As electric cars become more popular, one question that comes up a lot is how long it takes to charge them. So let’s take a quick look at it – how long does it take to charge an electric car?
In this guide, we discuss all the factors that play into the EV charging time. We also look at a few estimates on today’s most popular models and discuss the various types of chargers. At the very end, we also take a quick look at how to have a road trip with an EV when using the DC Fast Charging stations.
How Long Does it Take to Charge an Electric Car?
You can achieve a top-off charge on an electric vehicle in as little as 15 minutes with a DC Fast Charger. On the other hand, it could take overnight to charge a vehicle with a home outlet. The time varies based on the battery type, charger, charging rate, battery level and weather.
We can estimate some charging times on the most popular 2022 models while using a Level 2 power source. These estimates are taken from the manufacturer’s specs and are all in perfect conditions. Other factors could influence these charging times.
- Chevy Bolt – 7 hours
- Polestar 2 – 8 hours
- Nissan Leaf – 8 hours
- Audi E-Tron – 10.5 hours
- BMW i4 – less than 10 hours
- Porsche Taycan – 9.5 hours
- MINI SE – 5 hours
- Tesla Model 3 Long Range – 8 hours (when using a Tesla Wall Connector)
- Tesla Model S Long Range – 12 hours (when using a Tesla Wall Connector)
If you are looking at the charging time on another vehicle, you can find the specifications from the manufacturer. Level 1 charging is going to take more time, while a DC Fast Charger will cut the time significantly.
RELATED: The Hidden Costs of Owning an Electric Car
Factors Affecting How Long it Takes to Charge an Electric Car
1. Battery Size/Current Charge
Battery capacity is measured by kWh (kilowatt-hours). The higher the capacity of the battery is, the more range you receive. However, this high capacity also means it could take longer to charge back up.
As one example, the 2022 Tesla Model 3 Long Range model comes equipped with a 75-kWh battery and 11.5-kW charger. On a Level 2 charger, this battery could take 6.5 hours to fill up. With the Tesla Supercharger, you can get a 250 kW charge, significantly lowering the time.
Additionally, you have to consider how low the battery actually is when you go to charge it. In most cases, you aren’t going to be pulling in on a completely empty battery. For this reason, you may only need to top off the battery to get back on the road. This top-off requires significantly less charging time than that which is empty.
RELATED: How Long Does it Take to Charge a Tesla? (120v, 240v & 480v)
2. EV Charging Rate
Every vehicle has a different charging rate based on what the vehicle can accept. This rate is determined by the manufacturer based on what batteries and onboard equipment can handle.
If the charging rate of your vehicle is static, visiting a more powerful station isn’t going to make a difference, especially if it exceeds what your car is capable of. You can only receive the charge you’re your vehicle will take. That’s why it’s important to know these figures upfront.
3. Type of Charging Station
Each charging station has a differing amount of power it’s capable of producing. For this reason, you want to ensure you are visiting one with the maximum charging rate for your vehicle if you are in a hurry.
The most common public chargers are Level 3 chargers, otherwise known as DC Fast Chargers. We will discuss more about these different types in a minute.
4. Weather
You wouldn’t think that the weather would play a role in how the EV charges, but it can have a profound impact. If the temperatures are low, the vehicle efficiency is diminished, thereby increasing the charging time. This condition would be most noticeable while using a fast charger.
On the other hand, hotter weather is going to affect the thermal management functions, which can also reduce efficiency. Some EVs have electrical systems that don’t handle the heat well, even causing more internal resistance as the battery charge becomes higher.
Charging Station Levels Explained
1. Level 1 (AC)
You can charge nearly anything through your household 120-volt outlet. This 15-amp charger is known as Level 1. When you charge a vehicle through a Level 1 outlet, you aren’t looking at hours for the total time. Instead, it will usually take days to get a full charge.
For most people, Level 1 charging doesn’t make a lot of sense. You could spend a lot of time waiting for a full charge this way. Per hour, you might only receive three to six miles of driving range. However, if you are driving a plug-in hybrid, this might be a decent option since the driving range isn’t normally as long on electric-only power.
It could also make sense to charge your EV if you aren’t using it often. If you only need it for occasional travel, you might choose this option versus adding new equipment to your home that’s not needed.
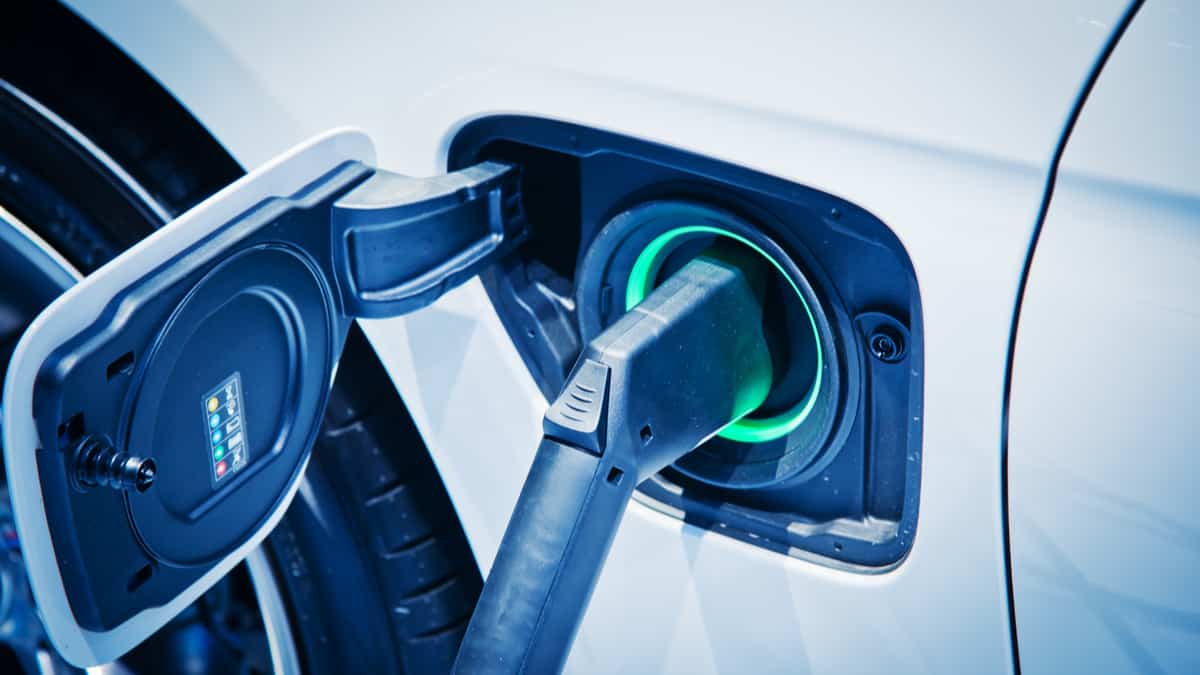
2. Level 2 (AC)
The majority of homeowners use a Level 2 charger. To accommodate this, a 240-volt outlet needs to be instead. These outlets run on a 50-amp circuit, allowing for safe charging at 40 amps maximum. However, these can vary from anywhere between 12 and 80 amps.
Many new EVs come with the option to add a portable charging adaptor. If you choose something providing more than 40 amps, you will need a hardwired charger. With the Level 2 charger, you might gain twenty to thirty miles per each hour it’s connected. By plugging it in overnight, you should get a full charge with most models.
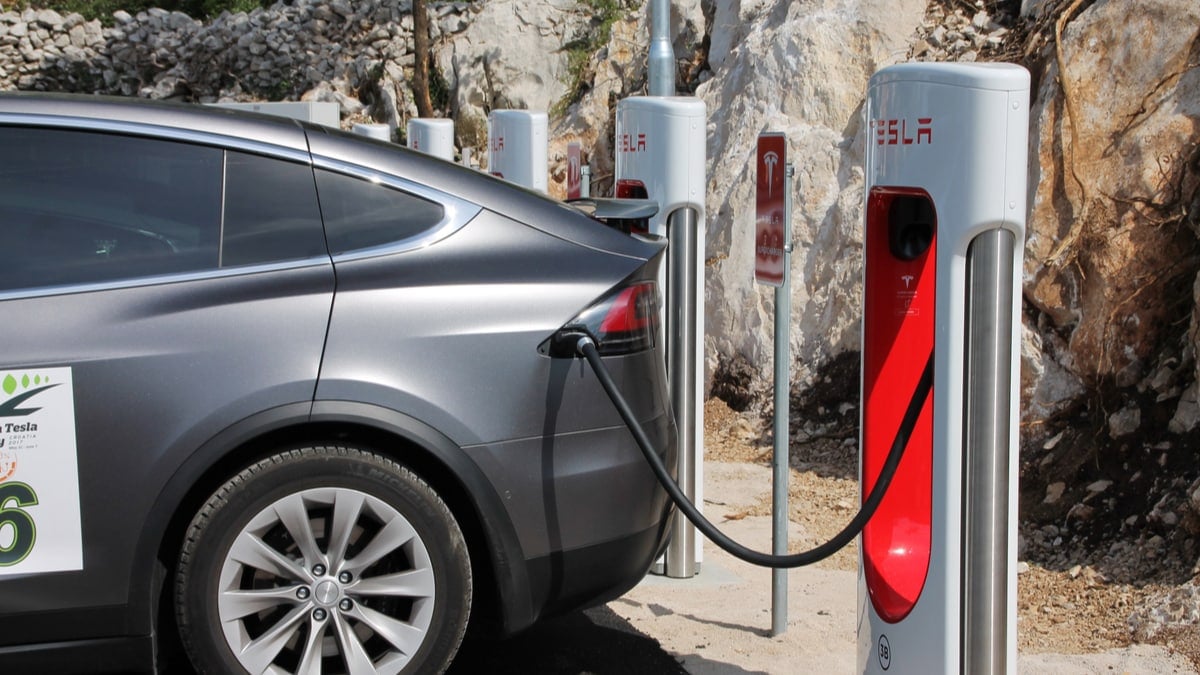
3. DC Fast Charger/Tesla Supercharger
If you want the fastest charge possible, you are looking for a DC Fast Charging Station. There are also Tesla Superchargers, which are different but similar. With the Level 3 charger, the power comes from direct current (DC) instead of alternating current (AC).
The DC Fast Charger is the ideal choice when looking for a quick top-off on the road. While it’s not as fast as filling up a fuel tank, it’s going to get the job done. While your car is plugged in, you can take a bathroom break and grab something to eat, so you are refueled as well.
For many vehicles, it’s possible to get an 80% charge in just thirty minutes to an hour. If you have to take a road trip, you can plan out the stops to ensure you never run the battery too low. With the right navigation system, you can find all of the fast chargers along the route so you can make it to your destination without a problem. Even if you are only stopping for twenty minutes, it might make sense to top off the batteries and get a little more range out of them.
Categories: Electric Vehicles