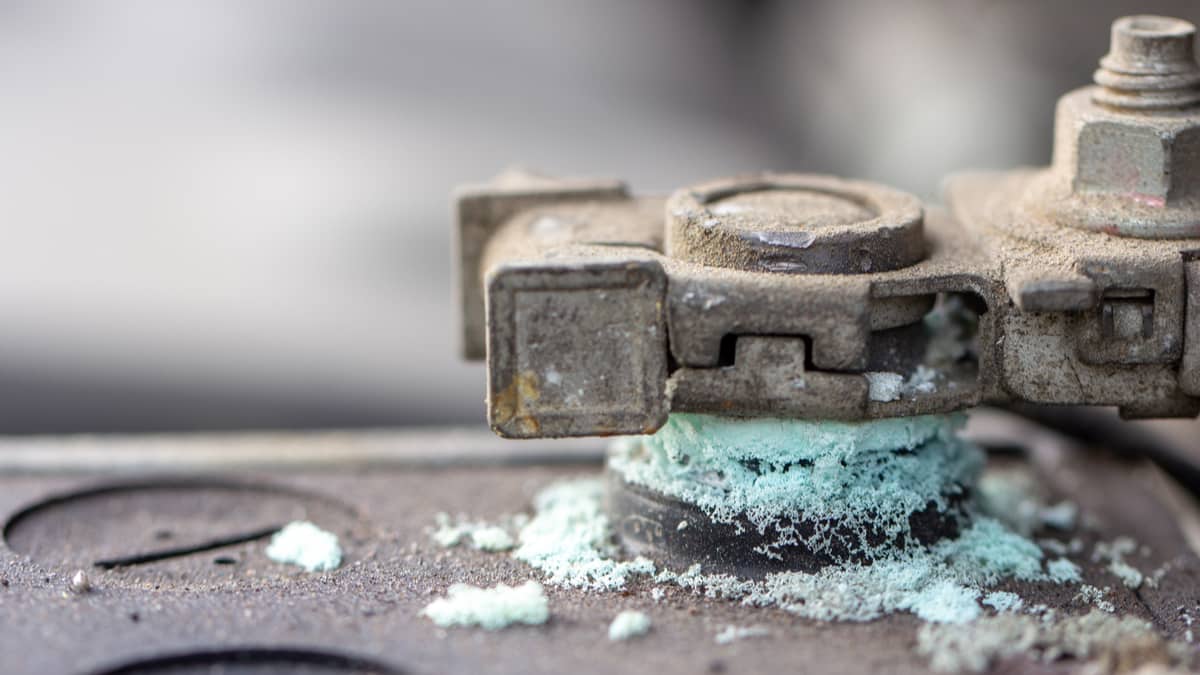
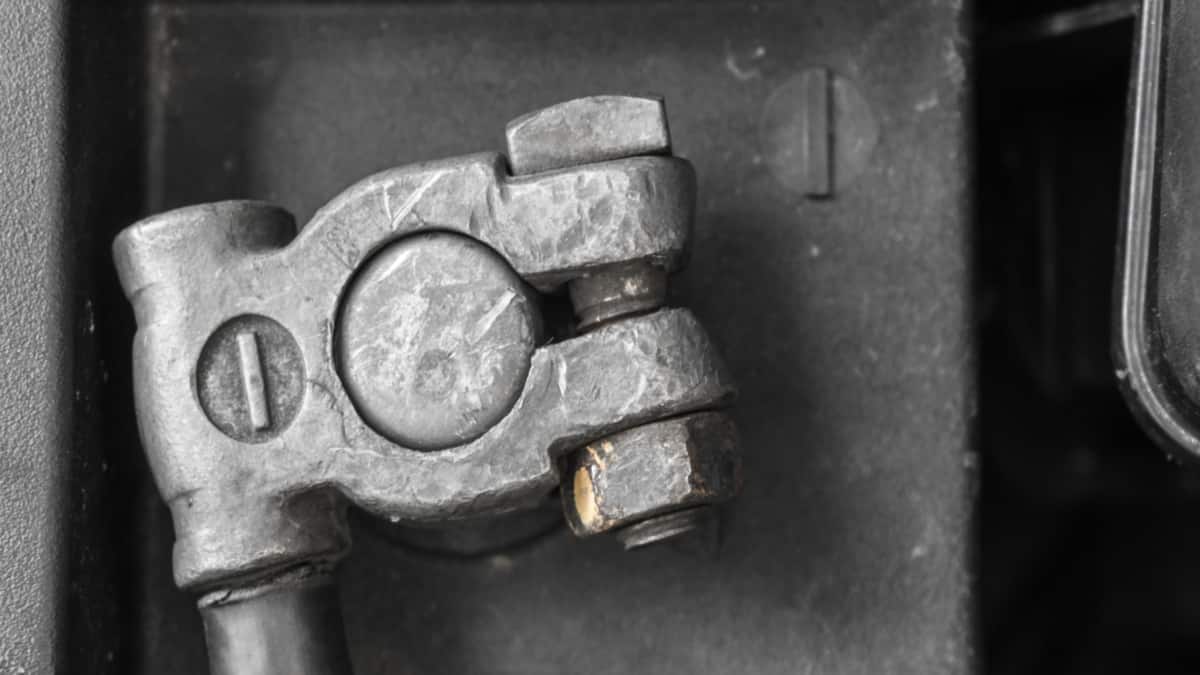
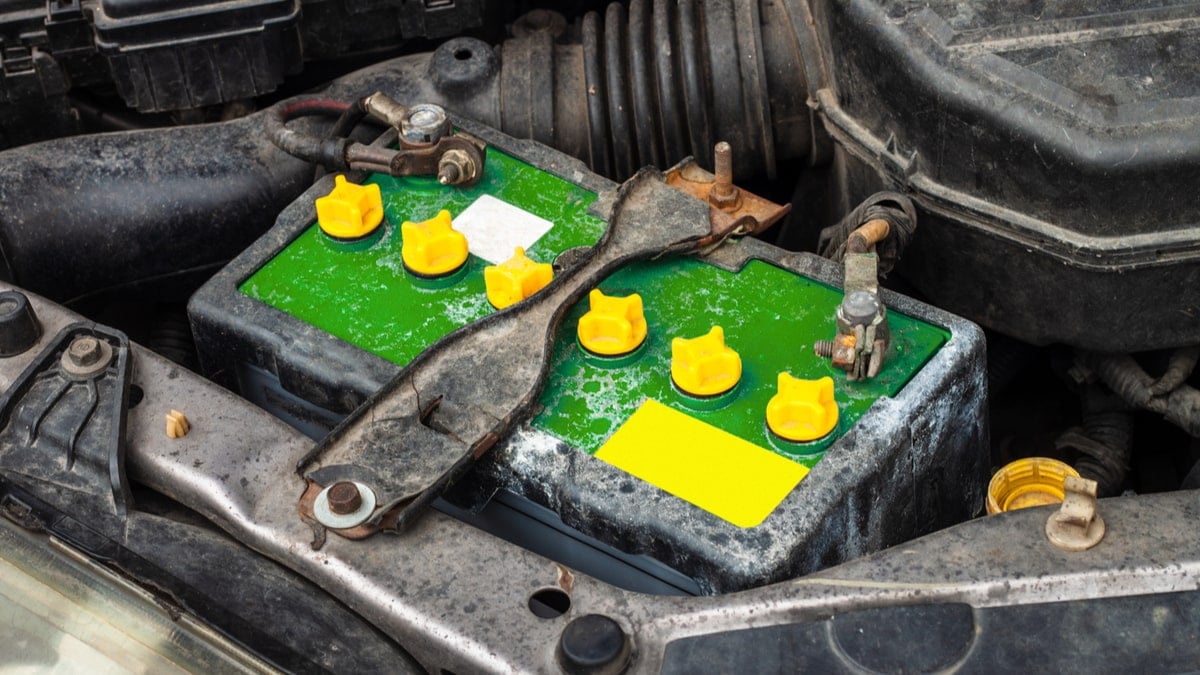
You have probably encountered a whiteish-blue substance on your battery terminal at least once before when opening your car hood.
The car’s battery is vital for the smooth operation of your car. It controls electric consumers like the ignition, headlights, radio, or AC. Having a car stall in the middle of the road can be embarrassing for many. So, what are the reasons for battery terminal corrosion?
The most common reason for battery terminal corrosion is hydrogen or electrolyte leakage from the battery. It can also be caused by an alternator slightly overcharging the car battery over a long period of time. Chemical reactions with copper clamps are not rare, either.
Battery terminal corrosion will appear after years of driving with the same battery, and you need to understand what causes it and how to fix it. Here is a more detailed list of the five most common reasons for battery terminal corrosion.
What Causes Battery Terminal Corrosion?
1. Hydrogen gas leakage
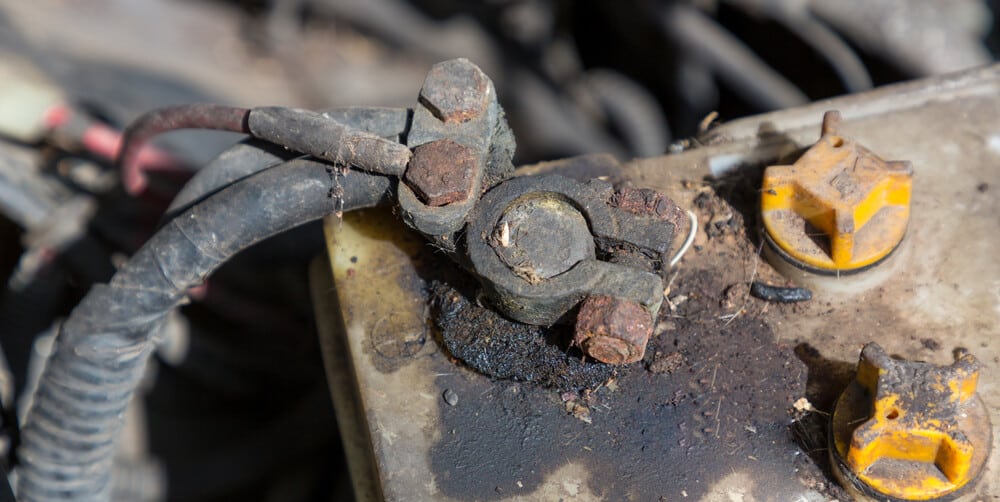

The battery turns acid into an electric current. Sometimes, the hydrogen gas in the battery leaks and finds its way into the atmosphere. It reacts with other substances, and battery terminal corrosion is the result.
Different problems relating to the battery will show up depending on which side of the battery corrosion has formed on. If it is on the negative terminal, this is a sign of undercharging. If it is on the positive terminal, it is due to overcharging.
2. Electrolyte leakage
This problem is synonymous with lead-acid batteries. Due to age or damage, the battery’s electrolyte can leak and accumulate on the battery terminals. The probability of the electrolyte leaking is increased if you overfill the battery water.
3. Chemical Reaction In The Copper Clamps
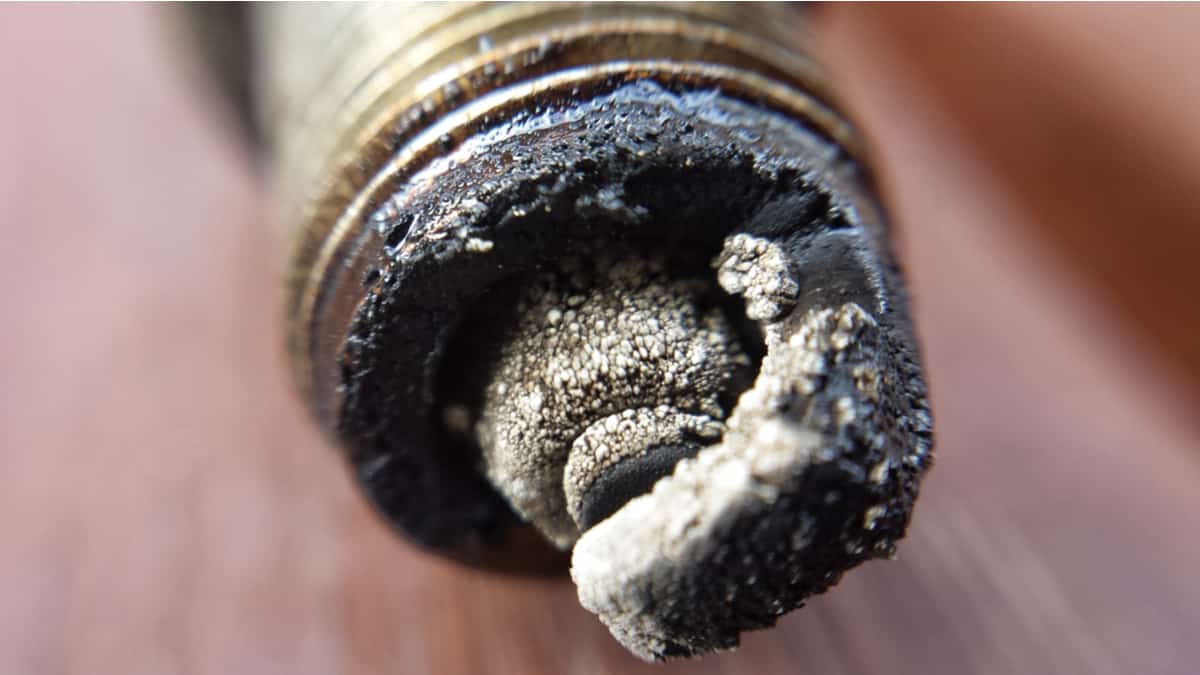
Copper is a good conductor and does not corrode easily. However, when electric currents pass through the copper terminals, copper sulfate is produced, and this leads to battery terminal corrosion.
A bluish precipitate on the copper terminals can signify copper sulfate. Copper sulfate does not conduct electricity well, and you will start experiencing trouble starting your car as a result.
4. Overcharging
If your alternator is slightly overcharging your car battery, it might cause corrosion on your car battery terminals. Check your voltage with a multimeter when your car runs to make sure it is not charging over 14.5 volts when you are revving the engine.
It can also be because you are frequently charging your car battery too hard with a car battery charger.
5. Overfilling the battery
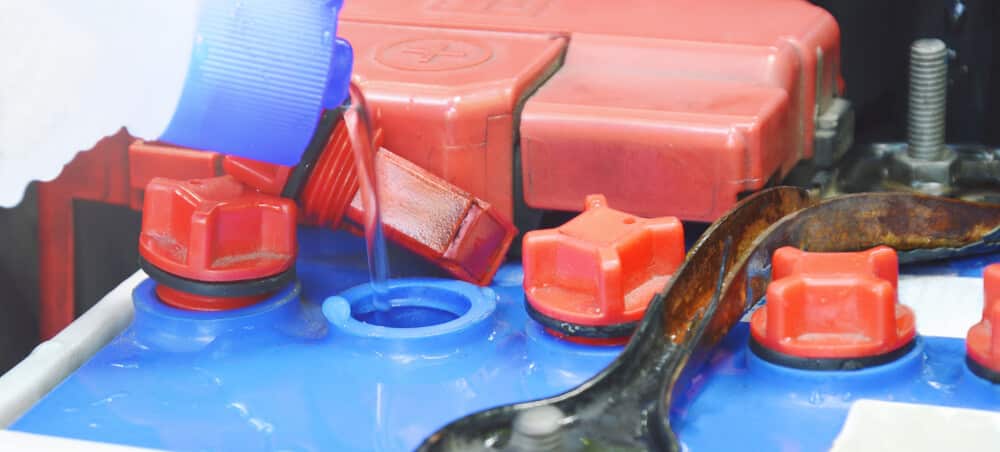

If you overfill your car battery, it might cause the electrolyte to leak out, as mentioned before. Not all car batteries are refillable, but you should absolutely double-check if you have one so it is not overfilled.
How to Fix battery terminal corrosion
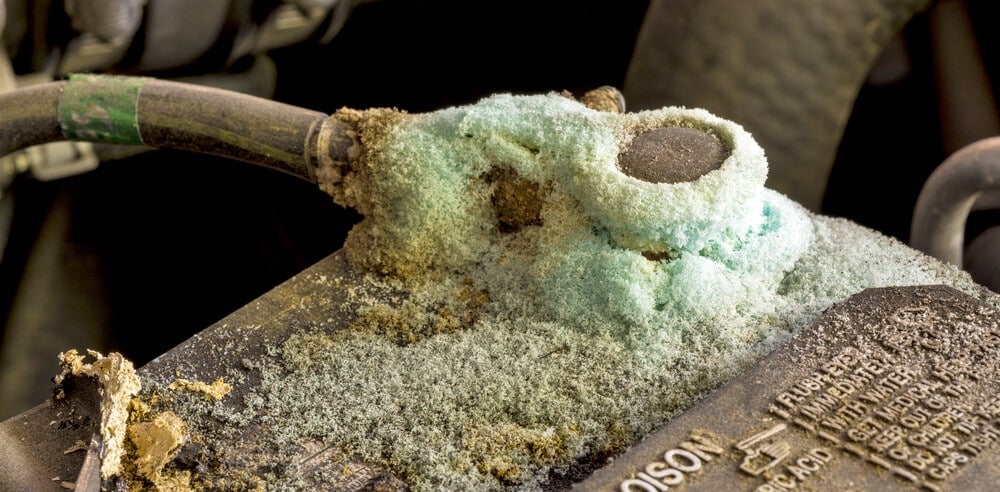

Now, that we know what causes car battery corrosion, we need to know how to fix it. There are some different methods you can use to clean the battery terminals.
1. Baking soda – water solution
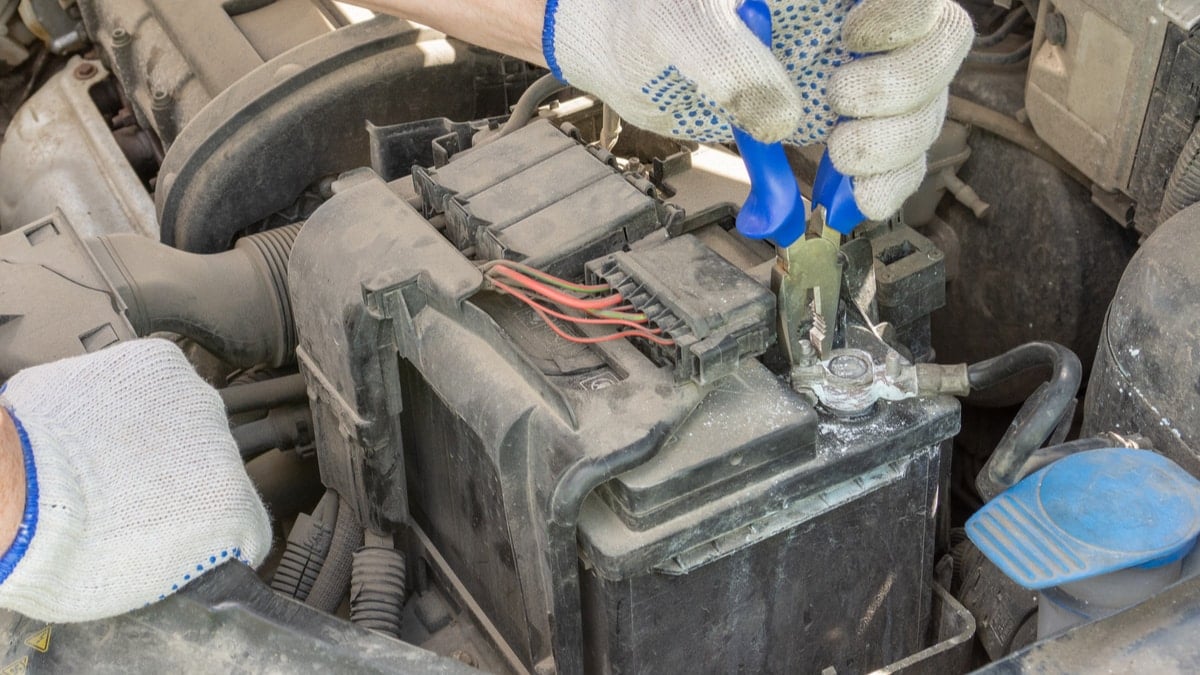
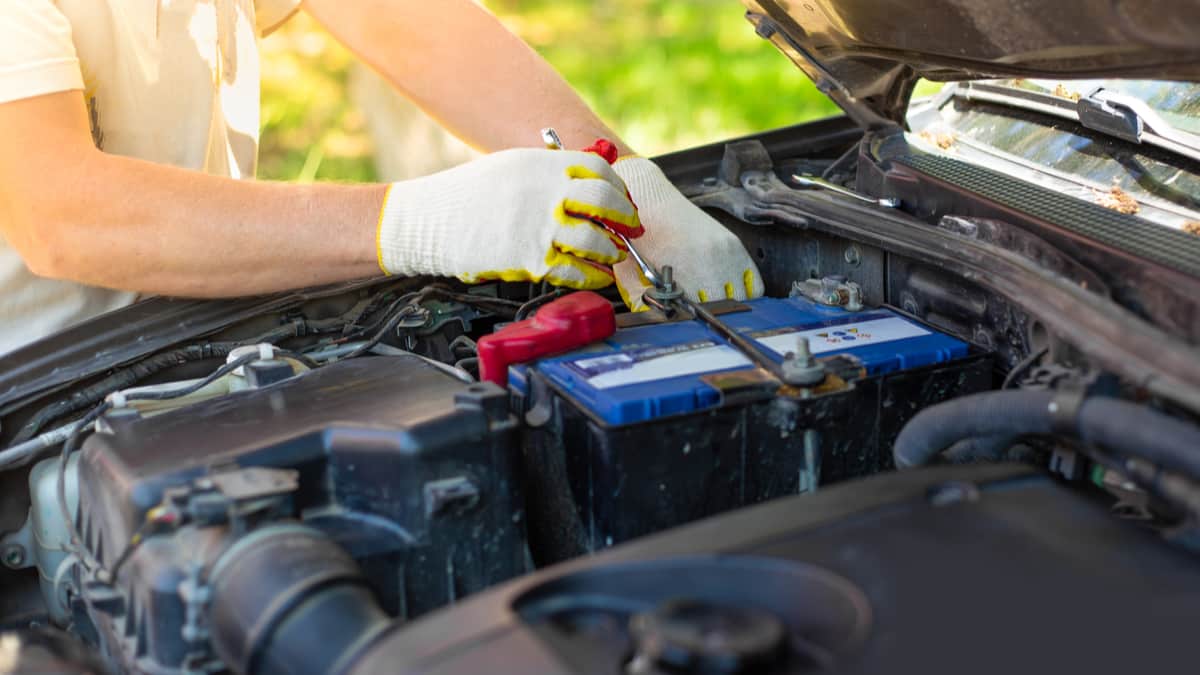
If you want to remove copper sulfate from the terminals, you will need a solution of baking soda and water, and a brush. First, ensure that the car’s ignition has been turned off. Remove the battery terminals and use your brush to remove some of the corrosion.
Pour the baking soda solution and continue removing the corrosion with your brush. Once you have finished, clean the terminals with clean water. It is prudent to smear some wheel bearing grease on the terminals to prevent further damage. Some people may opt for petroleum jelly, but this does not last as long as grease.
2. Soda
Most of the soft drinks that we take have some carbonic acid in them. Pour some of the soda on the terminals and use a soft sponge to remove the residue. This works well in the absence of a baking soda-water solution.
3. Cleaning heavy corrosion
If your battery has excessive corrosion on the terminals, you will need to use a baking soda-water solution and an old toothbrush. Start by removing the battery terminals – the negative should be first. Mix your baking soda solution and place it in cups. Soak each of the terminals in the solution and let it soak for the next 20 minutes.
Scrub off the corrosive materials on the terminals. Pour in the soda solution and make a fresh one. Soak the battery terminals again while removing the corrosive materials. Clean the terminals with water and let them dry or wipe them with a damp cloth. You can also use sandpaper to clean the terminals. Apply some grease or Vaseline and reattach the terminals, starting with the positive one.
How to Prevent Battery Corrosion
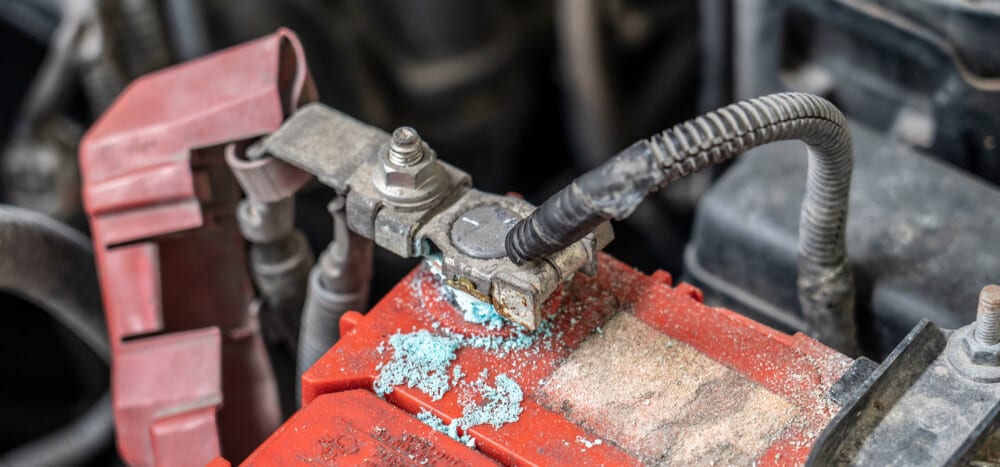

The best way to prevent battery terminal corrosion is to make sure the alternator is not overcharging the car battery. You also want to have a newer car battery in good condition. Anti-corrosive sprays are also effective at preventing corrosion.
Let’s take a little more detailed look over the few ways to prevent battery corrosion:
1. Replace the car battery
Because a leaking car battery causes a lot of battery corrosion, you may need to replace your car battery to prevent it from happening again soon.
It is recommended to replace your car battery every five years to keep it in good condition.
2. Copper compression terminals
These clamps are one of the best in the market and will help prevent further battery terminal corrosion. The clamps are made from tinned copper and ensure that the whole clamp comes into contact with the electric current.
3. Battery charging
One of the causes of battery terminal corrosion is a battery that is overcharged or undercharged. The manufacturer’s manual often has the recommended battery voltage. Make sure you are not charging it too hard with your car battery charger.
Also, check the voltage when the car is revving on idle with a multimeter. If the alternator is charging over 14.5 volts, there is something wrong with it.
4. Anti-corrosive sprays
Various sprays are available on the market to prevent terminal corrosion. You can also use Vaseline or grease if you find the sprays expensive. Coated felt pads could also be used to prevent corrosion of the battery terminals.
Categories: Car Battery, Electric