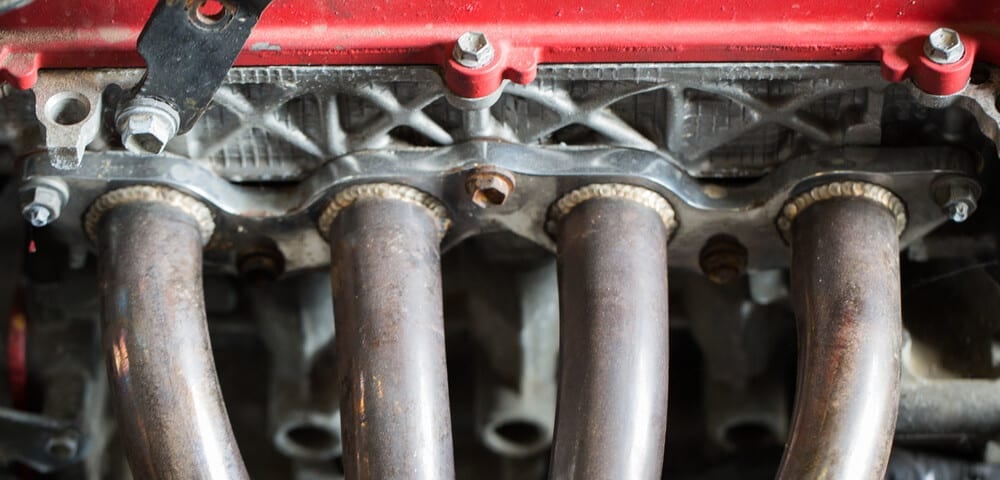

When the gases are coming out of the engine, they are at their hottest point. This is where the gases could easily reach 1,200 degrees Fahrenheit, especially if you are pushing the vehicle hard.
The closer you get to the cylinder heads, the hotter the gases will be. As they move away from the engine, they start to cool off slightly.
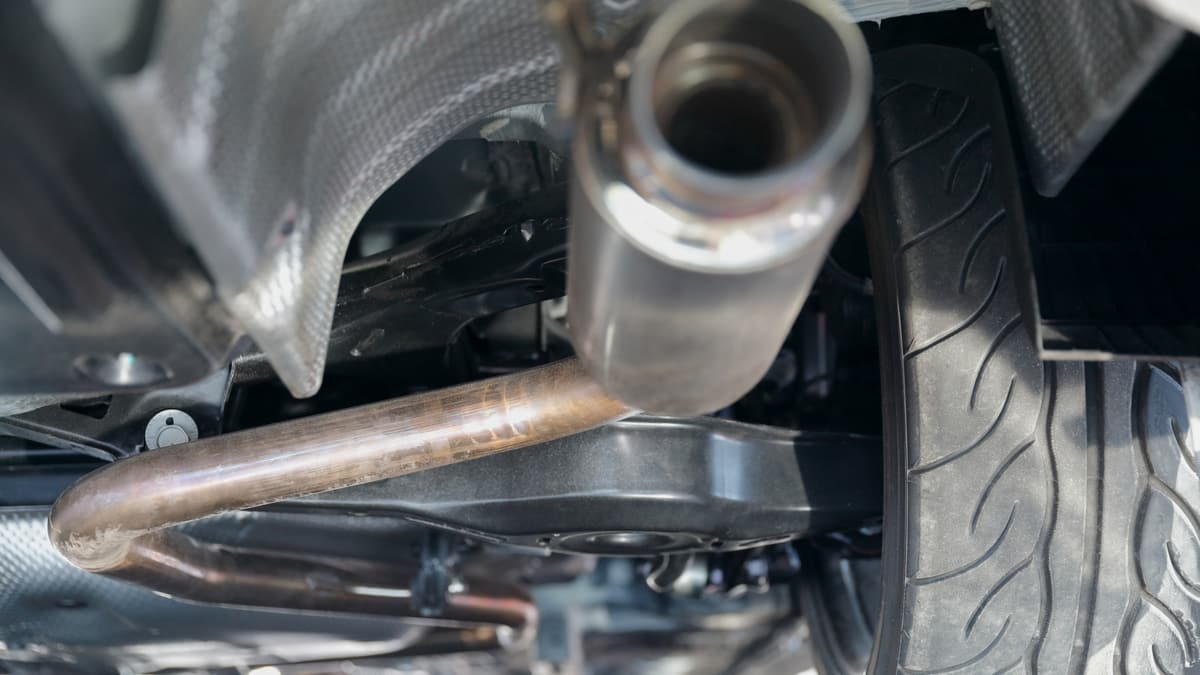
2. Muffler
Even though the muffler is near the end of the exhaust system, it still remains quite hot. In fact, most mufflers can reach temperatures between 300 and 500 degrees Fahrenheit.
The higher the RPMs of your engine, the hotter the gases are going to be. Because of these extreme temperatures, you must use caution when replacing or fixing a muffler.
3. Catalytic Converter
Because there is a chemical reaction taking place in the catalytic converter, this part has a higher temperature reading. You can expect most catalytic converters to reach around 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit.
However, when the converter becomes overheated, or if unburnt gases travel through, the temperature can rise significantly. In fact, overheated converters can reach over 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit and turn bright red.
4. Oxygen Sensors
The oxygen sensors are located throughout the exhaust system. Depending on what location you are looking at, the temperature can vary greatly.
At the point of leaving the engine, the first oxygen sensor is going to deal with the most extreme heat. However, the sensors after the catalytic converter doesn’t have it easy either, especially if the converter is overheated.
Factors Affecting Heat from Exhaust System
1. Condition
The condition of both the engine and exhaust system makes a huge difference in the temperatures you can expect. If the exhaust system is dealing with any constrictions, it will cause the temperatures to rise.
Additionally, the harder the engine has to work to produce power, the hotter the gases become. If the engine is overheating for any reason, the gases could exceed normal operating temperatures.
2. Engine Speed
The gases are produced from the combustion of the engine. The faster the vehicle moves, the more the engine must work, which means extra gases are moving through the pipes.
You are going to notice a big difference between the temperatures of the gases when the engine is running at 800 RPMs versus 1800 RPMs. In fact, if you are simply idling the engine, the pipes won’t get nearly as hot as they do when you are driving your vehicle.
3. Pipe Length & Design
Every exhaust system features a different design and pipe diameter. The length and width of these pipes affect how cool or hot the exhaust gets.
The further the exhaust gases need to travel, the more heat becomes lost in the process. However, if the gases don’t have far to travel, the gas is going to come out hotter, resulting in higher pipe temperatures.
What is the Exhaust System?
The main purpose of the exhaust system is to remove the gases from the engine. However, it’s also needed to reduce noise and improve the performance of the motor.
The exhaust system is made up of several components, including the manifold, catalytic converter, resonator, oxygen sensors, muffler, tail pipe and exhaust pipe. The exhaust system begins at the exhaust manifold. This is where the gases from the engine are collected and directed away from the motor.
Typically, the exhaust manifold is made from cast iron, designed to handle the hot fumes coming from the engine. Many manifolds contain multiple cylinders that remove the gases and route them into a single cylinder, known as the front pipe.
There will be an oxygen sensor in the beginning of the exhaust system, measuring the level of oxygen in the gas. This information is sent back to the ECU to determine how much fuel must be injected into the engine for proper combustion.
The exhaust gases then go through the catalytic converter, where a chemical reaction occurs to reduce toxicity. After this, there should be another oxygen sensor that compares how much oxygen is in the gases with the first reading. This sensor is responsible for making sure the catalytic converter is doing its job.
The altered gases move through the resonator, which changes the sounds coming out of the engine. These fumes hit the muffler, which also reduces the sound of the exhaust, based on what kind of chambers it has and what material is used for the construction. At the end of the line, the gases move into the atmosphere through the tail pipe.