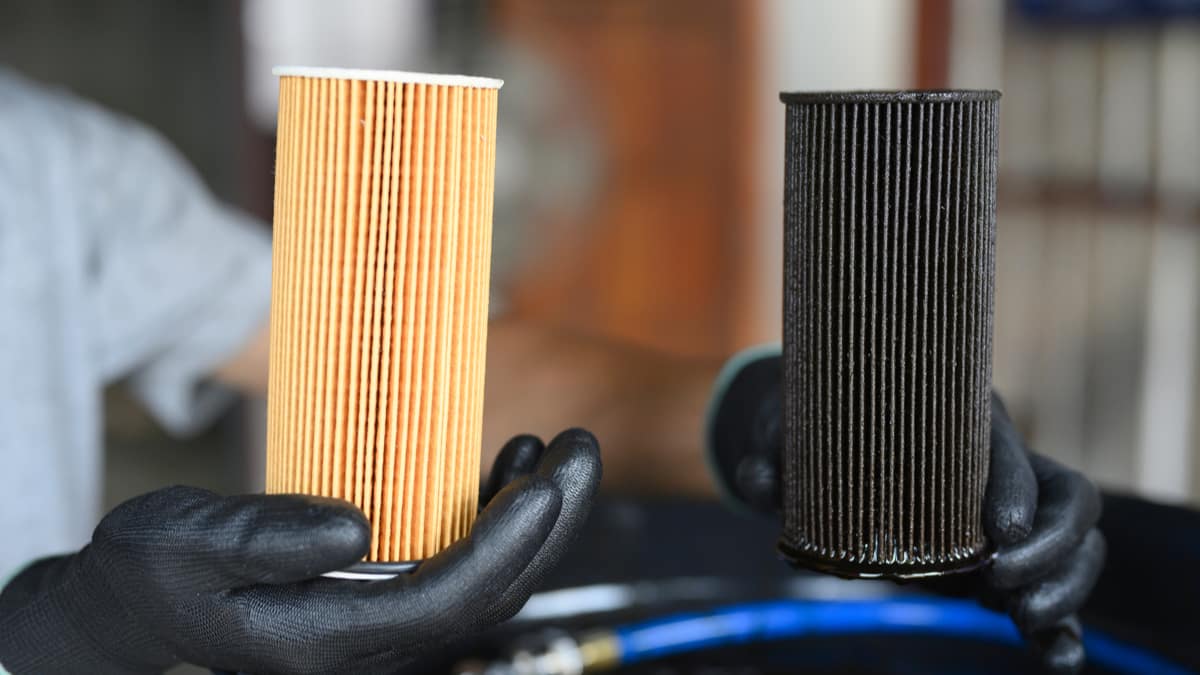
If you drive a diesel vehicle, you may have heard of the diesel particulate filter (DPF), but you might be unaware of its purpose. In fact, you may never figure out what this vital part is until you are trying to figure out if your vehicle has a bad diesel particulate filter (DPF). But how do you tell if your DPF is clogged or bad?
In this guide, I evaluate the symptoms of the clogged DPF filter. I will also show you why it is important and discuss how much it costs to replace it.
Symptoms Of A Clogged or Bad DPF Filter
When the DPF filter gets blocked or clogged, the engine becomes weaker and a check engine light often shows on your dashboard. It can also lead to higher fuel consumption and create a hard-starting situation. Additionally, you may also notice strange smells or turbocharger issues.
Here is a more detailed list of the signs of a bad or clogged diesel particulate filter (DPF) to look for:
1. Check Engine Light
The first, and most common sign of a bad DPF is a check engine light on your dashboard. The diesel particulate filter uses sensors to measure the pressure and temperature before and after the DPF filter. If the pressure is not correct, the engine control module will light up the check engine light on your dashboard.
If you see a check engine light on your dashboard, you need to scan the trouble code memory with a code scanner to figure out what’s wrong.
2. Decreased Engine Performance
When the DPF is blocked, the exhaust system becomes dramatically affected. The ability to remove the exhaust from the engine efficiently is hindered, causing there to be a backup in the system.
With the backup, the engine starts to feel weak and sluggish. The more exhaust gases that build up, the slower new fuel can be pumped in, leaving you without the ability to accelerate normally. Plus, the engine will need to use more power to push out the excess gases.
RELATED: Car Losing Power When Accelerating? (Here’re the Causes)
3. Poor Fuel Efficiency
With the engine not working efficiently, you will burn more fuel than normal. Part of the inefficiency comes from the blocked filter itself, causing more fuel to be pumped in to accomplish the same task. It’s also caused by the need for more fuel to get the desired results from your engine.
With these problems, you are going to spend more money at the pump. As the cost of diesel continues to rise, you are sure to notice the difference.
4. Trouble Starting
The blocked DPF creates a buildup of exhaust gas in the engine. This trapped gas isn’t able to go anywhere, creating more pressure than normal. During this time, it becomes difficult to get the engine cranked over. In fact, the engine won’t want to start unless that pressure gets released.
This problem is more of a safety design. If the engine starts with all that pressure inside, permanent damage could occur, leading to major repair bills. To save yourself this money, it’s best to clean the DPF before a blockage occurs.
RELATED: Car Hesitates to Start – Causes & How to Fix
5. Strange Smells
As the exhaust gas builds up in the engine, it can lead to a noticeable odor. Not only is this annoying, but it can also be dangerous.
Exhaust gases are not safe to breathe and they can be flammable, putting you at risk of a fire. Additionally, while these smells are occurring, it’s difficult to tell if something else is wrong.
6. Turbocharger Damage
With a blockage in the exhaust system, you must also consider the health of the turbocharger. When the gas flow is hindered or slowed down, the temperatures can quickly rise. When the problem isn’t resolved promptly, the turbine housing also gets hotter.
Left unchecked, the turbocharger becomes damaged. If the housing becomes damaged, leaks can occur and efficiency will drop. This problem can also cause the oil inside the turbocharger to carbonize, which becomes dangerous to the motor itself.
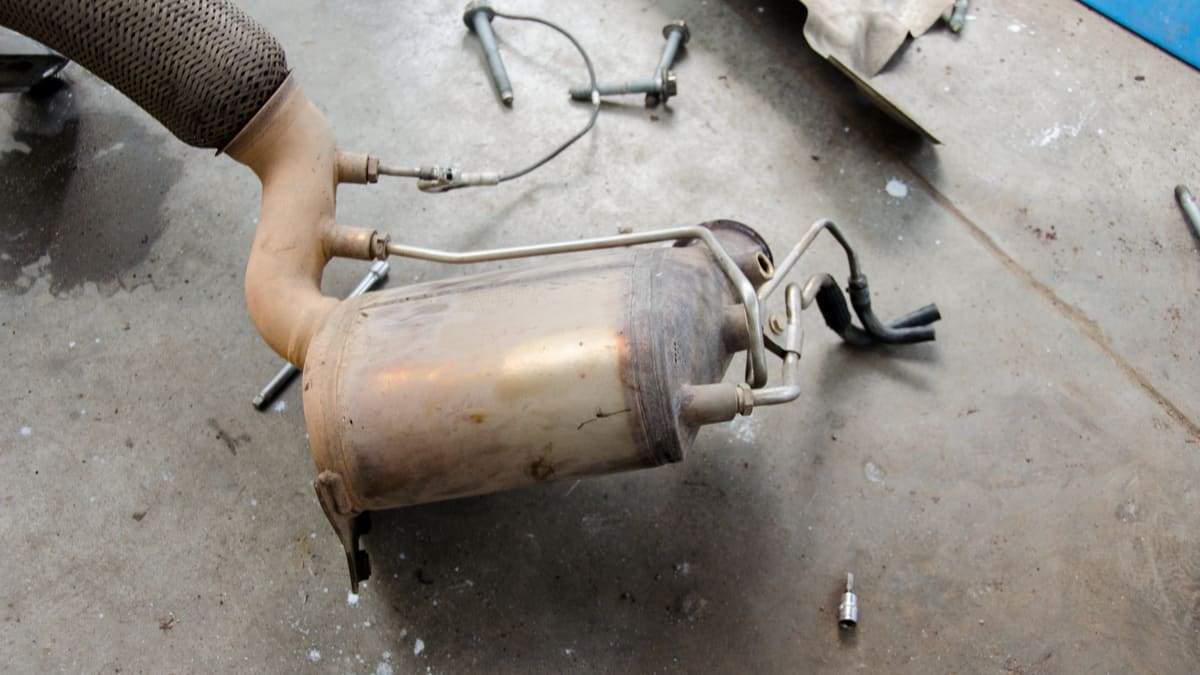
Diesel Particulate Filter Location
The diesel particulate filter (DPF) is part of the exhaust system in your diesel vehicle. You can find the filter sitting ahead of the NOx trap, otherwise known as the NOx storage catalytic converter. You will often find the DPF filter close to the exhaust manifold.
It’s also found ahead of the exhaust pipe but will be found behind the first temperature sensor. To remove the filter, you will need a screwdriver to take off the surrounding grills and plates. After the plates are removed, there could also be some O-rings or other clamps to take off.
Diesel Particulate Filter Function
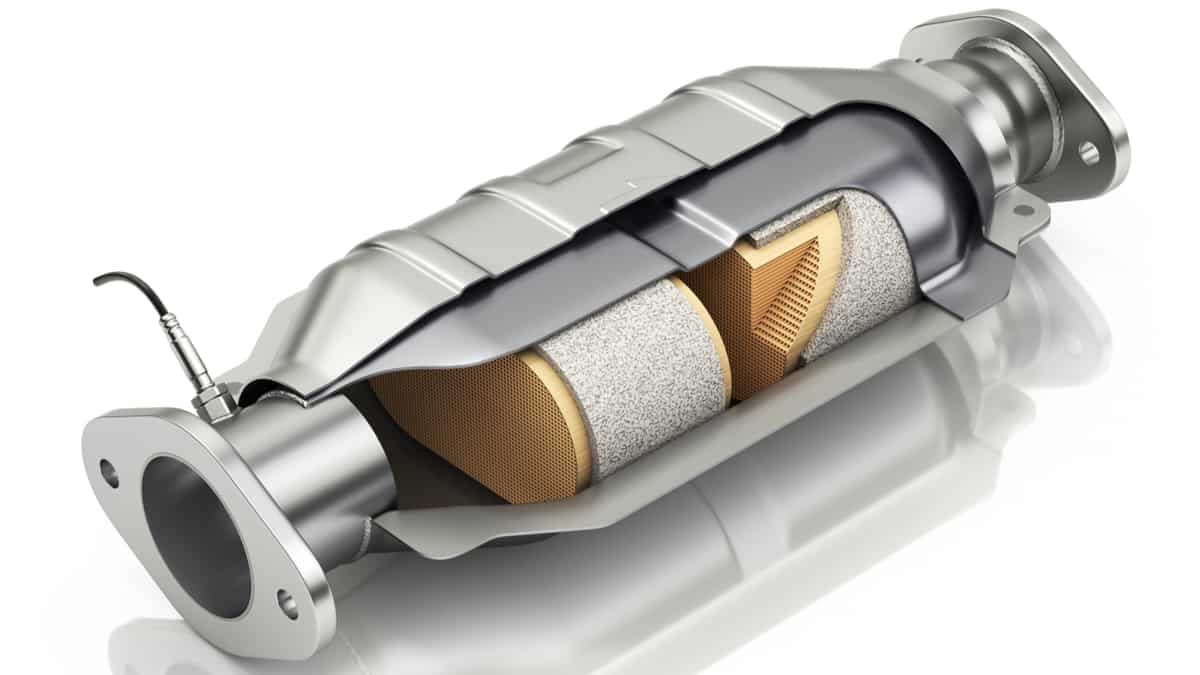
The diesel particulate filter is part of the exhaust system. It’s meant to trap particulate matter, such as ash and soot. The DPF is constructed with a substrate that is made from ceramic material. It forms a honeycomb structure that is effective at trapping debris.
The diesel particulate filter is meant to capture and store the soot from the exhaust, so the diesel vehicle can have reduced emissions. This soot is burned off periodically to help regenerate the DPF. With this regeneration process, excess soot gets burned off and deposited back in the filter, reducing the harmful emissions and black smoke you are used to seeing from diesel models during acceleration.
DPFs are now mandatory on all vehicles since 2007, as per EPA guidelines. These filters trap matter so the vehicle can adhere to strict emissions standards.
Diesel Particulate Filter Replacement Cost
A brand-new diesel particulate filter can cost between $1,000 and $7,000. These new parts are never inexpensive, which is why it’s important to keep the system running properly. Instead of replacing it, most people choose to clean it for more life.
Considering that the DPF doesn’t normally fail in a low-mileage vehicle, it makes more sense to clean it. After all, the cost of a new DPF could be more than the value of the vehicle itself. When properly maintained, the DPF shouldn’t need to be cleaned more than every 100,000 miles.
How to Clean a Diesel Particulate Filter
1. Thermal
If you take the DPF to a professional for cleaning, you might hear them using the thermal method. This cleaning technique is also known as the “bake and blow.”
The DPF is put in an oven. With the heat raised, the soot is oxidized, while the airflow pushes the ash out of the filter.
2. Aqueous
This other professional method has been shown to be effective. A surfactant surrounds the ash particles, making it easier for water to wash the debris away from the substrate.
Once the substrate is cleaned, it must be dried completely. A special cabinet is needed, so you will have to wait at least two hours before it can be reinstalled.
3. At-Home Cleaners
If you don’t want to take your vehicle to a professional for cleaning, you can try and do it yourself with a special additive. You can find some top brands for less than $25 per bottle. These products are meant to break down soot and ash.
Follow all of the directions found on the back of the bottle. You will have to put it into the fuel tank with the engine running. Once it has been added, it’s best to drive for thirty minutes. This helps the additive circulate in the system. It doesn’t matter what speed you travel at – it will work. Plus, the DPF warning light might disappear if it was previously on.
While cleaning additives can break up some clogs, they are best used for maintenance. If you are using a cleaner every three to six months, you shouldn’t have any clogging issues down the road.
If you are still having trouble after using an additive, you might need one of the professional cleaning methods instead. Visit your local diesel mechanic for more support.
A clogged DPF filter can cause many problems for your car. If you notice any of the signs mentioned above, it is important to take action and replace or repair your DPF filter as soon as possible. A new DPF filter will help improve your car’s emissions, performance and fuel efficiency.