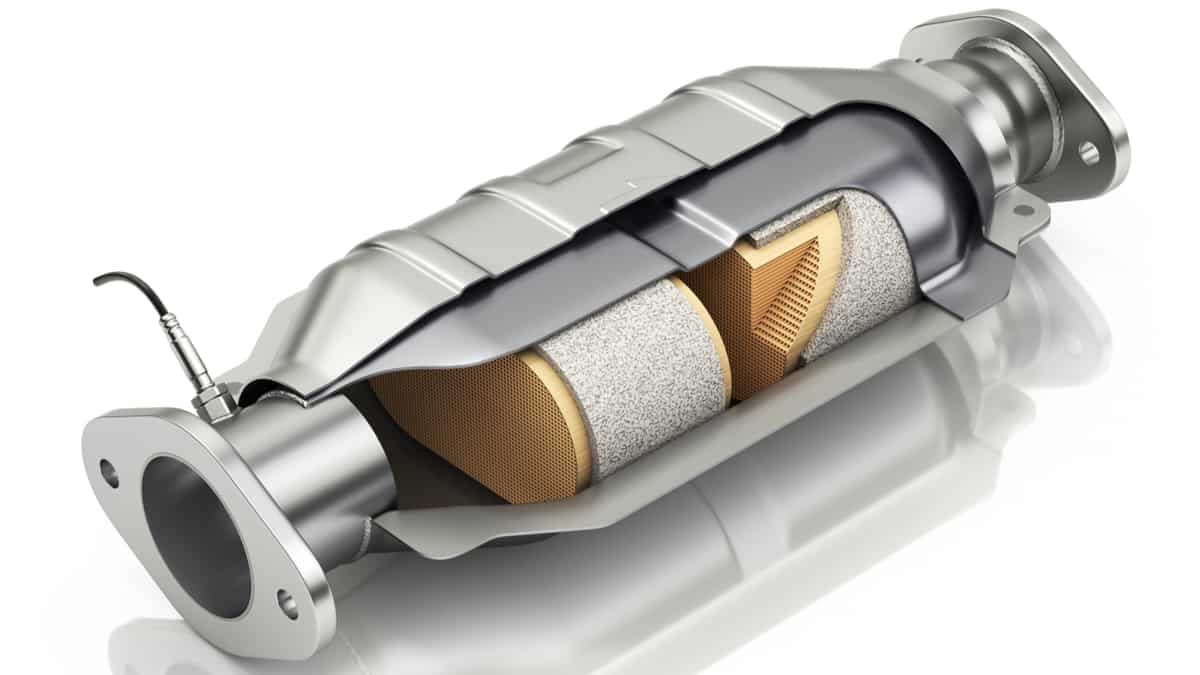
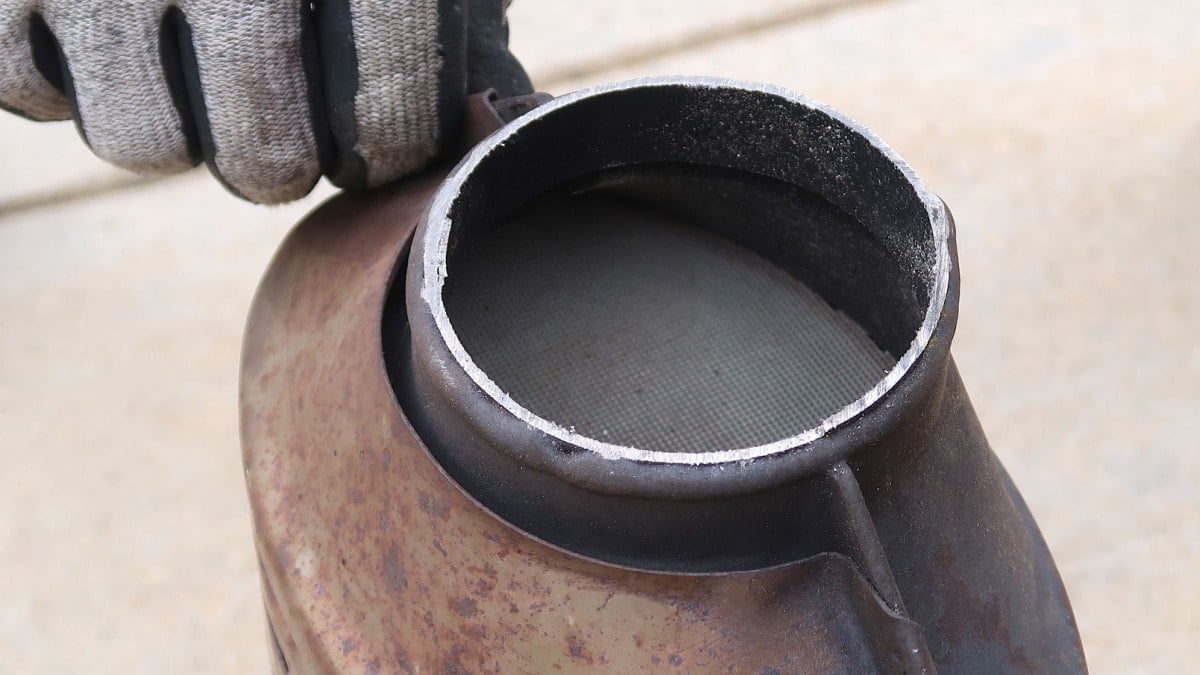
The catalytic converter in your vehicle is responsible for getting rid of emission gases in a responsible way. When it isn’t working as intended, your vehicle could fail an emissions test.
The only option in most cases is to replace the catalytic converter. How much does a catalytic converter replacement cost, and is it worth you keeping the vehicle to repair?
In this guide, I cover the basics of the catalytic converter, and show you what it will cost to repair. I also discuss some signs that the catalytic converter needs to be replaced.
How Much Does a Catalytic Converter Replacement Cost?
The average catalytic converter replacement cost is between $400 and $2,500, including both parts and labor. Despite the high cost, it’s not the labor that’s hurting your wallet. Rather, the catalytic converter makes up most of the cost, mainly because of the expensive materials used in the interior construction of the part.
Catalytic converter replacement can be one of the most expensive auto repair tasks. Depending on the value of your car, it might not be worth replacing the catalytic converter.
However, you can prevent the need for a new catalytic converter by maintaining your vehicle. If you get the spark plugs changed regularly and keep the engine running at its best, the catalytic converter will continue working as it was intended. It’s when you neglect your vehicle’s care that the catalytic converter starts to fail. If the Check Engine Light comes on, take it seriously and have it looked at.
RELATED: How to Clean a Catalytic Converter (Without Removing it)
Factors that Affect Catalytic Converter Replacement Cost
1. Vehicle Type
If you drive an older car, you might spend less to replace the catalytic converter. Older vehicles have cheaper catalytic converters, possibly only costing a few hundred dollars.
However, newer cars contain more sophisticated catalytic converters, which drastically increases the price. Additionally, if your vehicle has a dual exhaust system, there might be two catalytic converters to deal with.
2. Quality of New Part
As with any auto part, no two are created the same. You can find a generic catalytic converter that will get the job done, but it might not provide the best fit or superior materials.
A cheap catalytic converter won’t have the same level of precious metals inside, making it less efficient and not as durable. You will be replacing the catalytic converter again in the future. A higher-end catalytic converter can contain a density of six times the amount of materials when compared with a cheaper option. You may also notice a check engine light together with the P0420 code on your dashboard if you install a cheap catalytic converter.
3. Labor Expenses
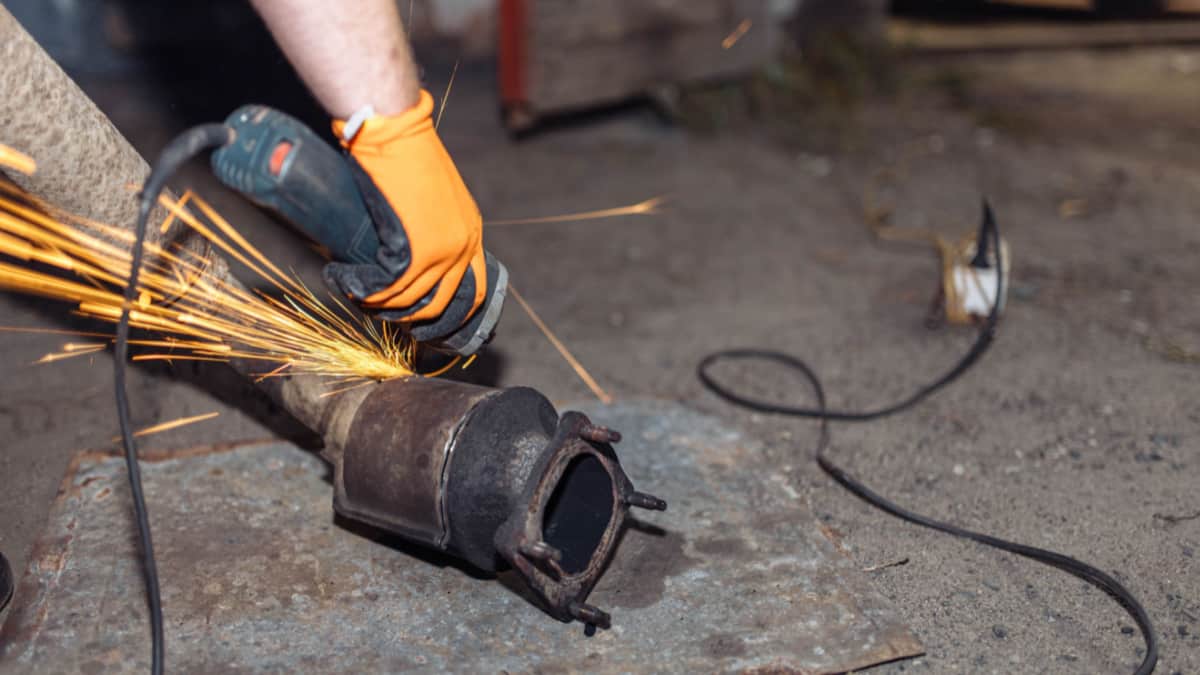
As with any auto repair, the labor expense factors into what you will spend. If you can do the job yourself, you might save some money. However, replacing a catalytic converter isn’t normally a job to be done in a home garage.
It’s possible that the old catalytic converter needs to be cut off, with the new one being welded in its place. If you have a dual exhaust, you’ll need to perform the task twice.
Additionally, labor rates are different within every region. If you live in a city, you might spend more than your countryside neighbors. You will also pay more if you visit a dealership or specialized exhaust shop instead of using your local auto repair garage. Evaluate the pricing around you, but don’t choose a shop based on the cheapest rates. If the job takes them twice the time to complete, you could actually end up spending more.
4. Other Diagnostics/Repairs
When you take your vehicle to the auto repair shop, you have more expenses than just getting the catalytic converter replaced. You will also need to pay for any relevant diagnostic charges.
Aside from that, if there are other issues with the exhaust system, those repairs could also be added in. It’s possible for multiple systems or parts to fail at the same time, especially if another fault has caused the catalytic converter to go bad.
Symptoms of Bad Catalytic Converter
Here is a brief overview of the most common symptoms you may notice. Check our other article if you want a more detailed guide: 8 Symptoms of a Bad Catalytic Converter
1. Failed Emissions Test
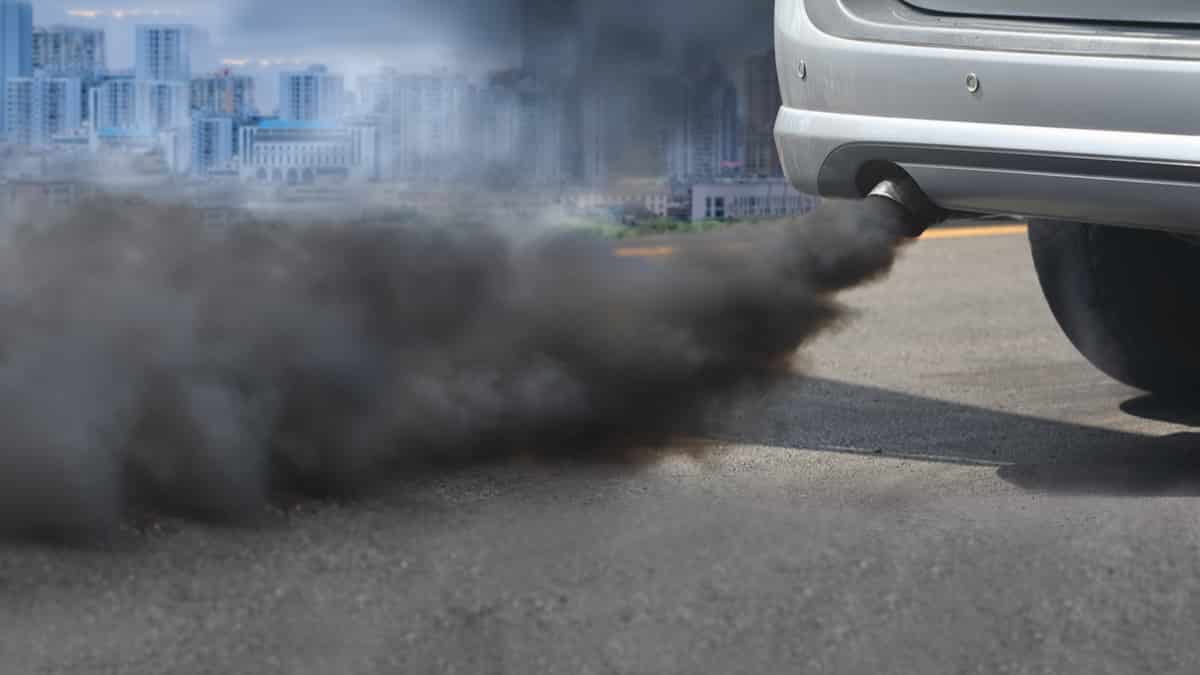
Thirty-four states now require emissions testing. Sometimes, the first time that drivers recognize something is wrong is when their car fails its emissions test.
When the catalytic converter isn’t working right, the emissions aren’t going to be ideal for the environment. Because additional gases are getting pumped into the atmosphere, you won’t be able to pass the test until you have the catalytic converter replaced.
2. Check Engine Light
Another one of the earliest signs is when the Check Engine Light comes on. As the catalytic converter starts to fail, the oxygen sensors send a signal to the ECU, letting it know that there’s a problem.
When you use your code scanner to read the Check Engine Light, you should see where the problem lies. Replacing the catalytic converter and any other failed parts will be required to get the Check Engine Light off once again.
3. Rotten Egg Smell
If you smell rotten eggs in your car, it could be that you just left some trash in the cabin. However, it’s more likely that there’s a problem with the catalytic converter.
The rotten egg smell occurs because of hydrogen sulfide. When the catalytic converter is working as it should, this compound gets turned into sulfur dioxide, which doesn’t have any smell. However, when the compound comes out of the tailpipe without being properly converted, it leads to a terrible stench.
4. Poor Acceleration
As carbon builds up in the catalytic converter’s honeycomb design, it becomes impossible for it to continue converting gases as it should. This blockage creates poor performance, because the engine needs a good amount of airflow to be optimized.
The blockage leads to the wrong amount of backpressure, which can dramatically influence the overall airflow. The less airflow there is, the more the power is reduced. You will notice the lack of power the most when you attempt to accelerate.
5. Decreased Fuel Economy
When the catalytic converters backs up, it causes more than just poor performance. As the engine becomes starved of air, it can’t run efficiently.
The harder the engine needs to work, the more fuel it will go through. You will see reduced fuel economy, which only further hurts your pocket every time you need to fill the tank.
RELATED: How To Protect Your Car Against Catalytic Converter Theft
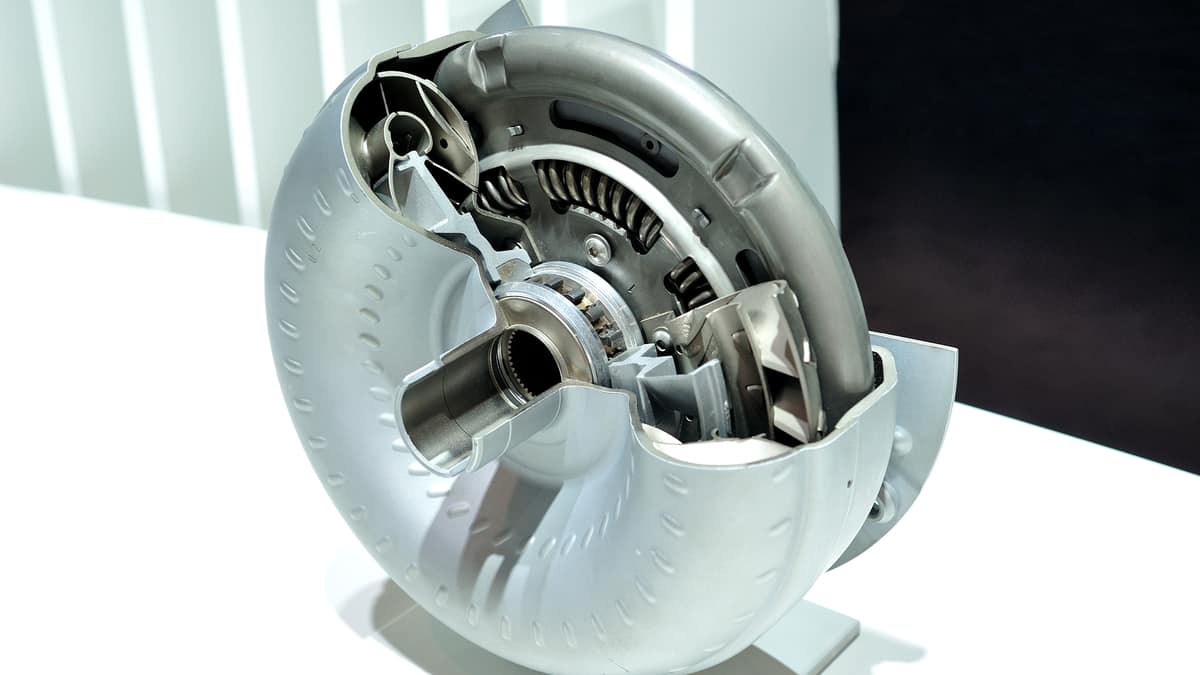
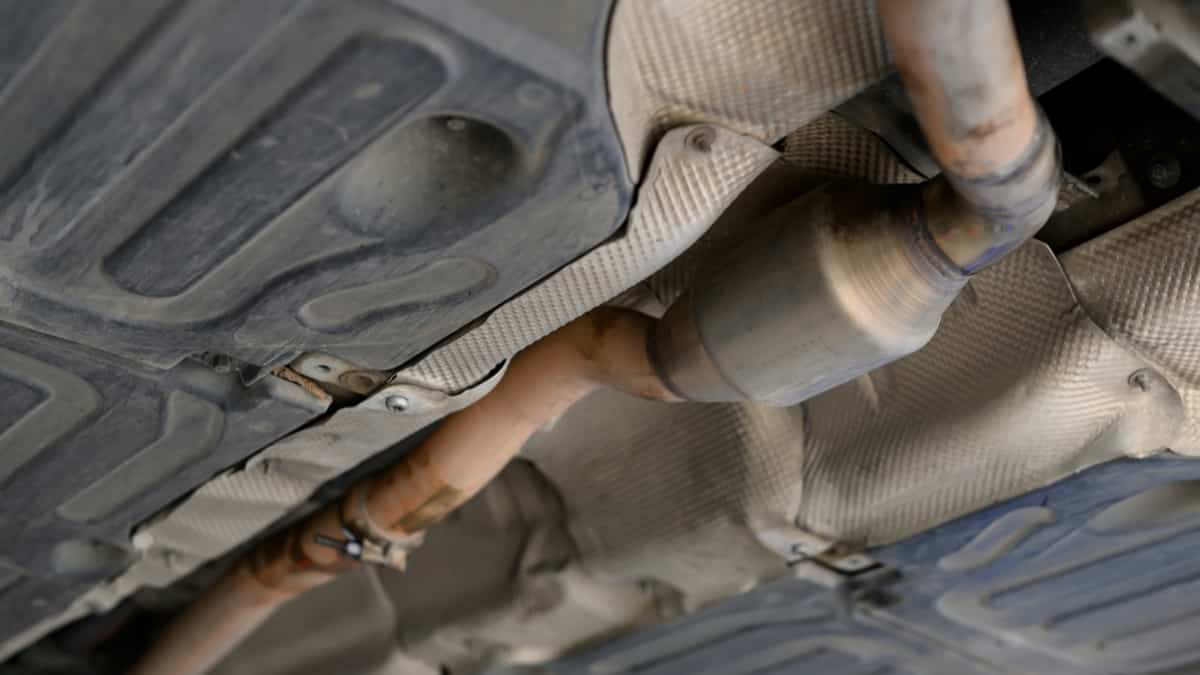
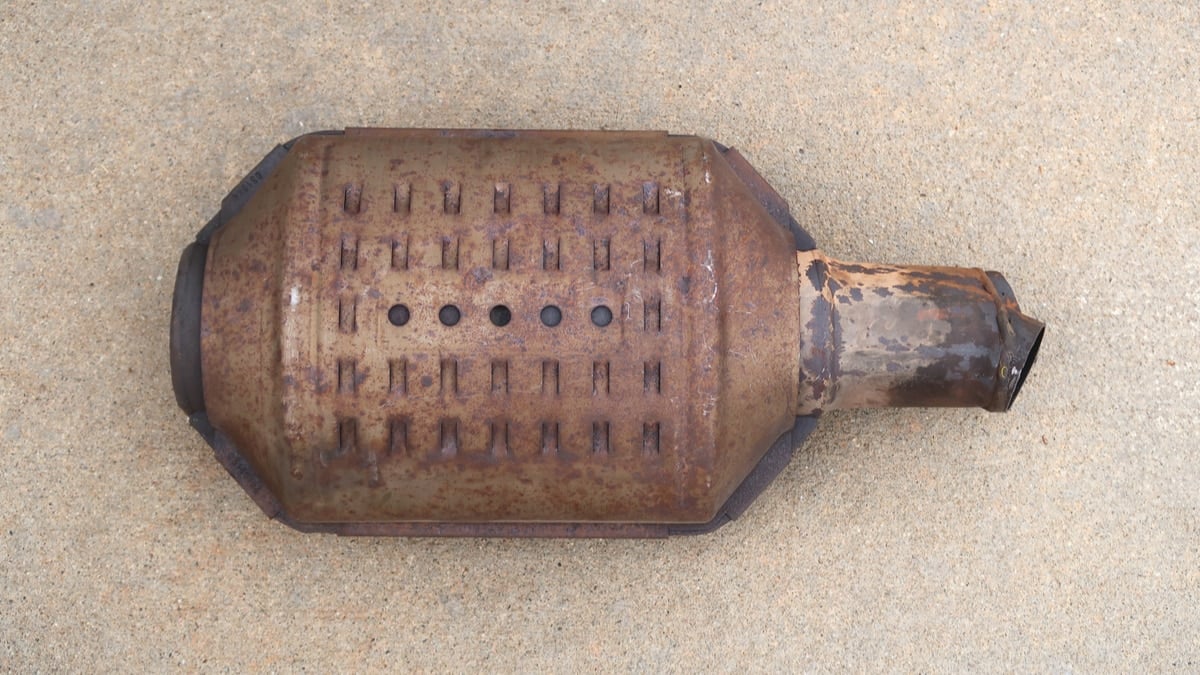
What is the Catalytic Converter?
The catalytic converter is part of your car’s exhaust system. It looks similar to a muffler, but it is constructed with different materials. Inside the catalytic converter, there’s a unique honeycomb-like structure that contains catalyst particles that interact with the exhaust gases. These particles can include rhodium, palladium and platinum.
The unburned hydrocarbons located in your car’s exhaust react with these materials in the catalytic converter. As the hydrocarbons are heated up, they break down into emissions that are less toxic and harmful to the environment. After the catalytic converter, these gases exit into the atmosphere through the tailpipe.
Can the Catalytic Converter Be Removed?
You might think that the most obvious solution is to simply take off the catalytic converter. Some people choose to do this and install a straight pipe, but is that the best solution? Yes, it makes for a cheaper repair, but there are reasons that it’s a terrible idea.
First of all, your car is going to fail emissions testing; there’s no way around it. Additionally, the car is going to dramatically suffer in terms of its performance and efficiency. On top of that, you are allowing more pollution to enter the environment, making you part of the problem.
The only real solution is to replace the catalytic converter. If the car isn’t worth the expense, then it’s time to get rid of it and buy a new one. Don’t take shortcuts when it comes to replacing the catalytic converter.