If you drive a vehicle with a manual transmission, chances are you have a clutch master cylinder. It’s a little-known component that has an extremely important job. But when you start to have problems shifting, it’s one of the first places you should look.
But what does a clutch master cylinder do, where’s it at, and how do you know when you need to replace it? Just as importantly, when you narrow down the problem to your clutch master cylinder, how much will it cost to replace it?
We’ll break down everything you need to know here. Let’s take a quick overview of which signs to look for.
Symptoms Of A Bad Clutch Master Cylinder
The most common symptom of a bad clutch master cylinder is a low clutch or brake fluid level due to a leak. It can also cause a soft or spongy clutch pedal or other issues with the clutch pedal. Sometimes, it can cause the clutch pedal to stay on the floor.
Here is a more detailed list of the signs of a bad or failing clutch master cylinder to look for:
1. Low Clutch Fluid
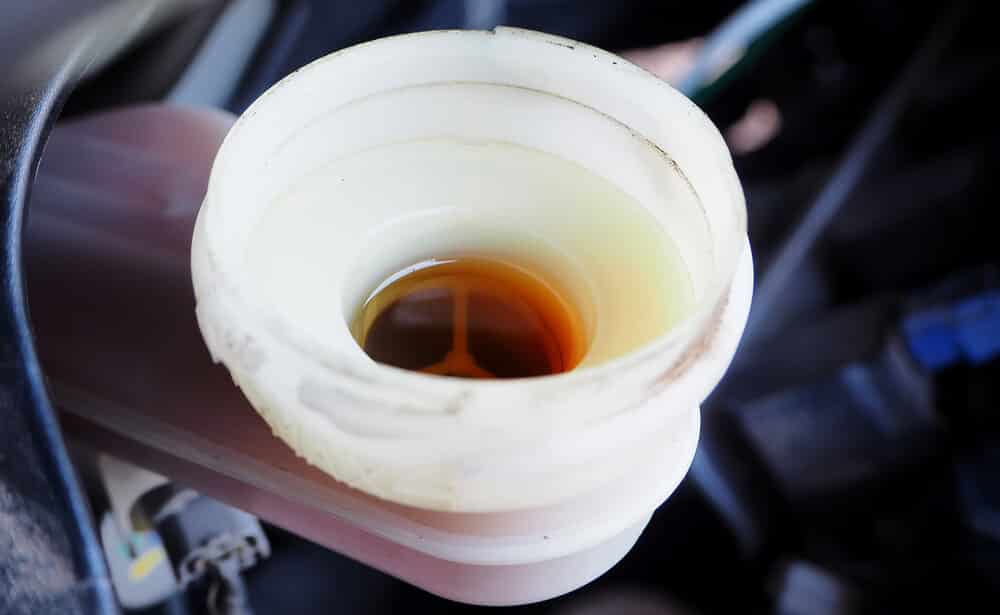

No, we’re not yanking your chain; clutch fluid is a real thing. And if you’re looking in the clutch fluid reservoir, the fluid should always be at the same height. Otherwise, you have a problem somewhere in the system, and the most likely culprit is a leaking clutch master cylinder.
In many car models, the clutch master cylinder uses the brake fluid, so they use a shared reservoir. Therefore, if you can’t find the clutch fluid reservoir, it is most likely using the brake fluid.
2. Soft or Spongy Clutch Pedal
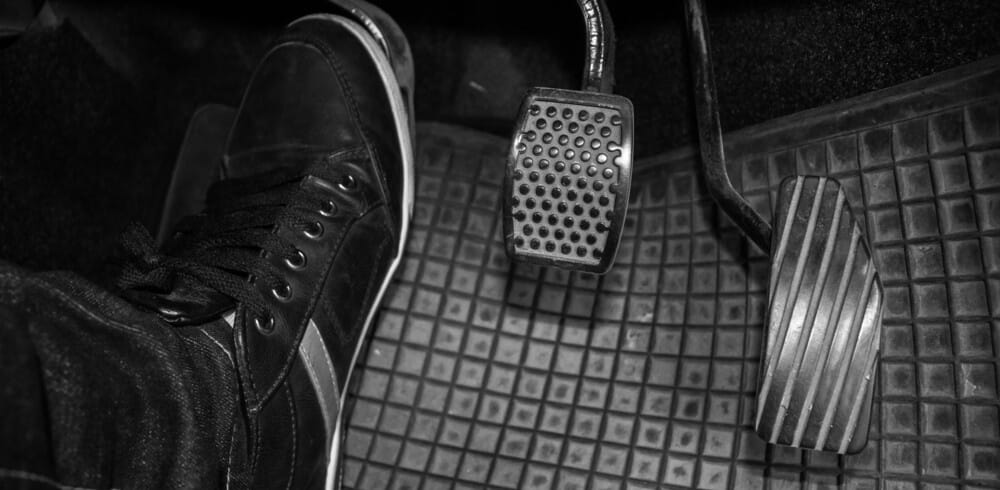

Your clutch fluid is like your brake fluid in that if it feels spongy or soft, you have water or air in the system. Moisture in a hydraulic system is a killer, and with clutch fluid, there’s no reason that it should ever be there.
So, if you have a soft or spongy clutch pedal, that means there’s a leak somewhere in the system. One of the most likely culprits is the clutch master cylinder.
3. Your Clutch Engages at a Different Point
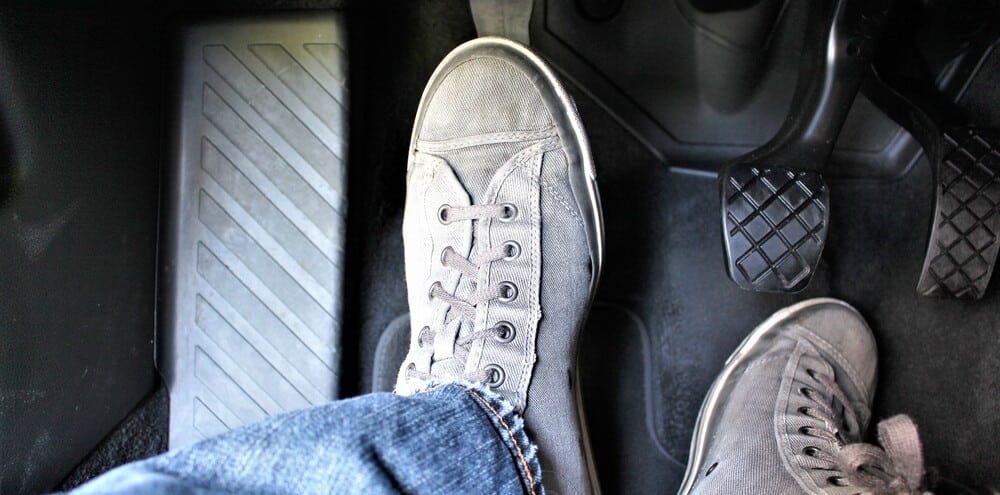

If your clutch fluid has dropped dramatically, then it’s likely that your clutch is going to engage at a different point too. The usual result is that you’ll have to fully depress the clutch pedal to disengage the clutch, which is typically far different than your usual engagement point.
Not only can it change the engagement point, but it can also do it over a short period of time. That means you might not have any problems on your way home from work, but when you hop in the car the next morning, you might stall it out a few times while you try to figure out what’s going on.
If that’s happening, take a look at your clutch fluid and make sure you still have enough.
4. Dark Clutch Fluid After Changing It
Clutch fluid will wear out and break down, so if you have a vehicle with over 100,000 or 200,000 miles and notice that the clutch fluid is a little dark, this is entirely normal. Go ahead and flush the fluid and see if that fixes your problem.
But if you check your fluid a few thousand miles after you changed it and it’s already getting darker, this is a sign of a bigger problem. Normally, it’s the gasket and seals in the clutch master cylinder breaking down. Not only are these contaminants creating a problem, but chances are your clutch master cylinder is leaking too.
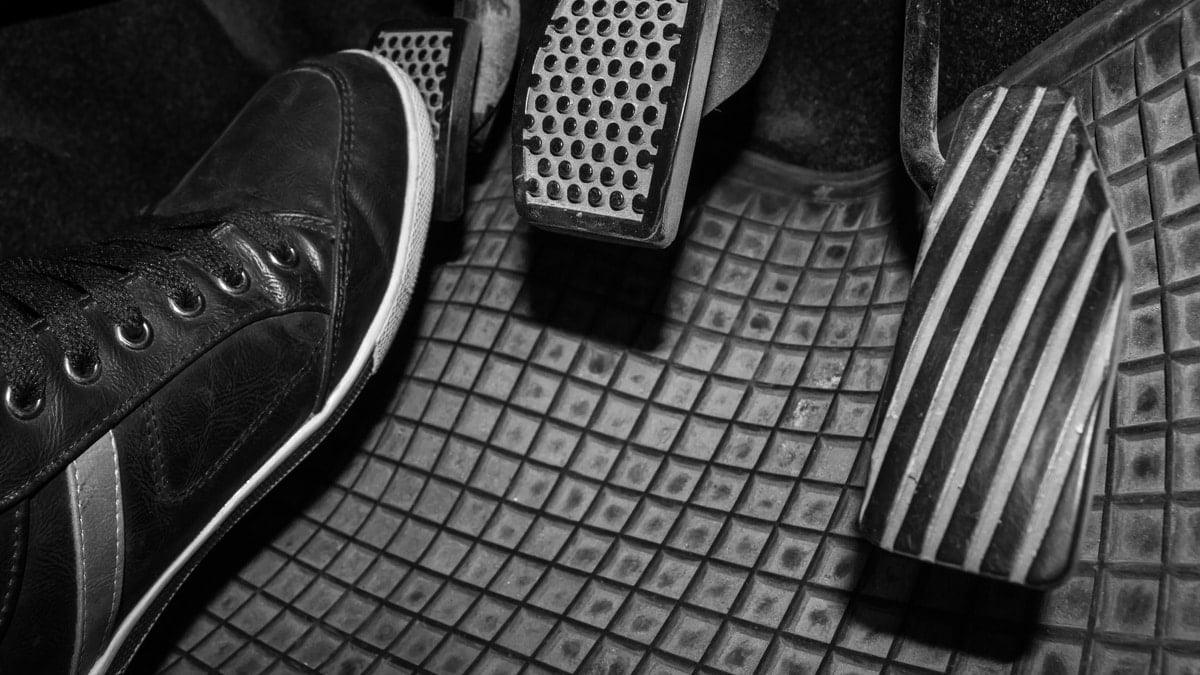
5. It’s Hard to Depress The Clutch
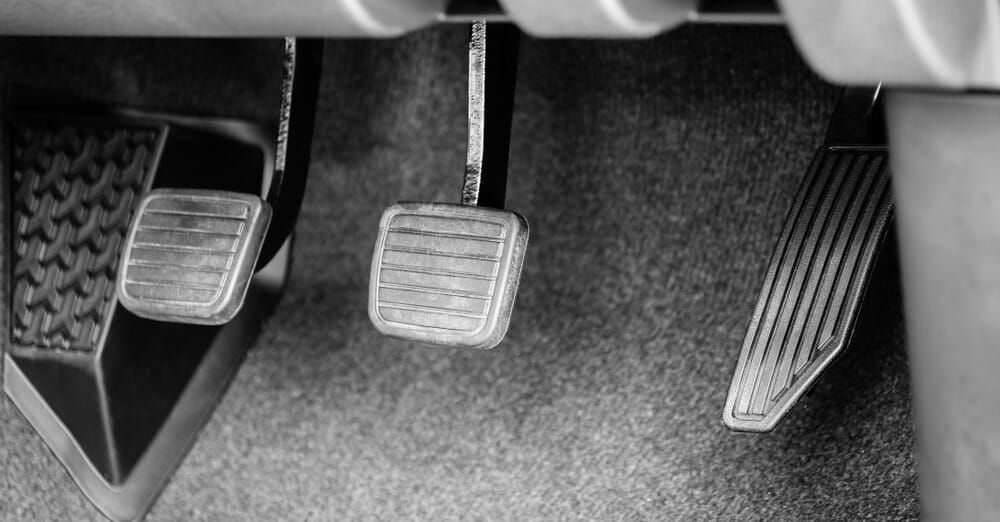

The entire purpose of the clutch master cylinder is to help you disengage the clutch. So, it makes sense that if your master clutch cylinder is leaking, it will get harder to depress the clutch. In fact, if the leak is bad enough, you won’t be able to disengage the clutch at all!
6. The Clutch Pedal Is Stuck to the Floor
If you find that your clutch pedal is stuck to the floor, you’ve lost the hydraulics in your clutch system. The most likely cause is a massive leak in your clutch master cylinder. If this happens, you’ll need to make repairs immediately, as you won’t be able to shift with a stuck clutch pedal.
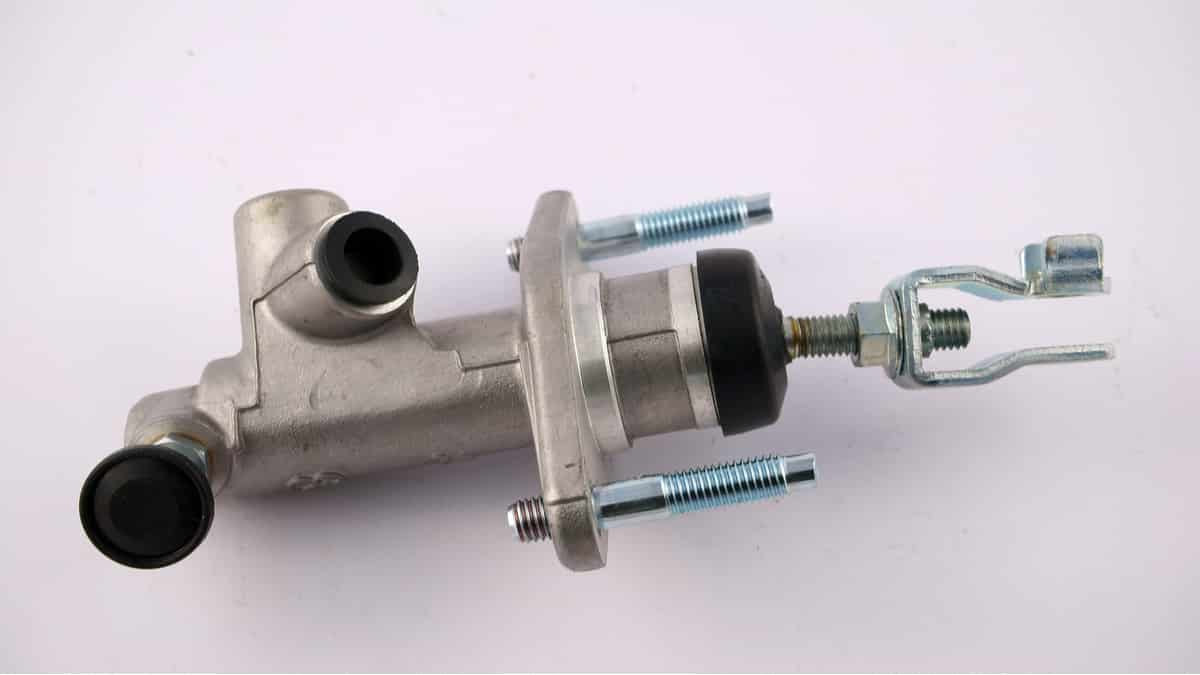
Clutch Master Cylinder Function
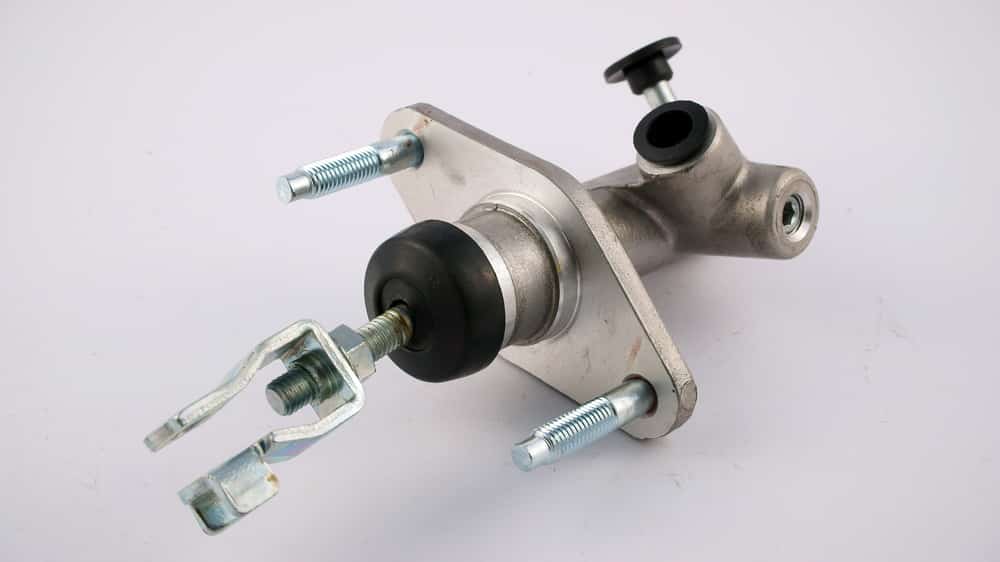

The clutch master cylinder is the chamber where your vehicle pushes the clutch fluid to help you disengage your clutch. There is a pushrod on one end of the cylinder, and when you depress the clutch, you push this rod against the clutch fluid, which pushes it to the slave cylinder and eventually to the clutch fork in the transmission.
The clutch master cylinder is what transfers the force of you pushing down the clutch pedal to the transmission!
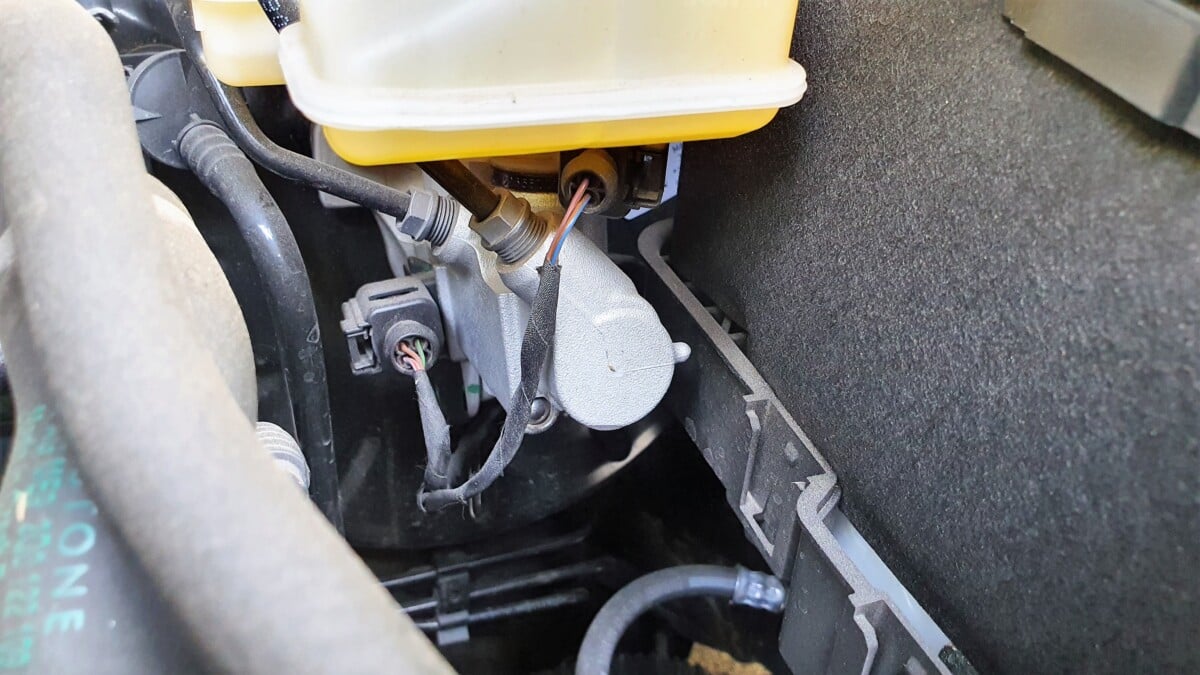
Clutch Master Cylinder Location
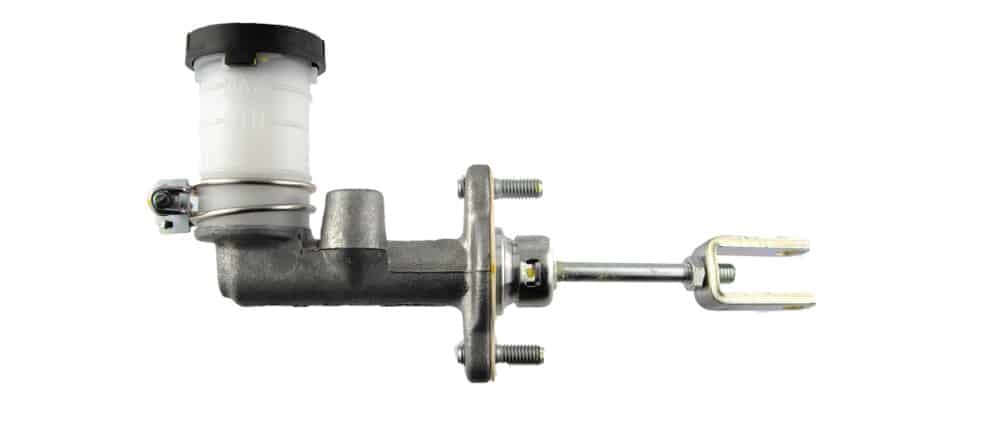

Your clutch master cylinder is typically located in front of the clutch pedal but on the other side of the firewall in the engine bay. You can often find it close to the brake master cylinder.
Typically, the clutch master cylinder directly connects to the clutch pedal via a pushrod, so if you draw a straight line from your clutch pedal into your engine bay, you’ll usually find the clutch master cylinder.
Clutch Master Cylinder Replacement Cost
The average clutch master cylinder replacement cost is between $200 and $350. But if you’re looking to save a little money, you can do it yourself for anywhere from $60 to $150.
However, these costs will vary depending on the type of vehicle you drive and where you take it for repairs.
For starters, you’ll need to purchase a new clutch master cylinder. An aftermarket clutch master cylinder usually costs between $30 and $60. However, an OEM part will usually cost more, which is where many additional costs come from if you take it to a dealership for repairs.
You’ll also need to replace the clutch fluid, which usually consists of brake fluid. This is a small cost, but you’ll need to factor it in.
Finally, if you’re not completing the repairs yourself, you’ll need to factor in labor. The clutch cylinder isn’t in a terrible spot, but it’s still going to typically cost anywhere between $150 and $200 for labor.
While you can save a little money by completing the repairs yourself, if you’re not mechanically savvy, you risk introducing air or other contaminants into the system, which can affect your overall performance.
Categories: Transmission